Related Research Articles

Alfonso IV, called the Monk, was King of León from 925 and King of Galicia from 929, until he abdicated in 931.

The Center for Research and Advanced Studies of the National Polytechnic Institute is a Mexican non-governmental scientific research institution affiliated with the National Polytechnic Institute and founded by president Adolfo López Mateos on 17 April 1961, initially planned as a postgraduate department of the National Polytechnic Institute; this was later modified by President José López Portillo, on 17 September 1982.
Paul Kirchhoff was a German-Mexican anthropologist, most noted for his seminal work in defining and elaborating the culture area of Mesoamerica, a term he coined.

Alonso de Molina was a Franciscan priest and grammarian, who wrote a well-known dictionary of the Nahuatl language published in 1571 and still used by scholars working on Nahuatl texts in the tradition of the New Philology. He also wrote a bilingual confessional manual for priests who served in Nahuatl-speaking communities.

Chinese people in Spain form the ninth-largest non-European Union foreign community in Spain. As of 2009, official figures showed 145,425 Chinese citizens residing in Spain; however, this figure does not include people with origins in other Overseas Chinese communities, nor Spanish citizens of Chinese origin or descent.

Vocabulario en lengua castellana y mexicana is a bilingual dictionary of Spanish and Nahuatl by Alonso de Molina, first published in 1555 originally entitled Aquí comiença un vocabulario en la lengua castellana y mexicana, edited by Juan Pablos. It was the first dictionary to be published in the New World. However the most relevant and most famous edition was the one made in 1571, edited by Antonio de Spinosa, which then came to be named Vocabulario en lengua castellana y mexicana. This new edition included the Nahuatl-to-Spanish section that the original didn't.

José de León Toral was a Roman Catholic who assassinated General Álvaro Obregón, then-president elect of Mexico, in 1928.
Latindex is a bibliographical information system available for free consultation. Established as a network in 1997, the project is based on the cooperation of 17 national resource centers that operate in a coordinated scheme for the gathering and dissemination of relevant information and data on the Iberoamerican journals.

Christian Carlos Hernan Castillo is an Argentinian activist, politician, sociologist and university teacher. He is a founding member of the Socialist Workers' Party (Argentina) (PTS). In the 2013 elections he was voted in as a deputy for the Buenos Aires Province for the Workers Left Front; he resigned to his seat on June 10, 2015 to leave his place to the next candidate based on the banking rotation between the different parties that make up the Front. He was pre-candidate to Governor of the Buenos Aires Province during the 2015 primary elections, losing to Néstor Pitrola.
Classical Otomi is the name used for the Otomi language as spoken in the early centuries of Spanish colonial rule in Mexico and documented by Spanish friars who learned the language in order to catechize the Otomi peoples. During the colonial period, many Otomis learned to write their language in Roman letters. As a consequence, a significant number of documents in Otomi, both secular and religious, exist from the period, and the most well-known documents are the Codices of Huichapan and Jilotepec. Text in classical Otomi is not easily accessible since the Spanish speaking friars failed to differentiate the varied vowel and consonant sounds of the Otomi language.

The Centre for Political and Constitutional Studies, previously known as the Institute for Political Studies, is an autonomous agency associated with the Ministry for the Presidency of Spain.
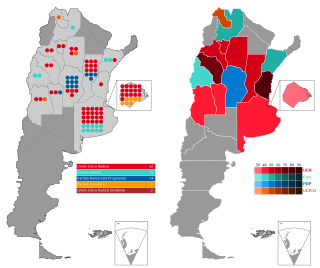
The Argentine legislative elections of 1920 were held on 7 March. Voters chose their legislators and numerous governors, and with a turnout of 53.7%.

John of Castile, called the "el de Tarifa" was an infante of Castile and León. He was engaged in a decades-long fight for control over the Lordship of Biscay with Diego López V de Haro, the uncle of his wife.
Juan Pedro Laporte Molina was a prominent Guatemalan archaeologist best known for his work on the ancient Maya civilization. He studied in the United States at the University of Arizona, in which he enrolled at the age of nineteen. After just one year he transferred to the Escuela Nacional de Antropología e Historia in Mexico. He continued his studies at the Universidad Autónoma de México from 1972 to 1976, from which he graduated with a doctorate in archaeology. He worked as a research assistant at the Museo Nacional de Antropología in Mexico City from 1967 through to 1976. Laporte worked at various archaeological sites while he was in Mexico, including Tlatilco, Chichen Itza and Dainzú. He first began working as an archaeologist in Guatemala in the 1970s, and was the head of the School of History of the Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala (USAC) for more than thirty years. He first entered USAC in 1977, soon after returning from Mexico. In 1974 he carried out investigations at the Maya archaeological site of Uaxactun in the northern Petén Department of Guatemala. Between 1974 and 1976 he carried out archaeological investigations in Antigua Guatemala, which has since been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and around Lake Izabal.

Mauricio García Vega is a Mexican painter whose work has been recognized by various awards and membership in the Salón de la Plástica Mexicana. His work is mostly focused on urban landscapes, often with dark themes and a chaotic feel. He works both alone and with his brother Antonio García Vega. He lives and works in the Mexico City suburb of Ciudad Nezahualcóyotl.
Jorge Erdely Graham is a Mexican theologian, religious studies scholar, and author.
Anarchism in Costa Rica emerged in the 1890s, when it first came to the attention of the country's ruling elites, including the Catholic Church.

María Teresa Rojas Rabiela is an ethnologist, ethnohistorian, Emeritus National Researcher and Mexican academic, specializing in Chinampas of Mexico's Basin, history of agriculture, hydraulics, technology, and labor organization in Mesoamerica during pre-Columbian and colonial eras, as well as historical photography of Mexico's peasants and indigenous people. She is recognized as a pioneer in historical studies on earthquakes in Mexico. From 2018 to 2021, Rojas Rabiela was involved in the restoration of the section of the pre-Hispanic aqueduct of Tetzcotzinco, Texcoco, known as El caño quebrado.
References
- ↑ Chapman, Debra D. (2014-01-10). The Struggle for Mexico: State Corporatism and Popular Opposition. McFarland. ISBN 978-0-7864-8960-2.
- ↑ Cuadernos C.E.I.P. "León Trotsky": revista del Centro de Estudios, Investigaciones y Publicaciones "León Trotsky" de Argentina (in Spanish). Centro de Estudios, Investigaciones y Publicaciones "León Trotsky". 2001.