Methods
Buildings

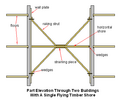
Raking shores
In this method, inclined members called rakers are used to give temporary lateral support to an unsafe wall. One or more timbers slope between the face of the structure to be supported and the ground. [2] The most effective support is given if the raker meets the wall at an angle of 60 to 70 degrees. A wall-plate is typically used to increase the area of support.
Foundations
Shoring is commonly used when installing the foundation of a building. A shoring system such as piles and lagging or shotcrete will support the surrounding loads until the underground levels of the building are constructed. Commonly used shoring equipment includes post shores, shoring beams, and timber jacks.
Trenches and pits

During excavation, shoring systems speed up excavation and provide safety for workers since trenches can be prone to collapse. In this case, shoring should not be confused with shielding. Shoring is designed to prevent collapse where shielding is only designed to protect workers when collapses occur. Concrete-structure and stone-building shoring, in these cases also referred to as falsework, provides temporary support until the concrete becomes hard and achieves the desired strength to support loads.
Hydraulic shoring
Hydraulic shoring is the use of hydraulic pistons that can be pumped outward until they press up against the trench walls. They are typically combined with steel plate or plywood, either being 1-1/8" thick plywood, or special heavy Finland Form (FINFORM) 7/8″ thick.
Beam and plate
Beam and plate steel I-beams are driven into the ground and steel plates are slid in amongst them. A similar method that uses wood planks is called soldier boarding. Hydraulics tend to be faster and easier; the other methods tend to be used for longer term applications or larger excavations.
Soil nailing
Soil nailing is a technique in which soil slopes, excavations or retaining walls are reinforced by the insertion of relatively slender elements – normally steel reinforcing bars. The bars are usually installed into a pre-drilled hole and then grouted into place or drilled and grouted simultaneously. They are usually installed untensioned at a slight downward inclination. A rigid or flexible facing (often sprayed concrete) or isolated soil nail heads may be used at the surface.
Shoring in ships
Shoring is used on board when damage has been caused to a vessel's integrity, and to hold leak-stopping devices in place to reduce or stop incoming water. Generally consists of timber 100 mm x 100 mm and used in conjunction with wedges, to further jam shoring in place, pad pieces to spread the load and dogs to hold it together. Also used on board is mechanical shoring as a quick, temporary solution, however it isn't favoured due to its inability to move with the vessel.
Proud
This consists of a timber member jammed on a pad piece on either the deck or deck head depending on water levels in the compartment and a strong point, this is called the proud. Then there is a horizontal timber cut to size to fit between this and what it is shoring up, e.g. a splinter box, bulkhead or door. Timber wedges are then used to tighten up the structure if necessary.
Vertical shoring
This is to support a hatch or splint box on the deck, consisting of a vertical timber between the deck and deck head, with two wedges used opposing each other to tighten it. Pad pieces are used to spread the load on weak structures.
Shoring in air freight
Shoring is a term used in the process of air freight container and pallet (ULD) buildup, e.g. making sure that the cargo placed in containers and on pallets is packed securely and efficiently. Specifically, shoring is done to affix cargo to the ULD and adapt different form factors of cargo items to maximize the use of the available ULD volume. Typically, wooden beams and various forms of boards are used. Most often, shoring material is re-used but as the airfreight industry uses high-quality timber, shoring material often disappears and is a non-insignificant cost of cargo transport.