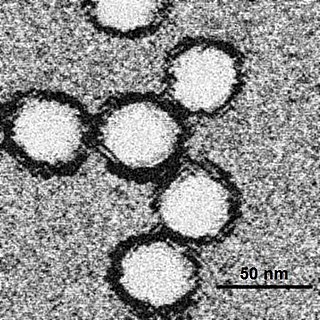
West Nile fever is an infection by the West Nile virus, which is typically spread by mosquitoes. In about 80% of infections people have few or no symptoms. About 20% of people develop a fever, headache, vomiting, or a rash. In less than 1% of people, encephalitis or meningitis occurs, with associated neck stiffness, confusion, or seizures. Recovery may take weeks to months. The risk of death among those in whom the nervous system is affected is about 10%.
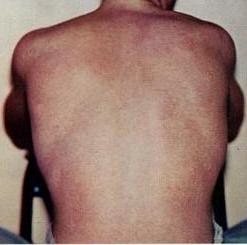
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic skin rash. Recovery generally takes two to seven days. In a small proportion of cases, the disease develops into severe dengue, also known as dengue hemorrhagic fever, resulting in bleeding, low levels of blood platelets and blood plasma leakage, or into dengue shock syndrome, where dangerously low blood pressure occurs.

Infectious mononucleosis, also known as glandular fever, is an infection usually caused by the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). Most people are infected by the virus as children, when the disease produces few or no symptoms. In young adults, the disease often results in fever, sore throat, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, and tiredness. Most people recover in two to four weeks; however, feeling tired may last for months. The liver or spleen may also become swollen, and in less than one percent of cases splenic rupture may occur.

Viral meningitis, also known as aseptic meningitis, is a type of meningitis due to a viral infection. It results in inflammation of the meninges. Symptoms commonly include headache, fever, sensitivity to light and neck stiffness.

Roseola, also known as sixth disease, is an infectious disease caused by certain types of virus. Most infections occur before the age of three. Symptoms vary from absent to the classic presentation of a fever of rapid onset followed by a rash. The fever generally lasts for three to five days, while the rash is generally pink and lasts for less than three days. Complications may include febrile seizures, with serious complications being rare.

Chikungunya is an infection caused by the Chikungunya virus (CHIKV). Symptoms include fever and joint pains. These typically occur two to twelve days after exposure. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a rash. Symptoms usually improve within a week; however, occasionally the joint pain may last for months or years. The risk of death is around 1 in 1,000. The very young, old, and those with other health problems are at risk of more severe disease.

Arbovirus is an informal name used to refer to any viruses that are transmitted by arthropod vectors. The word arbovirus is an acronym. The word tibovirus is sometimes used to more specifically describe viruses transmitted by ticks, a superorder within the arthropods. Arboviruses can affect both animals and plants. In humans, symptoms of arbovirus infection generally occur 3–15 days after exposure to the virus and last three or four days. The most common clinical features of infection are fever, headache, and malaise, but encephalitis and viral hemorrhagic fever may also occur.

Leptospirosis is a blood infection caused by the bacteria Leptospira. Signs and symptoms can range from none to mild to severe. Weil's disease, the acute, severe form of leptospirosis, causes the infected individual to become jaundiced, develop kidney failure, and bleed. Bleeding from the lungs associated with leptospirosis is known as "severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome".

Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea and gastro, is inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract—the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy and dehydration may also occur. This typically lasts less than two weeks. It is not related to influenza, though it has erroneously been called the "stomach flu".
La Crosse encephalitis is an encephalitis caused by an arbovirus which has a mosquito vector.
Murray Valley encephalitis virus (MVEV) is a zoonotic flavivirus endemic to northern Australia and Papua New Guinea. It is the causal agent of Murray Valley encephalitis. In humans, it can cause permanent neurological disease or death. MVEV is related to Kunjin virus, which has a similar ecology, but a lower morbidity rate. Although the arbovirus is endemic to Northern Australia, it has occasionally spread to the southern states during times of heavy rainfall during the summer monsoon season via seasonal flooding of the Murray-Darling River system. These outbreaks can be "...decades apart, with no or very few cases identified in between".

Oropouche fever is a tropical viral infection transmitted by biting midges and mosquitoes from the blood of sloths to humans. This disease is named after the region where it was first discovered and isolated at the Trinidad Regional Virus Laboratory in 1955 by the Oropouche River in Trinidad and Tobago. Oropouche fever is caused by a specific arbovirus, the Oropouche virus (OROV), of the Bunyaviridae family.
California encephalitis orthobunyavirus type strain California encephalitis virus was discovered in Kern County, California and causes encephalitis in humans. Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain that can cause minor symptoms, such as headaches, to more severe symptoms such as seizures. Mosquitoes serve as its carrier and for this reason this virus is known as an arbovirus.
Viral encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma, called encephalitis, by a virus. The different forms of viral encephalitis are called viral encephalitides. It is the most common type of encephalitis and often occurs with viral meningitis. Encephalitic viruses first cause infection and replicate outside of the central nervous system (CNS), most reaching the CNS through the circulatory system and a minority from nerve endings toward the CNS. Once in the brain, the virus and the host's inflammatory response disrupt neural function, leading to illness and complications, many of which frequently are neurological in nature, such as impaired motor skills and altered behavior.

Phlebovirus is one of four genera of the family Phenuiviridae in the order Bunyavirales. The genus currently comprises 60 species. It derives its name from Phlebotominae, the vectors of member species Sandfly fever Naples phlebovirus, which is said to be ultimately from the Greek phlebos, meaning "vein". The proper word for "vein" in ancient Greek is however phleps (φλέψ).

Pappataci fever is a vector-borne febrile arboviral infection caused by three serotypes of Phlebovirus. It occurs in subtropical regions of the Eastern Hemisphere. The name, pappataci fever, comes from the Italian word for sandfly, it is the union of the word "pappa" (food) and taci (silent) which distinguishes these insects from blood-feeding mosquitoes, which produce a typical noise while flying.
Toscana phlebovirus (TOSV) is an arbovirus belonging to Bunyavirales, an order of negative-stranded, enveloped RNA viruses. The virus can be transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected sandfly of the genus Phlebotomus. Toscana is not normally associated with disease, as indicated by high seroprevalence rates in endemic areas, but in common with other sandfly transmitted viruses such as Naples virus and Sicilian virus, infection may result in Pappataci fever, an illness with mild fever, headache and myalgia. In serious cases that go undiagnosed, acute meningitis, meningoencephalitis and encephalitis may occur. There is no specific treatment for infection, so treatment is supportive, reducing the severity of symptoms until the immune system has cleared the infection.
There are several forms of Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infection. These include asymptomatic infections, the primary infection, infectious mononucleosis, and the progression of asymptomatic or primary infections to: 1) any one of various Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative diseases such as chronic active EBV infection, EBV+ hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, Burkitt's lymphoma, and Epstein Barr virus positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified); 2) non-lymphoid cancers such as Epstein-Barr virus associated gastric cancer, soft tissue sarcomas, leiomyosarcoma, and nasopharyngeal cancers; and 3) Epstein-Barr virus-associated non-lymphoproliferative diseases such as some cases of the immune disorders of multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosis and the childhood disorders of Alice in Wonderland Syndrome and acute cerebellar ataxia.
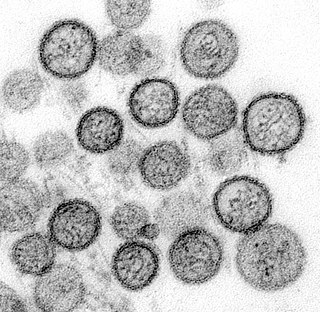
Hantavirus hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) is a group of clinically similar illnesses caused by species of hantaviruses from the family Hantaviridae, in the order Bunyavirales. It is also known as Korean hemorrhagic fever and epidemic hemorrhagic fever. The species that cause HFRS include Hantaan orthohantavirus, Dobrava-Belgrade orthohantavirus, Saaremaa virus, Seoul orthohantavirus, Puumala orthohantavirus and other orthohantaviruses. It is found in Europe, Asia, and Africa. Of these species, Hantaan River virus and Dobrava-Belgrade virus cause the most severe form of the syndrome and have the highest morbidity rates. When caused by the Puumala virus, it is also called nephropathia epidemica. This infection is known as sorkfeber in Swedish and myyräkuume in Finnish. In Norway, it is called musepest.
Adria virus (ADRV), named after the Adriatic Sea, is a phlebovirus transmitted by sandflies that can cause a febrile illness in people. It has been found in sandfly populations in Albania and northern Greece.











