
The geography of Egypt relates to two regions: North Africa and West Asia.
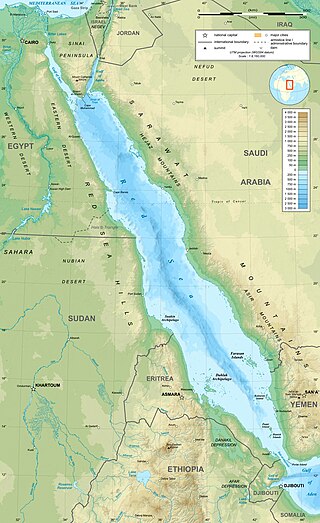
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez—leading to the Suez Canal. It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley.

Sudan is located in Northeast Africa. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west and Libya to the northwest. Sudan is the third largest country in Africa, after Algeria and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was the largest country on the continent until South Sudan split off from it in 2011.

Port Sudan is a port city on the Red Sea in eastern Sudan, and the capital of Red Sea State. Port Sudan is Sudan's main seaport and the source of 90% of the country's international trade. The population of Port Sudan was estimated in the 2008 Census of Sudan to be 394,561 people.

Red Sea Governorate is one of the 27 governorates (States) of Egypt. Located between the Nile and the Red Sea in the southeast of the country, its southern border forms part of Egypt's border with Sudan. Its capital and largest city is Hurghada.

The Beja people are a Cushitic ethnic group native to the Eastern Desert, inhabiting a coastal area from southeastern Egypt through eastern Sudan and into northwestern Eritrea. They are descended from peoples who have inhabited the area since 4000 BC or earlier, although they were Arabized by Arabs who settled in the region. They are nomadic and live primarily in the Eastern Desert. The Beja number around 1,900,000 to 2,759,000.

Red Sea State is one of the 18 states of Sudan. It has an area of 212,800 km2 and an estimated population of 1,482,053 in 2018. Port Sudan is the capital of the state. Sudan claims, but does not control, the Halaib Triangle, a region disputed between Sudan and Egypt. The original inhabitants of the state are the Beja people who constitute more than 65% of the total population, with lower wealth and power in the region.

Suakin or Sawakin is a port city in northeastern Sudan, on the west coast of the Red Sea. It was formerly the region's chief port, but is now secondary to Port Sudan, about 50 kilometres (30 mi) north.

The Halaib Triangle is an area of land measuring 20,580 square kilometres (7,950 sq mi) located on the Northeast African coast of the Red Sea. The area, which takes its name from the town of Halaib, is created by the difference in the Egypt–Sudan border between the "political boundary" set in 1899 by the Anglo-Egyptian Condominium, which runs along the 22nd parallel north, and the "administrative boundary" set by the British in 1902, which gave administrative responsibility for an area of land north of the line to Sudan, which was an Anglo-Egyptian client at the time. With the independence of Sudan in 1956, both Egypt and Sudan claimed sovereignty over the area. The area has been considered to be a part of the Sudan's Red Sea State, and was included in local elections until the late 1980s. In 1994, the Egyptian military moved to take control of the area as a part of Red Sea Governorate, and Egypt has been actively investing in it since then. Egypt has been recently categorical in rejecting international arbitration or even political negotiations regarding the area.

The Eastern Desert is the part of the Sahara Desert that is located east of the Nile River. It spans 223,000 square kilometres (86,000 sq mi) of northeastern Africa and is bordered by the Gulf of Suez and the Red Sea to the east, and the Nile River to the west. It extends through Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and the Sudan. The Eastern Desert consists of a mountain range which runs parallel to the coast, wide sedimentary plateaus extending from either side of the mountains and the Red Sea coast. The rainfall, climate, vegetation and animal life sustained in the desert varies between these different regions. The Eastern Desert has been a mining site for building materials, as well as precious and semi-precious metals, throughout history. It has historically contained many trade routes leading to and from the Red Sea, including the Suez Canal.
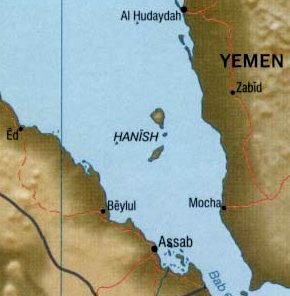
The Hanish Islands conflict was a dispute between Yemen and Eritrea over the island of Greater Hanish in the Red Sea, one of the largest in the then disputed Zukur-Hanish archipelago. Fighting took place over three days from 15 December to 17 December 1995. In 1998 the Permanent Court of Arbitration determined that the territory belonged to Yemen.

El Gouna is an Egyptian tourist city created in 1990, and is owned and developed by Samih Sawiris' Orascom Development. It is located on the Red Sea in the Red Sea Governorate of Egypt, 20 kilometres north of Hurghada. It is part of the Red Sea Riviera, and a host city of the El Gouna Film Festival.

Tiran, and Yotvat Island, is a Saudi Arabian island that was formerly administered by Egypt. Sovereignty of the two Red Sea islands, Tiran and Sanafir, was ceded officially to Saudi Arabia as part of a maritime border agreement between Egypt and Saudi Arabia. The agreement was subsequently approved by the Egyptian Parliament and finally ratified by President Abd el-Fattah el-Sisi on 24 June 2017.
Gabal Elba, or Elba Mountain refers to the mountain itself as well as the mountainous area in the Halaib Triangle of Northeast Africa. It is claimed by both Egypt and Sudan, but is under Egyptian control.

The wildlife of Sudan is composed of its flora and fauna. A variety of climate types in Sudan results in a wide range of habitats and the range of wildlife is diverse. Some 287 species of mammal have been recorded in the country and some 634 species of bird.

Bir Tawil is a 2,060 km2 (795.4 sq mi) area of land along the border between Egypt and Sudan, which is uninhabited and claimed by neither country. When spoken of in association with the neighbouring Halaib Triangle, it is sometimes referred to as the Bir Tawil Triangle, despite the area's quadrilateral shape; the two regions border at a quadripoint.

Various lists of the Wonders of the World have been compiled from antiquity to the present day, in order to catalogue the world's most spectacular natural features and human-built structures.
Halaib, is a Red Sea port and town, located in the Halaib Triangle, a 20,580 km2 (7,950 sq mi) area disputed between Egypt and Sudan. The town lies on the southern tip of what Egyptians refer to as the Red Sea Riviera and the north eastern corner of Sudan's Red Sea State and is near the ruins of medieval ʽAydhab. De facto control of the area is held by the Egyptian government.

The Albanian Ionian Sea Coast is a coastline of the north-eastern Ionian Sea, that encompasses the south-western border of the Republic of Albania, stretching from the southern half of Karaburun Peninsula, across the historical region of Labëria, the city of Sarandë, the mountains of the Ceraunians, and the Albanian Riviera, to the Lake of Butrint, where the Strait of Corfu separates the country from Greece.
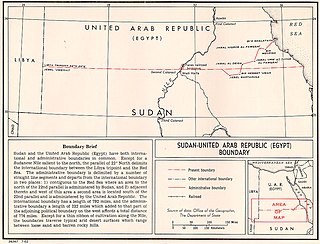
The Egypt–Sudan border is 1,276 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Libya in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The eastern section of the border is subject to a territorial dispute between the two states.




















