Related Research Articles

A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies, and autoimmune disorders.

Eric Arthur Blair was an English novelist, essayist, journalist, and critic who wrote under the pen name of George Orwell. His work is characterised by lucid prose, social criticism, opposition to totalitarianism, and support of democratic socialism.

Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth. This can be defined in two ways. Cohort LEB is the mean length of life of a birth cohort and can be computed only for cohorts born so long ago that all their members have died. Period LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year. National LEB figures reported by national agencies and international organizations for human populations are estimates of period LEB.

Keep the Aspidistra Flying, first published in 1936, is a socially critical novel by George Orwell. It is set in 1930s London. The main theme is Gordon Comstock's romantic ambition to defy worship of the money-god and status, and the dismal life that results.

Down and Out in Paris and London is the first full-length work by the English author George Orwell, published in 1933. It is a memoir in two parts on the theme of poverty in the two cities. Its target audience was the middle- and upper-class members of society—those who were more likely to be well educated—and it exposes the poverty existing in two prosperous cities: Paris and London. The first part is an account of living in near-extreme poverty and destitution in Paris and the experience of casual labour in restaurant kitchens. The second part is a travelogue of life on the road in and around London from the tramp's perspective, with descriptions of the types of hostel accommodation available and some of the characters to be found living on the margins.

The Road to Wigan Pier is a book by the English writer George Orwell, first published in 1937. The first half of this work documents his sociological investigations of the bleak living conditions among the working class in Lancashire and Yorkshire in the industrial north of England before World War II. The second half is a long essay on his middle-class upbringing, and the development of his political conscience, questioning British attitudes towards socialism. Orwell states plainly that he himself is in favour of socialism, but feels it necessary to point out reasons why many people who would benefit from socialism, and should logically support it, are in practice likely to be strong opponents.

Blackpool is a seaside resort town in Lancashire, England. It is located on the Irish Sea coast of the Fylde peninsula, approximately 27 miles (43 km) north of Liverpool and 14 miles (23 km) west of Preston. It is the main settlement in the borough of the same name. The population of Blackpool at the 2021 census was 141,000, a decrease of 1,100 in ten years.

The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, education, and per capita income indicators, which is used to rank countries into four tiers of human development. A country scores a higher level of HDI when the lifespan is higher, the education level is higher, and the gross national income GNI (PPP) per capita is higher. It was developed by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul-Haq and was further used to measure a country's development by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)'s Human Development Report Office.

Leigh syndrome is an inherited neurometabolic disorder that affects the central nervous system. It is named after Archibald Denis Leigh, a British neuropsychiatrist who first described the condition in 1951. Normal levels of thiamine, thiamine monophosphate, and thiamine diphosphate are commonly found, but there is a reduced or absent level of thiamine triphosphate. This is thought to be caused by a blockage in the enzyme thiamine-diphosphate kinase, and therefore treatment in some patients would be to take thiamine triphosphate daily. While the majority of patients typically exhibit symptoms between the ages of 3 and 12 months, instances of adult onset have also been documented.

Sanfilippo syndrome, also known as mucopolysaccharidosis type III (MPS III), is a rare autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease that primarily affects the brain and spinal cord. It is caused by a buildup of large sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs, or mucopolysaccharides) in the body's lysosomes.
The NCTE George Orwell Award for Distinguished Contribution to Honesty and Clarity in Public Language is an award given since 1975 by the Public Language Award Committee of the National Council of Teachers of English. It is awarded annually to "writers who have made outstanding contributions to the critical analysis of public discourse."

The sociology of health and illness, sociology of health and wellness, or health sociology examines the interaction between society and health. As a field of study it is interested in all aspects of life, including contemporary as well as historical influences, that impact and alter our health and wellbeing.

Diogenes syndrome, also known as senile squalor syndrome, is a disorder characterized by extreme self-neglect, domestic squalor, social withdrawal, apathy, compulsive hoarding of garbage or animals, and a lack of shame. Affected people may also display symptoms of catatonia.
Anodontia is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the congenital absence of all primary or permanent teeth. It is divided into two subsections, complete absence of teeth or only some absence of teeth. It is associated with the group of skin and nerve syndromes called the ectodermal dysplasias. Anodontia is usually part of a syndrome and seldom occurs as an isolated entity. There is usually no exact cause for anodontia. The defect results in the dental lamina obstruction during embryogenesis due to local, systemic and genetic factors.
The genetics and abortion issue is an extension of the abortion debate and the disability rights movement. Since the advent of forms of prenatal diagnosis, such as amniocentesis and ultrasound, it has become possible to detect the presence of congenital disorders in the fetus before birth. Specifically, disability-selective abortion is the abortion of fetuses that are found to have non-fatal mental or physical defects detected through prenatal testing. Many prenatal tests are now considered routine, such as testing for Down syndrome. Women who are discovered to be carrying fetuses with disabilities are often faced with the decision of whether to abort or to prepare to parent a child with disabilities.
A conspiracy of silence, or culture of silence, describes the behavior of a group of people that by unspoken consensus does not mention, discuss, or acknowledge a given subject. The practice may be motivated by positive interest in group solidarity or by negative impulses such as fear of political repercussion or social ostracism. Unlike a taboo subject or the use of euphemisms, a conspiracy of silence is limited to specific social and political contexts rather than to an entire culture.

Nineteen Eighty-Four is a dystopian novel and cautionary tale by English writer George Orwell. It was published on 8 June 1949 by Secker & Warburg as Orwell's ninth and final book completed in his lifetime. Thematically, it centres on the consequences of totalitarianism, mass surveillance and repressive regimentation of people and behaviours within society. Orwell, a democratic socialist, modelled the authoritarian state in the novel on the Soviet Union in the era of Stalinism, and Nazi Germany. More broadly, the novel examines the role of truth and facts within societies and the ways in which they can be manipulated.
Poverty in Sri Lanka is 31% of the population as of June 8, 2023 Sri Lanka's life expectancy and literacy rate are nearly on par with those of developed countries, and even top the rankings for the South Asia region. While all these indicate that Sri Lanka should be experiencing a high standard of living, until recently it has only ranked in the medium category of the Human Development Index (HDI). This is despite the fact that Sri Lanka has been experiencing moderate growth in its GDP averaging 5.5 per annum between 2006 and 2009. One of the reasons is due to its relatively low GDP per capital;. The Sri Lankan government has been successful in reducing poverty from 15.2% on 2006 to 8.9% in 2010, urban poverty was reduced from 6.7 to 5.3% while rural poverty was reduced from 15.7 to 9.5%, and the nation has made significant progress towards achieving Millennium Development Goals on eradicating extreme poverty and hunger.

The Glasgow effect is an outdated term which referred to the lower life expectancy of residents of Glasgow compared to the rest of the United Kingdom and Europe. The phenomenon is defined as an "[e]xcess mortality in the West of Scotland (Glasgow) after controlling for deprivation." Although lower income levels are generally associated with poor health and a shorter lifespan, epidemiologists have argued that poverty alone does not appear to account for the disparity found in Glasgow. Equally deprived areas of the UK such as Liverpool and Manchester have higher life expectancies, and the wealthiest ten percent of the Glasgow population have a lower life expectancy than the same group in other cities. One in four men in Glasgow will die before his sixty-fifth birthday.
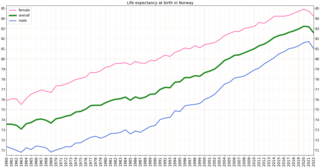
Health in Norway, with its early history of poverty and infectious diseases along with famines and epidemics, was poor for most of the population at least into the 1800s. The country eventually changed from a peasant society to an industrial one and established a public health system in 1860. Due to the high life expectancy at birth, the low under five mortality rate and the fertility rate in Norway, it is fair to say that the overall health status in the country is generally good.
References
- ↑ "Prize type: Exposing Britain's Social Evils prize". Orwell Foundation. Archived from the original on 28 August 2023. Retrieved 5 April 2019.
- 1 2 O'Connor, Sarah (16 November 2017). "Left behind: can anyone save the towns the economy forgot?". Financial Times . Archived from the original on 9 December 2019. Retrieved 5 April 2019.
- ↑ McManus, John (1 September 2018). "John McManus: Has Ireland developed shitlife syndrome?". The Irish Times . Retrieved 5 April 2019.
- ↑ Kinney, Fergal (2 November 2018). "Shit Life Syndrome: Mike Leigh Beyond The Hits". The Quietus . Retrieved 5 April 2019.
- ↑ Lees, John (29 January 2016). The Future of Psychological Therapy: From Managed Care to Transformational Practice. Routledge. p. 70. ISBN 978-1-317-48242-0 – via Google Books.