Related Research Articles

Mission Santa Inés was a Spanish mission in present-day Solvang, California, United States, and named after St. Agnes of Rome. Founded on September 17, 1804, by Father Estévan Tapís of the Franciscan order, the mission site was chosen as a midway point between Mission Santa Barbara and Mission La Purísima Concepción, and was designed to relieve overcrowding at those two missions and to serve the Indians living north of the Coast Range. Sunset magazine editors wrote of the Hidden Gem of the Missions: “With its simple, straightforward exterior, Santa Inés fits one’s impression of how a ripe old mission should look.”
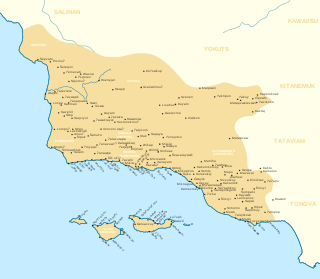
The Chumash are a Native American people of the central and southern coastal regions of California, in portions of what is now Kern, San Luis Obispo, Santa Barbara, Ventura and Los Angeles counties, extending from Morro Bay in the north to Malibu in the south to Mt Pinos in the east. Their territory includes three of the Channel Islands: Santa Cruz, Santa Rosa, and San Miguel; the smaller island of Anacapa was likely inhabited seasonally due to the lack of a consistent water source.

The Channel Islands are an eight-island archipelago located within the Southern California Bight in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of California. They define the Santa Barbara Channel, which sits between the islands and the California mainland. The four Northern Channel Islands are part of the Transverse Ranges geologic province, and the four Southern Channel Islands are part of the Peninsular Ranges province. Five of the islands are within the Channel Islands National Park, and the waters surrounding these islands make up Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary. The Nature Conservancy was instrumental in establishing the Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary.

The Conejo Valley is a region spanning both southeastern Ventura County and northwestern Los Angeles County in Southern California, United States. It is located in the northwestern part of the Greater Los Angeles Area.

Morro Bay State Park is a state park on the Morro Bay lagoon, in western San Luis Obispo County, on the Central Coast of California. On the lagoon's northeastern and eastern edges in the park, there are saltwater and brackish marshes that support thriving bird populations.

Chumashan was a family of languages that were spoken on the southern California coast by Native American Chumash people, from the Coastal plains and valleys of San Luis Obispo to Malibu, neighboring inland and Transverse Ranges valleys and canyons east to bordering the San Joaquin Valley, to three adjacent Channel Islands: San Miguel, Santa Rosa, and Santa Cruz.

The Tataviam are a Native American group in Southern California. The ancestral land of the Tataviam people includes northwest present-day Los Angeles County and southern Ventura County, primarily in the upper basin of the Santa Clara River, the Santa Susana Mountains, and the Sierra Pelona Mountains. They are distinct from the Kitanemuk and the Gabrielino-Tongva peoples.
Ventureño is a member of the extinct Chumashan languages, a group of Native American languages previously spoken by the Chumash people along the coastal areas of Southern California from as far north as San Luis Obispo to as far south as Malibu. Ventureño was spoken from as far north as present-day Ventura to as far south as present-day Malibu and the Simi Hills, California. Dialects probably also included Castac and Alliklik.
Chatsworth Hills Academy (CHA) is a private, coeducational day school located in Chatsworth, California, United States. CHA students are enrolled in Grades K through Eight and Preschool.
Chumash may refer to:

Chumash rock art is a genre of paintings on caves, mountains, cliffs, or other living rock surfaces, created by the Chumash people of Southern California. Pictographs and petroglyphs are common through interior California, the rock painting tradition thrived until the 19th century. Chumash rock art is considered to be some of the most elaborate and plentiful rock art tradition in the region.
Barbareño is one of the Chumashan languages, a group of Native American languages spoken almost exclusively in the area of Santa Barbara, California. The closely related Ineseño may have been a dialect of the same language. A dialect of the Barbareño language was also "spoken at San Emigdio near Buena Vista Lake" in the southern Central Valley. This dialect, called Emigdiano, "was heavily influenced by Buena Vista Yokuts." Barbareño lost its last known native speaker in 1965 with the death of Mary Yee. Both Barbareño and Ineseño are currently undergoing processes of language revitalization.

The Burro Flats site is a painted cave site located near Burro Flats, in the Simi Hills of eastern Ventura County, California, United States. The Chumash-style "main panel" and the surrounding 25-acres were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1976, with a boundary decrease in 2020. The main panel includes dozens of pictographs in a variety of colors. The cave is in the mountains, near the bi-lingual Chumash/Fernandeno village of Huwam/Jucjauynga. The Burro Flats painted cave and the rest of the former Santa Susana Field Laboratory are not accessible to the public.
Qasil was a Native American village of the Chumash people located in the county of Santa Barbara, California in the United States.
Obispeño was one of the Chumash Native American languages previously spoken along the coastal areas of California. The primary source of documentation on the language is from the work of linguist J. P. Harrington.

The Chumash revolt of 1824 was an uprising of the Chumash Native Americans against the Spanish and Mexican presence in their ancestral lands. The rebellion began in three of the California Missions in Alta California: Mission Santa Inés, Mission Santa Barbara, and Mission La Purisima, and spread to the surrounding villages. All three missions are located in present-day Santa Barbara County, California. The Chumash revolt was the largest organized resistance movement to occur during the Spanish and Mexican periods in California.
Satwiwa was a former Chumash village in the Santa Monica Mountains of Newbury Park, California. The current Satwiwa Native American Indian Culture Center is operated by the National Park Service in cooperation with the Friends of Satwiwa. Satwiwa has been inhabited by Chumash Indians for over 10,000 years. It is situated at the foothills of Boney Mountain, a sacred mountain for the Chumash.

Chumash Indian Museum is a Native American Interpretive Center in northeast Thousand Oaks, California. It is the site of a former Chumash village, known as Sap'wi. It is located in Oakbrook Regional Park, a 432-acre park which is home to a replica of a Chumash village and thousand year-old Chumash pictographs. The pictographs by nearby Birthing Cave are not open to the public, but can be observed on docent-led tours. Chumash people inhabited the village 10,000 years ago.

Chumash traditional medicine is a type of traditional medicine practiced by the Chumash people of the southern coastal regions of California.
Humaliwo was a Chumash village located in present-day Malibu, California. “Humaliwo” meant "where the surf sounds loudly." The village occupied a hill across from the lagoon in Malibu Lagoon State Beach. The neighboring Tongva referred to the village as Ongobehangna. The Humaliwo village was recorded on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) in 1976. Cultural remains are present at this site, consisting of numerous human burials, artifacts and other cultural materials. Sections of the site can be dated to 7,000 years old.
References
- ↑ Lynn H. Gamble (2008), The Chumash world at European contact: power, trade, and feasting among complex hunter-gatherers, University of California Press, ISBN 978-0-520-25441-1