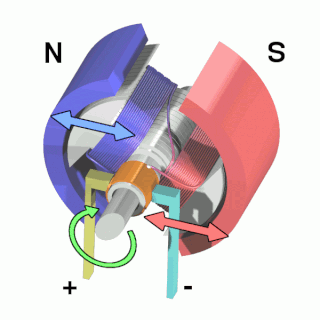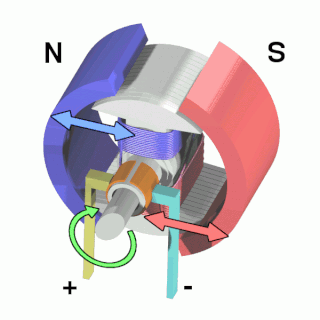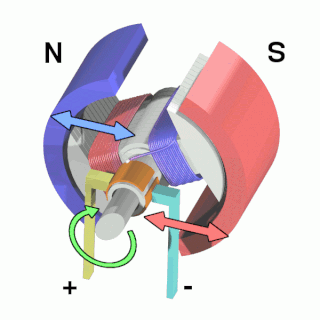
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries, or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, inverters or electrical generators. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates with a reversed flow of power, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
An heat shield is designed to protect an object from overheating by dissipating, reflecting, absorbing heat, or simply gradually burn and fall away from the aircraft, pulling the excess heat with it. The term is most often used in reference to exhaust heat management and to systems for dissipation of heat due to friction.

A thermosetting polymer, often called a thermoset, is a polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening ("curing") a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer (resin). Curing is induced by heat or suitable radiation and may be promoted by high pressure, or mixing with a catalyst. Heat is not necessarily applied externally, but is often generated by the reaction of the resin with a curing agent. Curing results in chemical reactions that create extensive cross-linking between polymer chains to produce an infusible and insoluble polymer network.

Lamination is the technique/process of manufacturing a material in multiple layers, so that the composite material achieves improved strength, stability, sound insulation, appearance, or other properties from the use of the differing materials, such as plastic. A laminate is a permanently assembled object created using heat, pressure, welding, or adhesives. Various coating machines, machine presses and calendering equipment are used.

Polyimide is a polymer of imide monomers belonging to the class of high performance plastics. With their high heat-resistance, polyimides enjoy diverse applications in roles demanding rugged organic materials, e.g. high temperature fuel cells, displays, and various military roles. A classic polyimide is Kapton, which is produced by condensation of pyromellitic dianhydride and 4,4'-oxydianiline.

A squirrel-cage rotor is the rotating part of the common squirrel-cage induction motor. It consists of a cylinder of steel laminations, with aluminum or copper conductors embedded in its surface. In operation, the non-rotating stator winding is connected to an alternating current power source; the alternating current in the stator produces a rotating magnetic field. The rotor winding has current induced in it by the stator field, like a transformer except that the current in the rotor is varying at the stator field rotation rate minus the physical rotation rate. The interaction of the magnetic fields of currents in the stator and rotor produce a torque on the rotor.

Metallic fibers are manufactured fibers composed of metal, metallic alloys, plastic-coated metal, metal-coated plastic, or a core completely covered by metal.
Micarta is a brand name for composites of linen, canvas, paper, fiberglass, carbon fiber, or other fabric in a thermosetting plastic. It was originally used in electrical and decorative applications. Micarta was developed by George Westinghouse at least as early as 1910 using phenolic resins invented by Leo Baekeland. These resins were used to impregnate paper and cotton fabric which were cured under pressure and high temperature to produce laminates. In later years this manufacturing method included the use of fiberglass fabric and other resin types were also used. Today Micarta high-pressure industrial laminates are produced with a wide variety of resins and fibers. The term has been used generically for most resin impregnated fiber compounds. Common uses of modern high-pressure laminates are as electrical insulators, printed circuit board substrates, and knife handles.

A turbo generator is an electric generator connected to the shaft of a steam turbine or gas turbine for the generation of electric power. Large steam-powered turbo generators provide the majority of the world's electricity and are also used by steam-powered turbo-electric ships.
An induction heater is a key piece of equipment used in all forms of induction heating. Typically an induction heater operates at either medium frequency (MF) or radio frequency (RF) ranges.

Wind turbine design is the process of defining the form and configuration of a wind turbine to extract energy from the wind. An installation consists of the systems needed to capture the wind's energy, point the turbine into the wind, convert mechanical rotation into electrical power, and other systems to start, stop, and control the turbine.
Energy technology is an interdisciplinary engineering science having to do with the efficient, safe, environmentally friendly, and economical extraction, conversion, transportation, storage, and use of energy, targeted towards yielding high efficiency whilst skirting side effects on humans, nature, and the environment.

A hydrogen-cooled turbo generator is a turbo generator with gaseous hydrogen as a coolant. Hydrogen-cooled turbo generators are designed to provide a low-drag atmosphere and cooling for single-shaft and combined-cycle applications in combination with steam turbines. Because of the high thermal conductivity and other favorable properties of hydrogen gas, this is the most common type in its field today.

A wind turbine is a device that converts the wind's kinetic energy into electrical energy.

Flywheel energy storage (FES) works by accelerating a rotor (flywheel) to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy. When energy is extracted from the system, the flywheel's rotational speed is reduced as a consequence of the principle of conservation of energy; adding energy to the system correspondingly results in an increase in the speed of the flywheel.
Three-dimensional composites use fiber preforms constructed from yarns or tows arranged into complex three-dimensional structures. These can be created from a 3D weaving process, a 3D knitting process, a 3D braiding process, or a 3D lay of short fibers. A resin is applied to the 3D preform to create the composite material. Three-dimensional composites are used in highly engineered and highly technical applications in order to achieve complex mechanical properties. Three-dimensional composites are engineered to react to stresses and strains in ways that are not possible with traditional composite materials composed of single direction tows, or 2D woven composites, sandwich composites or stacked laminate materials.

Starting in 1975, NASA managed a program for the United States Department of Energy and the United States Department of Interior to develop utility-scale wind turbines for electric power, in response to the increase in oil prices. A number of the world's largest wind turbines were developed and tested under this pioneering program. The program was an attempt to leap well beyond the then-current state of the art of wind turbine generators, and developed a number of technologies later adopted by the wind turbine industry. The development of the commercial industry however was delayed by a significant decrease in competing energy prices during the 1980s.
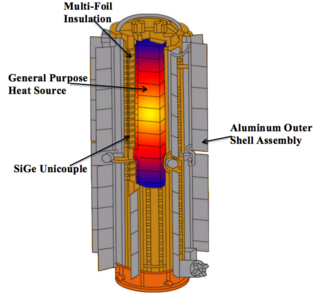
Silicon-germanium (SiGe) thermoelectrics have been used for converting heat into power in spacecraft designed for deep-space NASA missions since 1976. This material is used in the radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) that power Voyager 1, Voyager 2, Galileo, Ulysses, Cassini, and New Horizons spacecraft. SiGe thermoelectric material converts enough radiated heat into electrical power to fully meet the power demands of each spacecraft. The properties of the material and the remaining components of the RTG contribute towards the efficiency of this thermoelectric conversion.

In electrical engineering, coil winding is the manufacture of electromagnetic coils. Coils are used as components of circuits, and to provide the magnetic field of motors, transformers, and generators, and in the manufacture of loudspeakers and microphones. The shape and dimensions of a winding are designed to fulfill the particular purpose. Parameters such as inductance, Q factor, insulation strength, and strength of the desired magnetic field greatly influence the design of coil windings. Coil winding can be structured into several groups regarding the type and geometry of the wound coil. Mass production of electromagnetic coils relies on automated machinery.

In electrical engineering, a vacuum interrupter is a switch which uses electrical contacts in a vacuum. It is the core component of medium-voltage circuit-breakers, generator circuit-breakers, and high-voltage circuit-breakers. Separation of the electrical contacts results in a metal vapour arc, which is quickly extinguished. Vacuum interrupters are widely used in utility power transmission systems, power generation unit, and power-distribution systems for railways, arc furnace applications, and industrial plants.















