
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes and other features etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. PCBs are used to connect or "wire" components to one another in an electronic circuit. Electrical components may be fixed to conductive pads on the outer layers, generally by soldering, which both electrically connects and mechanically fastens the components to the board. Another manufacturing process adds vias, metal-lined drilled holes that enable electrical interconnections between conductive layers, to boards with more than a single side.

A ball grid array (BGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging used for integrated circuits. BGA packages are used to permanently mount devices such as microprocessors. A BGA can provide more interconnection pins than can be put on a dual in-line or flat package. The whole bottom surface of the device can be used, instead of just the perimeter. The traces connecting the package's leads to the wires or balls which connect the die to package are also on average shorter than with a perimeter-only type, leading to better performance at high speeds.

Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referred to as a surface-mount device (SMD). In industry, this approach has largely replaced through-hole technology construction method of fitting components, in large part because SMT allows for increased manufacturing automation which reduces cost and improves quality. It also allows for more components to fit on a given area of substrate. Both technologies can be used on the same board, with the through-hole technology often used for components not suitable for surface mounting such as large transformers and heat-sinked power semiconductors.

Flip chip, also known as controlled collapse chip connection or its abbreviation, C4, is a method for interconnecting dies such as semiconductor devices, IC chips, integrated passive devices and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), to external circuitry with solder bumps that have been deposited onto the chip pads. The technique was developed by General Electric's Light Military Electronics Department, Utica, New York. The solder bumps are deposited on the chip pads on the top side of the wafer during the final wafer processing step. In order to mount the chip to external circuitry, it is flipped over so that its top side faces down, and aligned so that its pads align with matching pads on the external circuit, and then the solder is reflowed to complete the interconnect. This is in contrast to wire bonding, in which the chip is mounted upright and fine wires are welded onto the chip pads and lead frame contacts to interconnect the chip pads to external circuitry.

Integrated circuit packaging is the final stage of semiconductor device fabrication, in which the die is encapsulated in a supporting case that prevents physical damage and corrosion. The case, known as a "package", supports the electrical contacts which connect the device to a circuit board.

The land grid array (LGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits (ICs) that is notable for having the pins on the socket — as opposed to pins on the integrated circuit, known as a pin grid array (PGA). An LGA can be electrically connected to a printed circuit board (PCB) either by the use of a socket or by soldering directly to the board.

A quad flat package (QFP) is a surface-mounted integrated circuit package with "gull wing" leads extending from each of the four sides. Socketing such packages is rare and through-hole mounting is not possible. Versions ranging from 32 to 304 pins with a pitch ranging from 0.4 to 1.0 mm are common. Other special variants include low-profile QFP (LQFP) and thin QFP (TQFP).

In electronics, rework is repair or refinish of a printed circuit board (PCB) assembly, usually involving desoldering and re-soldering of surface-mounted electronic components (SMD). Mass processing techniques are not applicable to single device repair or replacement, and specialized manual techniques by expert personnel using appropriate equipment are required to replace defective components; area array packages such as ball grid array (BGA) devices particularly require expertise and appropriate tools. A hot air gun or hot air station is used to heat devices and melt solder, and specialised tools are used to pick up and position often tiny components. A rework station is a place to do this work—the tools and supplies for this work, typically on a workbench. Other kinds of rework require other tools.

A chip scale package or chip-scale package (CSP) is a type of integrated circuit package.

Flat no-leads packages such as quad-flat no-leads (QFN) and dual-flat no-leads (DFN) physically and electrically connect integrated circuits to printed circuit boards. Flat no-leads, also known as micro leadframe (MLF) and SON, is a surface-mount technology, one of several package technologies that connect ICs to the surfaces of PCBs without through-holes. Flat no-lead is a near chip scale plastic encapsulated package made with a planar copper lead frame substrate. Perimeter lands on the package bottom provide electrical connections to the PCB. Flat no-lead packages usually, but not always, include an exposed thermally conductive pad to improve heat transfer out of the IC. Heat transfer can be further facilitated by metal vias in the thermal pad. The QFN package is similar to the quad-flat package (QFP), and a ball grid array (BGA).
Package on a package (PoP) is an integrated circuit packaging method to vertically combine ball grid array (BGA) packages for discrete logic and memory. Two or more packages are installed atop each other, i.e. stacked, with a standard interface to route signals between them. PoP allows higher component density in devices, such as mobile phones, personal digital assistants (PDA), and digital cameras, at the cost of being slightly taller. Stacks with more than 2 packages are uncommon, due to heat dissipation considerations.
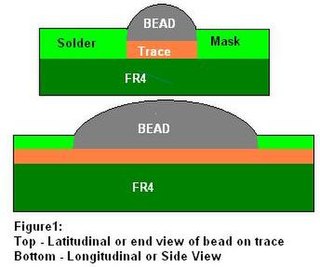
Bead probe technology (BPT) is technique used to provide electrical access to printed circuit board (PCB) circuitry for performing in-circuit testing (ICT). It makes use of small beads of solder placed onto the board's traces to allow measuring and controlling of the signals using a test probe. This permits test access to boards on which standard ICT test pads are not feasible due to space constraints.

A thermal copper pillar bump, also known as a "thermal bump", is a thermoelectric device made from thin-film thermoelectric material embedded in flip chip interconnects for use in electronics and optoelectronic packaging, including: flip chip packaging of CPU and GPU integrated circuits (chips), laser diodes, and semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOA). Unlike conventional solder bumps that provide an electrical path and a mechanical connection to the package, thermal bumps act as solid-state heat pumps and add thermal management functionality locally on the surface of a chip or to another electrical component. The diameter of a thermal bump is 238 μm and 60 μm high.

Wafer-level packaging (WLP) is a process in integrated circuit manufacturing where packaging components are attached to an integrated circuit (IC) before the wafer – on which the IC is fabricated – is diced. In WLP, the top and bottom layers of the packaging and the solder bumps are attached to the integrated circuits while they are still in the wafer. This process differs from a conventional process, in which the wafer is sliced into individual circuits (dice) before the packaging components are attached.
Pad cratering is a mechanically induced fracture in the resin between copper foil and outermost layer of fiberglass of a printed circuit board (PCB). It may be within the resin or at the resin to fiberglass interface.
In the assembly of integrated circuit packages to printed circuit boards, a head-in-pillow defect, also called ball-and-socket, is a failure of the soldering process. For example, in the case of a ball grid array (BGA) package, the pre-deposited solder ball on the package and the solder paste applied to the circuit board may both melt, but the melted solder does not join. A cross-section through the failed joint shows a distinct boundary between the solder ball on the part and the solder paste on the circuit board, rather like a section through a head resting on a pillow.
Digital image correlation analyses have applications in material property characterization, displacement measurement, and strain mapping. As such, DIC is becoming an increasingly popular tool when evaluating the thermo-mechanical behavior of electronic components and systems.

Chip on board (COB) is a method of circuit board manufacturing in which integrated circuits (e.g. microprocessors) are attached (wired, bonded directly) to a printed circuit board, and covered by a blob of epoxy. Chip on board eliminates the packaging of individual semiconductor devices, which allows a completed product to be less costly, lighter, and more compact. In some cases, COB construction improves the operation of radio frequency systems by reducing the inductance and capacitance of integrated circuit leads.
Glossary of microelectronics manufacturing terms






















