
A flood is an overflow of water that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrology and are of significant concern in agriculture, civil engineering and public health. Human changes to the environment often increase the intensity and frequency of flooding, for example land use changes such as deforestation and removal of wetlands, changes in waterway course or flood controls such as with levees, and larger environmental issues such as climate change and sea level rise. In particular climate change's increased rainfall and extreme weather events increases the severity of other causes for flooding, resulting in more intense floods and increased flood risk.

A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions.
The Delta Works is a series of construction projects in the southwest of the Netherlands to protect a large area of land around the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta from the sea. Constructed between 1954 and 1997, the works consist of dams, sluices, locks, dykes, levees, and storm surge barriers located in the provinces of South Holland and Zeeland.
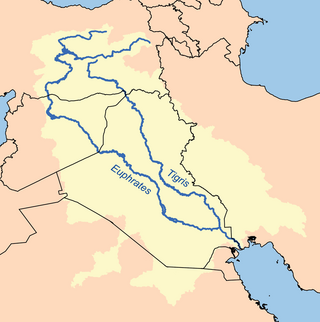
The Tigris–Euphrates river system is a large river system in Western Asia that discharges into the Persian Gulf. Its principal rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates, along with smaller tributaries.

Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower. Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. However, when constructed in lowland rainforest areas, where part of the forest is inundated, substantial amounts of greenhouse gases may be emitted.

The ca. 1000 km long Tana River is the longest river in Kenya, it is also called Sagana River in the Mt Kenya region and gives its name to the Tana River County. Its catchment covers ca. 100,000 km² and can be divided into the headwaters and the lower Tana consisting of the section downstream of Kora where the river flows for ca. 700 km through semi-arid plains. Its tributaries include some major rivers in the Central Region like Thika, Ragati River, Nyamindi, Thiba ,Mathioya, Chania in short all Rivers flowing from Mt Kenya and Aberdare Ranges all end up in River Tana. The river rises from Mt Kenya in Nyeri. Initially it runs east before turning south around the massif of Mount Kenya and meanders all the way up to Indian Ocean. A series of hydroelectric dams has been constructed along the river. These include the Masinga Dam, the Kamburu Dam, the Gitaru Dam, the Kindaruma Dam and the Kiambere Dam. en The Masinga Reservoir and the Kiambere Reservoir, created by the Masinga and Kiambere dams respectively, serve a dual purpose: hydro-electric power (HEP) generation and agricultural irrigation. The other three are used exclusively for HEP generation. A 2003 study reported that two-thirds of Kenya's electrical needs were supplied by the series of dams along the Tana River. Many people believe this river has groundwater underneath it, but it doesn't. The electricity is then supplied to the national grid system and distributed countrywide through a series of substations, transformers and cables.

Bisha, also known as Qal`at Bishah, is a town in the south-western Saudi Arabian province, 'Asir. Bisha was its own province before merging with its neighboring province, 'Asir. Bisha has a population of 205,346 according to the 2010 Census, with nearly 240 villages and 58 larger settlements that are spread out on both sides of the Bisha Valley. The city is located to the south of the Arabian Peninsula, which is almost entirely under the administration of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. It stands at an altitude of approximately 610 meters (2,000 ft.) above sea level.

Aburagi Dam (油木ダム) is a dam built upstream on the class-B Imagawa River, located in the town of Soeda, in the Tagawa District of Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan.

Egawa Dam (江川ダム) is a dam in Asakura, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. The dam was completed in 1972.

California's interconnected water system serves over 30 million people and irrigates over 5,680,000 acres (2,300,000 ha) of farmland. As the world's largest, most productive, and potentially most controversial water system, it manages over 40 million acre-feet (49 km3) of water per year.

Sand dams are a simple, low-cost and low-maintenance, replicable rainwater harvesting technology. They provide a clean, local water supply for domestic and farming use and are suited to semi-arid areas of the world.
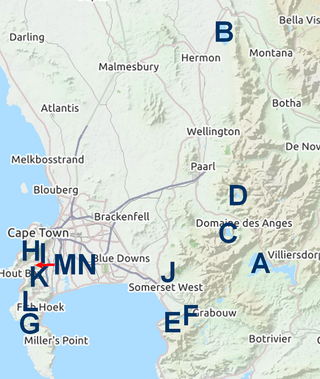
The Western Cape Water Supply System (WCWSS) is a complex water supply system in the Western Cape region of South Africa, comprising an inter-linked system of six main dams, pipelines, tunnels and distribution networks, and a number of minor dams, some owned and operated by the Department of Water and Sanitation and some by the City of Cape Town.

The Berg River Dam is a 68-metre (223 ft) high dam on the Berg River in South Africa. It is the centerpiece of the Berg Water Project (BWP) which is designed to capture the winter rainfall and store it for supply to Cape Town during the dry summer months. The project in turn forms an important part of the Western Cape Water Supply System (WCWSS), an intricate system of dams and bulk water infrastructure that provides water to more than 3 million people. At the inauguration of the dam in 2009, then President of South Africa Kgalema Motlanthe called the project "a good example of how public infrastructure projects can be used to contribute meaningfully to poverty eradication and to foster social empowerment of the people." The Berg River Dam was the first dam in South Africa to be designed and constructed, and is due to be operated, in accordance with the guidelines of the World Commission on Dams. It has been completed on time and within budget. The Berg River basin and the adjacent metropolitan area of Cape Town are of particular importance to the Western Cape region because, although the basin generates only about 3% of the country's water resources, it is home to about 8% of South Africa's population, and produces about 12% of GDP.

Zayanderud Dam, also spelled Zayandeh Rud Dam formerly known as the Shah Abbas Dam, is an arch dam on the Zayandeh River about 10 km (6.2 mi) east of Chadegan, Iran. The Zayanderud Dam is the main water reservoir with 1450 MCM capacity and has been exploited since 1971. The Zayanderud has provided the needs of water for important economic activities including agricultural, industrial and domestic consumptions. The primary purpose of the dam is water supply to Isfahan which lies 88 km (55 mi) to the east. It also supports a power station with an installed capacity of 55 MW. In recent years, the Zayandeh River has experienced significant reductions in flow due to a combination of drought, climate change, and overuse of water resources.
Water supply and sanitation in Japan is characterized by numerous achievements and some challenges. The country has achieved universal access to water supply and sanitation; has one of the lowest levels of water distribution losses in the world; regularly exceeds its own strict standards for the quality of drinking water and treated waste water; uses an effective national system of performance benchmarking for water and sanitation utilities; makes extensive use of both advanced and appropriate technologies such as the jōkasō on-site sanitation system; and has pioneered the payment for ecosystem services before the term was even coined internationally. Some of the challenges are a decreasing population, declining investment, fiscal constraints, ageing facilities, an ageing workforce, a fragmentation of service provision among thousands of municipal utilities, and the vulnerability of parts of the country to droughts that are expected to become more frequent due to climate change.

Tsukabaru Dam is a concrete gravity dam built on the Mimi River for hydro-electric power generation in the Miyazaki Prefecture in Japan. The dam, built by the Kyushu Electric Power Co, Ltd. in 1938, was commissioned only in 1993. When built to a height of 87 m (285 ft) it was the highest gravity type dam in Japan, only to be surpassed later by the Kamishiba Dam raised in the uppermost reaches of the Mimi River.

Mahabad Dam is an embankment dam on the Mahabad River near the city of Mahabad, West Azerbaijan province, Iran. It was built before the Islamic revolution by Yugoslavian engineers and is one of the ten largest dams in Iran. On average, the total volume of annual water input is equal to 339.304 million cubic meters. The Mahabad Dam provides water for agriculture (71%), industry (11%), drinking (7%), and other miscellaneous purposes (11%). The dam also has a hydroelectric power station. Construction began in 1968 and the dam was completed in 1970.

The Turkey–Northern Cyprus water pipeline was built by the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus Water Supply Project which was an international water diversion project designed to supply water for drinking and irrigation from southern Turkey to Northern Cyprus via pipeline under Mediterranean Sea. The pipeline was completed in September 2014. As such, the project is unique in the world.

Climate change in Kentucky encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. state of Kentucky.

















