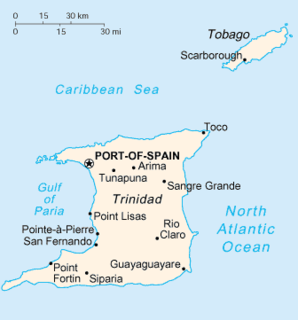
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies 11 km (6.8 mi) off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of 5,131 km2 (1,981 sq mi), it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies.

San Fernando, officially the City of San Fernando, is the most populous city and second most populous municipality in Trinidad and Tobago, after Chaguanas. Sando, as it is also known, occupies 19 km² and is located in the southwestern part of the island of Trinidad. It is bounded to the north by the Guaracara River, the south by the Oropouche River, the east by the Sir Solomon Hochoy Highway, and the west by the Gulf of Paria. The former borough was elevated to the status of a city corporation on 18 November 1988. The motto of San Fernando is: "Sanitas Fortis" - In a Healthy Environment We Will Find Strength. Many local Trinidadians refer to the city with the shortened name "Sando." San Fernando is called Trinidad and Tobago's "industrial capital" because of its proximity to the Pointe-à-Pierre oil refinery and many other petrochemical, LNG, iron and steel and aluminium smelters in places such as Point Lisas in Couva, Point Fortin, and La Brea.
Siparia is a town in southern Trinidad, in Trinidad and Tobago, south of San Fernando, southwest of Penal and Debe and southeast of Fyzabad. Also called "The Sand City", it was originally a non-Mission Amerindian settlement. Siparia grew to be the administrative centre for Saint Patrick County, and later the Siparia Regional Corporation. Today it is a commercial centre and market town serving the surrounding agricultural areas and oil fields. Siparia is also the seat of the Siparia Regional Corporation.

Penal is a town in south Trinidad, Trinidad and Tobago. It lies south of San Fernando, Princes Town, and Debe, and north of Moruga, Morne Diablo and Siparia. It was originally a rice- and cocoa-producing area but is now a rapidly expanding and developing town. The population is 12,281.

Hinduism is the second largest religion in Trinidad and Tobago. Hindu culture arrived in 1845 in Trinidad and Tobago. According to the 2011 census there were 240,100 declared Hindus in Trinidad and Tobago. There are also various temples in Trinidad and Tobago to accommodate Hindus.

Saint Patrick is a county in Trinidad and Tobago which occupies an area of 673 km2 (260 mi2). It occupies the southwestern peninsula of the island of Trinidad and is bounded by the Columbus Channel to the south, the Gulf of Paria to the west, and Victoria to the north. It includes the towns of Point Fortin, La Brea, Siparia, Cedros, Fyzabad and Penal. Saint Patrick is divided into four Wards: Cedros, La Brea, Erin and Siparia.

Diego Martin is a Region of Trinidad and Tobago. The region has a land area of 127.53 km². Urban areas within the region include Carenage, Diego Martin, Maraval and parts of Saint James. The local government body is the Diego Martin Regional Corporation.

Penal–Debe region is a region of Trinidad. The local government body is Penal–Debe Regional Corporation, a Regional Corporation of Trinidad and Tobago. The region has a land area of 246.91 km². Urban areas within Penal–Debe include Penal, where the corporation is headquartered, and Debe.
San Juan–Laventille is a region of Trinidad. It has a land area of 220.39 km². The San Juan–Laventille Regional Corporation is headquartered at MTS Plaza in Aranguez, San Juan. Other urban areas include Barataria, Laventille, Morvant and San Juan. It is the smallest region in Trinidad. The region is bordered by Port of Spain in the west to St. Joseph in the east.

Tunapuna–Piarco is one of the 9 regions of Trinidad and Tobago. It is the most populous region in the country by total population and the fifth-largest by total land area. Geographically located in Northern Trinidad, Tunapuna–Piarco shares its borders with the regions of San Juan–Laventille to the west, Couva–Tabaquite–Talparo to the south, the Borough of Chaguanas to the south-west, Sangre Grande to the east and the Caribbean Sea to the north. The region also completely surrounds the Royal Chartered Borough of Arima, which is located in the south-eastern corner of the region.

Maxi taxis are private, owner-operated minibuses in Romania and Trinidad and Tobago that are used in public transport. They operate along fixed routes, having fixed fares and meeting points, but do not operate under a timetable.

General elections were held in Trinidad and Tobago on 5 November 2007. Nomination day was 15 October. Five parties contested the elections; the ruling People's National Movement, the official opposition United National Congress–Alliance, the Congress of the People, the Tobago United Front–Democratic Action Congress and the Democratic National Assembly. Five independent candidates also ran.
Santa Flora is a community in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located in southern Trinidad, and is administered by the Siparia Regional Corporation.

The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago.

At the ceremonial opening of the Tenth Republican Parliament on June 18, 2010, the Prime Minister Kamla Persad-Bissessar announced that the date for the 2010 Local Elections was to be on July 26, 2010.

South Oropouche is a community in Trinidad and Tobago. It is at sea level. There is an archaeological site at St John's Road, South Oropouche. Dow Village is in South Oropouche.

Local elections in Trinidad and Tobago were held on 2 December 2019, contesting 139 electoral districts across Trinidad's 14 municipal corporation electoral areas.
















