The Alps are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately 1,200 km (750 mi) across eight Alpine countries : France, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia.

The Balkans, also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographic area in Southeast Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish Straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Mount Musala, 2,925 metres (9,596 ft), in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria.

Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and its largest city is Leipzig. Saxony is the tenth largest of Germany's sixteen states, with an area of 18,413 square kilometres (7,109 sq mi), and the sixth most populous, with more than 4 million inhabitants.

The Sudetes are a mountain range in Central Europe, shared by Germany, Poland and the Czech Republic. They are the highest part of Bohemian Massif. They stretch from the Saxon capital of Dresden in the northwest across to the region of Lower Silesia in Poland and to the Moravian Gate in Czechia in the east. Geographically the Sudetes are a Mittelgebirge with some characteristics typical of high mountains. Its plateaus and subtle summit relief makes the Sudetes more akin to mountains of Northern Europe than to the Alps.

Paul Thomas Mann was a German novelist, short story writer, social critic, philanthropist, essayist, and the 1929 Nobel Prize in Literature laureate. His highly symbolic and ironic epic novels and novellas are noted for their insight into the psychology of the artist and the intellectual. His analysis and critique of the European and German soul used modernized versions of German and Biblical stories, as well as the ideas of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Friedrich Nietzsche, and Arthur Schopenhauer.

The Battle of Monte Cassino was a costly series of four assaults by the Allies against the Winter Line in Italy held by Axis forces during the Italian Campaign of World War II. The intention was a breakthrough to Rome.

The Dolomites, also known as the Dolomite Mountains, Dolomite Alps or Dolomitic Alps, are a mountain range located in northeastern Italy. They form part of the Southern Limestone Alps and extend from the River Adige in the west to the Piave Valley in the east. The northern and southern borders are defined by the Puster Valley and the Sugana Valley. The Dolomites are located in the regions of Veneto, Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol and Friuli Venezia Giulia, covering an area shared between the provinces of Belluno, Vicenza, Verona, Trentino, South Tyrol, Udine and Pordenone.

Mount Kilimanjaro is a dormant volcano in Tanzania. It has three volcanic cones: Kibo, Mawenzi, and Shira. It is the highest mountain in Africa and the highest single free-standing mountain in the world: 5,895 metres (19,341 ft) above sea level and about 4,900 metres (16,100 ft) above its plateau base.

The Ore Mountains or Ore Mountain Range in Central Europe have formed a natural border between Bohemia and Saxony for around 800 years, from the 12th to the 20th centuries. Today, the Czech Republic–Germany border runs just north of the main crest of the mountain range. The highest peaks are the Klínovec in the Czech Republic, which rises to 1,244 metres (4,081 ft) above sea level and the Fichtelberg in Germany.

The Vosges are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a single geomorphological unit and low mountain range of around 8,000 km2 (3,100 sq mi) in area. It runs in a north-northeast direction from the Burgundian Gate to the Börrstadt Basin, and forms the western boundary of the Upper Rhine Plain.

The German Army is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German Bundeswehr together with the Marine and the Luftwaffe. As of April 2020, the German Army had a strength of 64,036 soldiers.
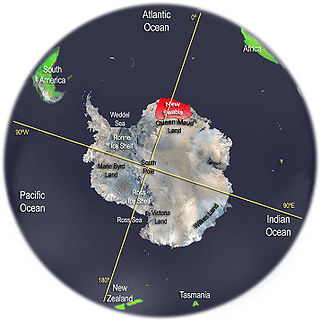
New Swabia was a disputed Antarctic claim by Nazi Germany within the Norwegian territorial claim of Queen Maud Land and is now a cartographic name sometimes given to an area of Antarctica between 20°E and 10°W in Queen Maud Land. New Swabia was explored by Germany in early 1939 and named after that expedition's ship, Schwabenland, itself named after the German region of Swabia.
The 1st Mountain Division was an elite formation of the German Wehrmacht during World War II, and is remembered for its involvement in multiple large-scale war crimes. It was created on 9 April 1938 in Garmisch Partenkirchen from the Mountain Brigade which was itself formed on 1 June 1935. The division consisted mainly of Bavarians and some Austrians.

Oberstdorf is a municipality and skiing and hiking town in Germany, located in the Allgäu region of the Bavarian Alps. It is the southernmost settlement in Germany and one of its highest towns.

Gebirgsjäger are the light infantry part of the alpine or mountain troops (Gebirgstruppe) of Germany, Austria and Switzerland. The word Jäger is a characteristic term used for light infantry in German speaking countries.

Walchensee or Lake Walchen is one of the deepest and largest alpine lakes in Germany, with a maximum depth of 192.3 metres (631 ft) and an area of 16.4 square kilometres (6.3 sq mi). The lake is 75 kilometres (47 mi) south of Munich in the middle of the Bavarian Alps. The entire lake, including the island of Sassau, is within the municipality of Kochel. Landowner of the lake and island area is the Bavarian State. To the east and the south, the lake borders the municipality of Jachenau.

The 7th Mountain Division was formed through the redesignation of 99th Light Infantry Division, which had fought on the southern sector of the Eastern Front until being withdrawn to Germany in October 1941. In 1942, it was sent to Finland and remained there until the Finnish withdrawal from the war. The Division retreated into Norway where it remained until the end of the War.

During World War II, the Lapland War saw fighting between Finland and Nazi Germany – effectively from September to November 1944 – in Finland's northernmost region, Lapland. Though the Finns and the Germans had been fighting against the Soviet Union since 1941 during the Continuation War (1941–1944) the peace negotiations had already been conducted intermittently during 1943–1944 between Finland, the Western Allies and the USSR, but no agreement had been reached. The Moscow Armistice, signed on 19 September 1944, demanded that Finland break diplomatic ties with Germany and expel or disarm any German soldiers remaining in Finland after 15 September 1944.

The Giant Mountains, Krkonoše or Karkonosze are a mountain range located in the north of the Czech Republic and the south-west of Poland, part of the Sudetes mountain system. The Czech-Polish border, which divides the historic regions of Bohemia and Silesia, runs along the main ridge. The highest peak, Sněžka, is the Czech Republic's highest point with an elevation of 1,603 metres (5,259 ft).