Related Research Articles

The CFA franc is the name of two currencies, the West African CFA franc, used in eight West African countries, and the Central African CFA franc, used in six Central African countries. Although separate, the two CFA franc currencies have always been at parity and are effectively interchangeable. The ISO currency codes are XAF for the Central African CFA franc and XOF for the West African CFA franc. On 22 December 2019, it was announced that the West African currency would be reformed and replaced by an independent currency to be called Eco.

The euro is the official currency of 20 of the 27 member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 344 million citizens as of 2023. The euro is divided into 100 cents.

ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individual currencies and their minor units. This data is published in three tables:

The peseta was the currency of Spain between 1868 and 2002. Along with the French franc, it was also a de facto currency used in Andorra.

The Sucre was the currency of Ecuador between 1884 and 2000. Its ISO code was ECS and it was subdivided into 10 decimos and 100 centavos. The sucre was named after Latin American political leader Antonio José de Sucre. The currency was replaced by the United States dollar as a result of the 1998–99 financial crisis.
A currency symbol or currency sign is a graphic symbol used to denote a currency unit. Usually it is defined by the monetary authority, like the national central bank for the currency concerned.

A currency union is an intergovernmental agreement that involves two or more states sharing the same currency. These states may not necessarily have any further integration.
Peso dominicano has been the name of the currency of the Dominican Republic since 2011. Its symbol is "$", with "RD$" used when distinction from other pesos is required; its ISO 4217 code is "DOP". Each peso is divided into 100 centavos ("cents"), for which the ¢ symbol is used. With exception of the United States dollar, it is the only currency that is legal tender in the Dominican Republic for all monetary transactions, whether public or private.

The Union of South American Nations (USAN), sometimes also referred to as the South American Union, abbreviated in Spanish as UNASUR and in Portuguese as UNASUL, is an intergovernmental regional organization set up by Hugo Chavez to counteract the influence of the United States in the region. It once comprised twelve South American countries; as of 2019, most have withdrawn.
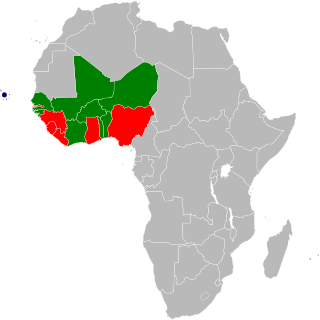
The eco is the name for the proposed common currency of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS). Plans originally called for the West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ) states to introduce the currency first, which would eventually be merged with the CFA franc which is used by the French-speaking west African region within the West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA). This will also enable the UEMOA states to gain complete fiscal and monetary independence from France. The UEMOA states have alternatively proposed to reform the CFA franc into the eco first, which could then be extended to all ECOWAS states.

The peso was a currency of Ecuador until 1884.

The West African CFA franc is the currency used by eight independent states in West Africa which make up the West African Economic and Monetary Union : Benin, Burkina Faso, Côte d'Ivoire, Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Niger, Senegal and Togo. These eight countries had a combined population of 105.7 million people in 2014, and a combined GDP of US$128.6 billion.

The currencies of Puerto Rico closely follow the historic development of Puerto Rico. As a Province of Spain and a territory of the United States, Puerto Rico was granted the use of both foreign and provincial currencies. Following the Spanish colonization in 1502, Puerto Rico became an important port, with its own supply of gold. However, as the mineral reserves ran empty within the century, the archipelago's economy suffered. The Spanish Crown issued the Situado Mexicano, which meant that a semi-regular shipment of gold from the Viceroyalty of New Spain would be sent to the island, as a way to provide economic support. Between 1636 and 1637, Philip IV of Spain imposed a tax which had to be paid using a revenue stamp. Inspired by this, Puerto Rico began producing banknotes in 1766, becoming the first Overseas Province to print 8-real banknotes in the Spanish Empire and which in the Spanish government's approval of subsequent issues.

In international finance, a world currency, supranational currency, or global currency is a currency that would be transacted internationally, with no set borders.

The African Monetary Union (AMU) is the proposed creation of an economic and monetary union for the countries of the African Union, administered by the African Central Bank. Such a union would call for the creation of a new unified currency, similar to the euro; the hypothetical currency is sometimes referred to as the afro or afriq.
Currency in Colombia denotes the ingots, coins, and banknotes that have been used in Colombia since 1622. It was in that year, under a licence purchased from King Philip III of Spain, that Turrillo de Yebra established a mint at Santa Fe de Bogotá and a branch mint at Cartagena de las Indias, where gold cobs were produced as part of Colombia's first currency. Silver milled coins date from 1627. In 1831, Gran Colombia dissolved into Venezuela and New Granada. In 1836, in New Granada, new monetary laws were passed, to standardise the money produced in the country. From 1861 to 1862, due to financial instability, the United States of New Granada accepted British currency, the name of the country becoming the United States of Colombia in 1862. In 1880, Colombia pegged the peso to the gold standard due to the falling price of silver. In 1886, the paper peso was introduced. In 1931, Colombia abandoned the gold standard and switched to the current form of the peso.
The article provides a historical summary of the currency used in Ecuador. The present currency of Ecuador is the United States dollar.

The (first) cruzeiro (Cr$) was the official currency of Brazil from 1942 to 1967. It replaced the old real, which had been in use since colonial times, at the rate of Rs 1$000 = Cr$1, It was in turn replaced by the cruzeiro novo, at the rate of Cr$1,000 = NCr$1.
References
- ↑ Morales propõe moeda única para União de Nações Sul-Americanas, Folha.com, 21 de abril de 2007]
- ↑ Guedes e Ciro defendem moeda única sul-americana, DCI, 9 de abril de 2008
- ↑ Ecuador apoya una moneda única para Suramérica, El País, 12 de dezembro de 2007