Related Research Articles

Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a mass spectrum, a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures.

Electrospray ionization (ESI) is a technique used in mass spectrometry to produce ions using an electrospray in which a high voltage is applied to a liquid to create an aerosol. It is especially useful in producing ions from macromolecules because it overcomes the propensity of these molecules to fragment when ionized. ESI is different from other ionization processes since it may produce multiple-charged ions, effectively extending the mass range of the analyser to accommodate the kDa-MDa orders of magnitude observed in proteins and their associated polypeptide fragments.
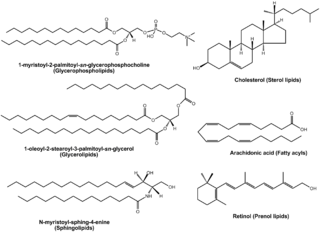
Lipidomics is the large-scale study of pathways and networks of cellular lipids in biological systems The word "lipidome" is used to describe the complete lipid profile within a cell, tissue, organism, or ecosystem and is a subset of the "metabolome" which also includes other major classes of biological molecules. Lipidomics is a relatively recent research field that has been driven by rapid advances in technologies such as mass spectrometry (MS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, dual polarisation interferometry and computational methods, coupled with the recognition of the role of lipids in many metabolic diseases such as obesity, atherosclerosis, stroke, hypertension and diabetes. This rapidly expanding field complements the huge progress made in genomics and proteomics, all of which constitute the family of systems biology.

Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites, the small molecule substrates, intermediates, and products of cell metabolism. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprints that specific cellular processes leave behind", the study of their small-molecule metabolite profiles. The metabolome represents the complete set of metabolites in a biological cell, tissue, organ, or organism, which are the end products of cellular processes. Messenger RNA (mRNA), gene expression data, and proteomic analyses reveal the set of gene products being produced in the cell, data that represents one aspect of cellular function. Conversely, metabolic profiling can give an instantaneous snapshot of the physiology of that cell, and thus, metabolomics provides a direct "functional readout of the physiological state" of an organism. There are indeed quantifiable correlations between the metabolome and the other cellular ensembles, which can be used to predict metabolite abundances in biological samples from, for example mRNA abundances. One of the ultimate challenges of systems biology is to integrate metabolomics with all other -omics information to provide a better understanding of cellular biology.

Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) is an analytical chemistry technique that combines the physical separation capabilities of liquid chromatography with the mass analysis capabilities of mass spectrometry (MS). Coupled chromatography – MS systems are popular in chemical analysis because the individual capabilities of each technique are enhanced synergistically. While liquid chromatography separates mixtures with multiple components, mass spectrometry provides spectral information that may help to identify each separated component. MS is not only sensitive, but provides selective detection, relieving the need for complete chromatographic separation. LC–MS is also appropriate for metabolomics because of its good coverage of a wide range of chemicals. This tandem technique can be used to analyze biochemical, organic, and inorganic compounds commonly found in complex samples of environmental and biological origin. Therefore, LC–MS may be applied in a wide range of sectors including biotechnology, environment monitoring, food processing, and pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and cosmetic industries. Since the early 2000s, LC–MS has also begun to be used in clinical applications.

Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) is an ionization method used in mass spectrometry which utilizes gas-phase ion-molecule reactions at atmospheric pressure (105 Pa), commonly coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). APCI is a soft ionization method similar to chemical ionization where primary ions are produced on a solvent spray. The main usage of APCI is for polar and relatively less polar thermally stable compounds with molecular weight less than 1500 Da. The application of APCI with HPLC has gained a large popularity in trace analysis detection such as steroids, pesticides and also in pharmacology for drug metabolites.

The lipidome refers to the totality of lipids in cells. Lipids are one of the four major molecular components of biological organisms, along with proteins, sugars and nucleic acids. Lipidome is a term coined in the context of omics in modern biology, within the field of lipidomics. It can be studied using mass spectrometry and bioinformatics as well as traditional lab-based methods. The lipidome of a cell can be subdivided into the membrane-lipidome and mediator-lipidome.

Protein mass spectrometry refers to the application of mass spectrometry to the study of proteins. Mass spectrometry is an important method for the accurate mass determination and characterization of proteins, and a variety of methods and instrumentations have been developed for its many uses. Its applications include the identification of proteins and their post-translational modifications, the elucidation of protein complexes, their subunits and functional interactions, as well as the global measurement of proteins in proteomics. It can also be used to localize proteins to the various organelles, and determine the interactions between different proteins as well as with membrane lipids.

Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is an ambient ionization technique that can be coupled to mass spectrometry (MS) for chemical analysis of samples at atmospheric conditions. Coupled ionization sources-MS systems are popular in chemical analysis because the individual capabilities of various sources combined with different MS systems allow for chemical determinations of samples. DESI employs a fast-moving charged solvent stream, at an angle relative to the sample surface, to extract analytes from the surfaces and propel the secondary ions toward the mass analyzer. This tandem technique can be used to analyze forensics analyses, pharmaceuticals, plant tissues, fruits, intact biological tissues, enzyme-substrate complexes, metabolites and polymers. Therefore, DESI-MS may be applied in a wide variety of sectors including food and drug administration, pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring, and biotechnology.
Shotgun proteomics refers to the use of bottom-up proteomics techniques in identifying proteins in complex mixtures using a combination of high performance liquid chromatography combined with mass spectrometry. The name is derived from shotgun sequencing of DNA which is itself named after the rapidly expanding, quasi-random firing pattern of a shotgun. The most common method of shotgun proteomics starts with the proteins in the mixture being digested and the resulting peptides are separated by liquid chromatography. Tandem mass spectrometry is then used to identify the peptides.
Sample preparation for mass spectrometry is used for the optimization of a sample for analysis in a mass spectrometer (MS). Each ionization method has certain factors that must be considered for that method to be successful, such as volume, concentration, sample phase, and composition of the analyte solution. Quite possibly the most important consideration in sample preparation is knowing what phase the sample must be in for analysis to be successful. In some cases the analyte itself must be purified before entering the ion source. In other situations, the matrix, or everything in the solution surrounding the analyte, is the most important factor to consider and adjust. Often, sample preparation itself for mass spectrometry can be avoided by coupling mass spectrometry to a chromatography method, or some other form of separation before entering the mass spectrometer. In some cases, the analyte itself must be adjusted so that analysis is possible, such as in protein mass spectrometry, where usually the protein of interest is cleaved into peptides before analysis, either by in-gel digestion or by proteolysis in solution.

Matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization (MALDESI) was first introduced in 2006 as a novel ambient ionization technique which combines the benefits of electrospray ionization (ESI) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI). An infrared (IR) or ultraviolet (UV) laser can be utilized in MALDESI to resonantly excite an endogenous or exogenous matrix. The term 'matrix' refers to any molecule that is present in large excess and absorbs the energy of the laser, thus facilitating desorption of analyte molecules. The original MALDESI design was implemented using common organic matrices, similar to those used in MALDI, along with a UV laser. The current MALDESI source employs endogenous water or a thin layer of exogenously deposited ice as the energy-absorbing matrix where O-H symmetric and asymmetric stretching bonds are resonantly excited by a mid-IR laser.

Capillary electrophoresis–mass spectrometry (CE–MS) is an analytical chemistry technique formed by the combination of the liquid separation process of capillary electrophoresis with mass spectrometry. CE–MS combines advantages of both CE and MS to provide high separation efficiency and molecular mass information in a single analysis. It has high resolving power and sensitivity, requires minimal volume and can analyze at high speed. Ions are typically formed by electrospray ionization, but they can also be formed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization or other ionization techniques. It has applications in basic research in proteomics and quantitative analysis of biomolecules as well as in clinical medicine. Since its introduction in 1987, new developments and applications have made CE-MS a powerful separation and identification technique. Use of CE–MS has increased for protein and peptides analysis and other biomolecules. However, the development of online CE–MS is not without challenges. Understanding of CE, the interface setup, ionization technique and mass detection system is important to tackle problems while coupling capillary electrophoresis to mass spectrometry.

Ambient ionization is a form of ionization in which ions are formed in an ion source outside the mass spectrometer without sample preparation or separation. Ions can be formed by extraction into charged electrospray droplets, thermally desorbed and ionized by chemical ionization, or laser desorbed or ablated and post-ionized before they enter the mass spectrometer.

Laser ablation electrospray ionization (LAESI) is an ambient ionization method for mass spectrometry that combines laser ablation from a mid-infrared (mid-IR) laser with a secondary electrospray ionization (ESI) process. The mid-IR laser is used to generate gas phase particles which are then ionized through interactions with charged droplets from the ESI source. LAESI was developed in Professor Akos Vertes lab by Peter Nemes in 2007 and it was marketed commercially by Protea Biosciences, Inc until 2017. Fiber-LAESI for single-cell analysis approach was developed by Bindesh Shrestha in Professor Vertes lab in 2009. LAESI is a novel ionization source for mass spectrometry (MS) that has been used to perform MS imaging of plants, tissues, cell pellets, and even single cells. In addition, LAESI has been used to analyze historic documents and untreated biofluids such as urine and blood. The technique of LAESI is performed at atmospheric pressure and therefore overcomes many of the obstacles of traditional MS techniques, including extensive and invasive sample preparation steps and the use of high vacuum. Because molecules and aerosols are ionized by interacting with an electrospray plume, LAESI's ionization mechanism is similar to SESI and EESI techniques.

Extractive electrospray ionization (EESI) is a spray-type, ambient ionization source in mass spectrometry that uses two colliding aerosols, one of which is generated by electrospray. In standard EESI, syringe pumps provide the liquids for both an electrospray and a sample spray. In neutral desorption EESI (ND-EESI), the liquid for the sample aerosol is provided by a flow of nitrogen.

Ceramide synthase 3 (CersS3), also known as longevity assurance homologue 3, is an enzyme that is encoded in humans by the CERS3 gene.
The MasSpec Pen, or the precìso MasSpec Pen System, is a mass spectrometry (MS) based cancer detection and diagnosis system that can be used for ex vivo and in vivo tissue sample analysis. The system collects biological molecules from a tissue sample surface via a solid-liquid extraction mechanism and transports the molecules to a mass spectrometer for analysis. The composition of the extracted molecules can then be used to predict if the tissue sample analyzed contains cancerous cells using machine learning algorithms and statistical models. In early-stage clinical research, the MasSpec Pen system was able to distinguish various cancer tissues, including thyroid, breast, lung, and ovarian tumor tissues, from their normal counterparts with an overall accuracy of 96.3%. A follow-up study in illustrating the use of the device for detection of serous ovarian carcinoma in ex vivo tissue biopsies allowed for the discrimination of normal and cancerous ovarian samples with a clinical sensitivity and specificity of 94.0% and 94.4%, respectively.

Secondary electro-spray ionization (SESI) is an ambient ionization technique for the analysis of trace concentrations of vapors, where a nano-electrospray produces charging agents that collide with the analyte molecules directly in gas-phase. In the subsequent reaction, the charge is transferred and vapors get ionized, most molecules get protonated and deprotonated. SESI works in combination with mass spectrometry or ion-mobility spectrometry.
Probe electrospray ionization (PESI) is an electrospray-based ambient ionization technique which is coupled with mass spectrometry for sample analysis. Unlike traditional mass spectrometry ion sources which must be maintained in a vacuum, ambient ionization techniques permit sample ionization under ambient conditions, allowing for the high-throughput analysis of samples in their native state, often with minimal or no sample pre-treatment. The PESI ion source simply consists of a needle to which a high voltage is applied following sample pick-up, initiating electrospray directly from the solid needle.
References
- ↑ Han X, Gross RW (2005). "Shotgun lipidomics: electrospray ionization mass spectrometric analysis and quantitation of cellular lipidomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples". Mass Spectrom Rev. 24 (3): 367–412. Bibcode:2005MSRv...24..367H. doi:10.1002/mas.20023. PMID 15389848. Archived from the original on 2013-01-05.
- ↑ Han X, Gross RW (April 2005). "Shotgun lipidomics: multidimensional MS analysis of cellular lipidomes". Expert Rev Proteomics. 2 (2): 253–64. doi:10.1586/14789450.2.2.253. PMID 15892569. S2CID 29752390.
- ↑ Han X, Gross RW (June 2003). "Global analyses of cellular lipidomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples by ESI mass spectrometry: a bridge to lipidomics". J. Lipid Res. 44 (6): 1071–9. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R300004-JLR200 . PMID 12671038.