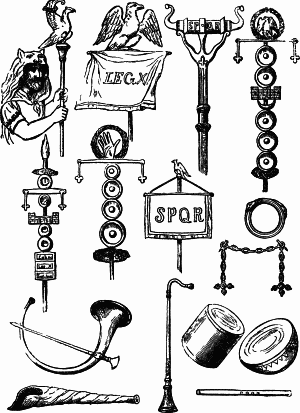Hoplites were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with fewer soldiers. The formation discouraged the soldiers from acting alone, for this would compromise the formation and minimize its strengths. The hoplites were primarily represented by free citizens – propertied farmers and artisans – who were able to afford a linen or bronze armour suit and weapons. They also appear in the stories of Homer, but it is thought that their use began in earnest around the 7th century BC, when weapons became cheap during the Iron Age and ordinary citizens were able to provide their own weapons. Most hoplites were not professional soldiers and often lacked sufficient military training. Some states maintained a small elite professional unit, known as the epilektoi or logades since they were picked from the regular citizen infantry. These existed at times in Athens, Sparta, Argos, Thebes, and Syracuse, among other places. Hoplite soldiers made up the bulk of ancient Greek armies.
A spear is a polearm consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as bone, flint, obsidian, copper, bronze, iron, or steel. The most common design for hunting and/or warfare, since ancient times has incorporated a metal spearhead shaped like a triangle, diamond, or leaf. The heads of fishing spears usually feature multiple sharp points, with or without barbs.
The pilum was a javelin commonly used by the Roman army in ancient times. It was generally about 2 m long overall, consisting of an iron shank about 7 mm (0.28 in) in diameter and 600 mm (24 in) long with a pyramidal head, attached to a wooden shaft by either a socket or a flat tang.

The chakram is a throwing weapon from the Indian subcontinent. It is circular with a sharpened outer edge and a diameter of 12–30 centimetres. It is also known as chalikar meaning "circle", and was sometimes referred to in English writings as a "war-quoit". The chakram is primarily a throwing weapon, but can also be used hand-to-hand. A smaller variant called chakri is worn on the wrist. A related weapon is the chakri dong, a bamboo staff with a chakri attached at one end.

The sarissa or sarisa was a long spear or pike about 5 to 7 meters in length. It was introduced by Philip II of Macedon and was used in his Macedonian phalanxes as a replacement for the earlier dory, which was considerably shorter. These longer spears improved the strength of the phalanx by extending the rows of overlapping weapons projecting towards the enemy. After the conquests of Alexander the Great, the sarissa was a mainstay during the Hellenistic era by the Hellenistic armies of the diadochi Greek successor states of Alexander's empire, as well as some of their rivals.

An assegai or assagai is a polearm used for throwing, usually a light spear or javelin made up of a wooden handle with an iron tip.
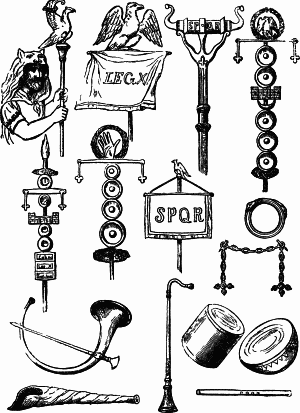
Roman military personal equipment was produced in large numbers to established patterns, and used in an established manner. These standard patterns and uses were called the res militaris or disciplina. Its regular practice during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire led to military excellence and victory. The equipment gave the Romans a very distinct advantage over their barbarian enemies, especially so in the case of armour. This does not mean that every Roman soldier had better equipment than the richer men among his opponents. Roman equipment was not of a better quality than that used by the majority of Rome's adversaries. Other historians and writers have stated that the Roman army's need for large quantities of "mass produced" equipment after the so-called "Marian Reforms" and subsequent civil wars led to a decline in the quality of Roman equipment compared to the earlier Republican era:
The production of these kinds of helmets of Italic tradition decreased in quality because of the demands of equipping huge armies, especially during civil wars...The bad quality of these helmets is recorded by the sources describing how sometimes they were covered by wicker protections, like those of Pompeius' soldiers during the siege of Dyrrachium in 48 BC, which were seriously damaged by the missiles of Caesar's slingers and archers.
It would appear that armour quality suffered at times when mass production methods were being used to meet the increased demand which was very high the reduced size cuirasses would also have been quicker and cheaper to produce, which may have been a deciding factor at times of financial crisis, or where large bodies of men were required to be mobilized at short notice, possibly reflected in the poor-quality, mass produced iron helmets of Imperial Italic type C, as found, for example, in the River Po at Cremona, associated with the Civil Wars of AD 69 AD; Russell Robinson, 1975, 67
Up until then, the quality of helmets had been fairly consistent and the bowls well decorated and finished. However, after the Marian Reforms, with their resultant influx of the poorest citizens into the army, there must inevitably have been a massive demand for cheaper equipment, a situation which can only have been exacerbated by the Civil Wars...

A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon. Today, the javelin is predominantly used for sporting purposes such as the javelin throw. The javelin is nearly always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distances, such as spear-throwers or the amentum.

The dory or doru was the chief spear of hoplites in Ancient Greece. The word doru is first attested in the Homeric epics with the meanings of "wood" and "spear". Homeric heroes hold two dorata. In classical antiquity, the dory was a symbol of military power, possibly more important than the sword, as can be inferred from expressions like "Troy conquered by dory" and words like "doryktetos" (spear-won) and "doryalotos" (spear-taken).
The verutum, plural veruta, was a short javelin used in the Roman army. This javelin was used by the velites for skirmishing purposes, unlike the heavier pilum, which was used by the hastati and principes for weakening the enemy before advancing into close combat. The shafts were about 1.1 metres long, substantially shorter than the 2-metre pilum, and the point measured about 13 centimetres (5 in) long. The verutum had either an iron shank like the pilum or a tapering metal head. It was sometimes thrown with the aid of a throwing strap, or amentum.
Falarica, also Phalarica, was an ancient Iberian ranged polearm that was sometimes used as an incendiary weapon.

The angon is a type of javelin that was used during the Early Middle Ages by the Anglo-Saxons, Franks, Goths, and other Germanic peoples. It was similar to, and probably derived from, the pilum used by the Roman army and had a barbed head and long narrow socket or shank made of iron mounted on a wooden haft.

Major innovations in the history of weapons have included the adoption of different materials – from stone and wood to different metals, and modern synthetic materials such as plastics – and the developments of different weapon styles either to fit the terrain or to support or counteract different battlefield tactics and defensive equipment.

Listed here are the weapons of pencak silat. The most common are the machete, staff, kris, sickle, spear, and kerambit. Because Southeast Asian society was traditionally based around agriculture, many of these weapons were originally farming tools.

Ancient Greek weapons and armor were primarily geared towards combat between individuals. Their primary technique was called the phalanx, a formation consisting of massed shield wall, which required heavy frontal armor and medium-ranged weapons such as spears. Soldiers were required to provide their own panoply, which could prove expensive, however the lack of any official peace-keeping force meant that most Greek citizens carried weapons as a matter of course for self-defence. Because individuals provided their own equipment, there was considerable diversity in arms and armor among the Hellenistic troops.

Mughal weapons significantly evolved during the ruling periods of its various rulers. During its conquests throughout the centuries, the military of the Mughal Empire used a variety of weapons including swords, bows and arrows, horses, camels, elephants, some of the world's largest cannons, muskets and flintlock blunderbusses.

Many different weapons were created and used in Anglo-Saxon England between the fifth and eleventh centuries. Spears, used for piercing and throwing, were the most common weapon. Other commonplace weapons included the sword, axe, and knife—however, bows and arrows, as well as slings, were not frequently used by the Anglo-Saxons. For defensive purposes, the shield was the most common item used by warriors, although sometimes mail and helmets were used.

The Caetrati were a type of light infantry in ancient Iberia who often fought as skirmishers. They were armed with a caetra shield, swords, and javelins.

Caetra was the shield used by Iberian, Celtiberian, Gallaecian and Lusitanian warriors. The shield was circular shaped with a diameter between 30 cm to 90 cm. It was tied to the warrior's body with ropes or leather strips that passed over the shoulder and that gave great mobility to fight both on foot and on horseback. The shapes and decorations of the shields had variations in their metal, wood or leather protection. Warriors that carried this shield were usually light infantry called caetratus.

Warfare in ancient Iberian Peninsula occupied an important place in historical chronicles, first during the Carthaginian invasion of Hispania, including the Punic Wars, and later during the Roman conquest of the peninsula. The densely bellicose character of the Pre-Roman peoples who inhabited Hispania was repeatedly shown in their conflicts against Rome, Carthage and each other.