Related Research Articles

The European pied flycatcher is a small passerine bird in the Old World flycatcher family. One of the four species of Western Palearctic black-and-white flycatchers, it hybridizes to a limited extent with the collared flycatcher. It breeds in most of Europe and across the Western Palearctic. It is migratory, wintering mainly in tropical Africa. It usually builds its nests in holes on oak trees. This species practices polygyny, usually bigamy, with the male travelling large distances to acquire a second mate. The male will mate with the secondary female and then return to the primary female in order to help with aspects of child rearing, such as feeding.

Parental investment, in evolutionary biology and evolutionary psychology, is any parental expenditure that benefits offspring. Parental investment may be performed by both males and females, females alone or males alone. Care can be provided at any stage of the offspring's life, from pre-natal to post-natal.

Hypergamy is a term used in social science for the act or practice of a person dating or marrying a spouse of higher social status or sexual capital than themselves, and continuingly attempting to replace their current partner with someone they deem superior.
In evolutionary biology and evolutionary psychology, the Trivers–Willard hypothesis, formally proposed by Robert Trivers and Dan Willard in 1973, suggests that female mammals adjust the sex ratio of offspring in response to maternal condition, so as to maximize their reproductive success (fitness). For example, it may predict greater parental investment in males by parents in "good conditions" and greater investment in females by parents in "poor conditions". The reasoning for this prediction is as follows: Assume that parents have information on the sex of their offspring and can influence their survival differentially. While selection pressures exist to maintain a 1:1 sex ratio, evolution will favor local deviations from this if one sex has a likely greater reproductive payoff than is usual.
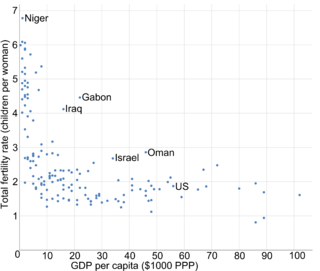
Income and fertility is the association between monetary gain on one hand, and the tendency to produce offspring on the other. There is generally an inverse correlation between income and the total fertility rate within and between nations. The higher the degree of education and GDP per capita of a human population, subpopulation or social stratum, the fewer children are born in any developed country. In a 1974 United Nations population conference in Bucharest, Karan Singh, a former minister of population in India, illustrated this trend by stating "Development is the best contraceptive." In 2015, this thesis was supported by Vogl, T.S., who concluded that increasing the cumulative educational attainment of a generation of parents was by far the most important predictor of the inverse correlation between income and fertility based on a sample of 48 developing countries.

The status of women in Ghana and their roles in Ghanaian society has changed over the past few decades. There has been a slow increase in the political participation of Ghanaian women throughout history. Women are given equal rights under the Constitution of Ghana, yet disparities in education, employment, and health for women remain prevalent. Additionally, women have much less access to resources than men in Ghana do. Ghanaian women in rural and urban areas face slightly different challenges. Throughout Ghana, female-headed households are increasing.

Women in Nigeria are a diverse group of individuals who have a wide range of experiences and backgrounds. They are mothers, daughters, sisters, wives, entrepreneurs, professionals, and activists. Women in Nigeria face numerous challenges, including gender inequality, poverty, and a lack of access to education and healthcare. Despite these challenges, Nigerian women are making strides in all areas of life and are becoming increasingly empowered to take control of their lives and their futures.
In sexual relationships, concepts of age disparity, including what defines an age disparity, have developed over time and vary among societies. Differences in age preferences for mates can stem from partner availability, gender roles, and evolutionary mating strategies, and age preferences in sexual partners may vary cross-culturally. There are also social theories for age differences in relationships as well as suggested reasons for 'alternative' age-hypogamous relationships. Age-disparate relationships have been documented for most of recorded history and have been regarded with a wide range of attitudes dependent on sociocultural norms and legal systems.
In criminology, the power-control theory of gender and delinquency holds the gender distribution of delinquency is caused by stratification from gender relations within the family. The theory seeks to explain gender differences in the rates of delinquency by attributing them to the level of social/parental control practiced. The theory states that the class, gender, and type of family structure will influence the severity of social/parental control practiced which will in turn set the "accepted norm" for the child/individual. This norm will in turn control the level of delinquency by the individual.
Mate preferences in humans refers to why one human chooses or chooses not to mate with another human and their reasoning why. Men and women have been observed having different criteria as what makes a good or ideal mate. A potential mate's socioeconomic status has also been seen important, especially in developing areas where social status is more emphasized.

Women's health in India can be examined in terms of multiple indicators, which vary by geography, socioeconomic standing and culture. To adequately improve the health of women in India multiple dimensions of wellbeing must be analysed in relation to global health averages and also in comparison to men in India. Health is an important factor that contributes to human wellbeing and economic growth.

Social monogamy in mammals is defined as sexually mature adult organisms living in pairs. While there are many definitions of social monogamy, this social organization can be found in invertebrates, reptiles and amphibians, fish, birds, mammals, and humans.

In evolutionary psychology and behavioral ecology, human mating strategies are a set of behaviors used by individuals to select, attract, and retain mates. Mating strategies overlap with reproductive strategies, which encompass a broader set of behaviors involving the timing of reproduction and the trade-off between quantity and quality of offspring.
Father absence occurs when parents separate and the father no longer lives with his children and provides no parental investment. Parental separation has been proven to affect a child's development and behavior. Early parental divorce has been associated with greater internalizing and externalizing behaviors in the child, while divorce later in childhood or adolescence may dampen academic performance.

Female empowerment in Nigeria is an economic process that involves empowering Nigerian women as a poverty reduction measure. Empowerment is the development of women in terms of politics, social and economic strength in nation development. It is also a way of reducing women's vulnerability and dependency in all spheres of life. It can be noted that the aggregate of educational, political, health and legal empowerment are key to women's empowerment in Nigeria. Like many African women, Nigerian women have a subordinate role to their male counterparts. There are twice as many women below the poverty line than men and up to 19 times as many men in executive positions than women.
Shelly J. Lundberg is an economist and currently holds the positions of Leonard Broom Professor of Demography at the University of California, Santa Barbara, where she serves as Associate Director of the Broom Center for Demography. Lundberg is one of the world's leading population economists.
Son preference in China is a gender preference issue underpinned by the belief that boys have more value than girls. In China, the bias towards male over female offspring is demonstrated by the sex ratio at birth (SRB).

Gender disappointment is the feeling of sadness parents experience when the desire for a child of a preferred sex is not met. It can create feelings of shame which cannot always be expressed openly. It is often noticed in cultures where women are viewed as of a lower status and the preferred choice is for a male infant, i.e. son preference. It may result in sex-selective killing, or the neglection of female children.
Daughter preference describes human families seeking to bear and raise daughters, rather than sons.
The colonization of the West African region that lies across the Niger took place between the mid 19th century to 1960 when Nigeria became recognized as an independent nation. This systemic invasion introduced new social, economic, and political structures that significantly altered Indigenous notions of gender fluidity and gender roles. The imposition of Western ideologies and patriarchal systems impacted the pre-existing gender dynamics, leading to shifts in power relations, societal expectations, and individual identities and expressions, becoming a complex interplay between colonial influence and Indigenous cultural practices. European colonial powers introduced legal frameworks that often reinforced patriarchal structures and diminished the recognition of Indigenous practices that embraced gender diversity. The imposition of Western legal systems had lasting consequences, influencing inheritance laws, property rights, and marital practices. This not only marginalized women within the legal framework but also eroded the traditional roles of certain societies where women held significant economic and political power. The juxtaposition of colonial legal norms with Indigenous customs created tension and reshaped the social fabric, contributing to the evolving landscape of gender roles and fluidity in Nigerian cultures. This impact of colonial legal systems and educational structures interacted with the diverse cultural landscapes of Nigeria, affecting communities in distinct ways. The consequences of colonial impositions on legal frameworks and educational curricula were filtered through the lenses of diverse cultural contexts, shaping unique challenges and opportunities for different ethnic groups.
References
- 1 2 Le, Kien; Nguyen, My (2022-03-01). "Son preference and health disparities in developing countries". SSM - Population Health. 17: 101036. doi:10.1016/j.ssmph.2022.101036. ISSN 2352-8273. PMC 8804262 . PMID 35128024.
- ↑ Freese, Jeremy; Powell, Brian (May 1999). "Sociobiology, Status, and Parental Investment in Sons and Daughters: Testing the Trivers-Willard Hypothesis". American Journal of Sociology. 104 (6): 1709. doi:10.1086/210221. ISSN 0002-9602. S2CID 145335823.
- 1 2 Shah, Mussawar (2005-07-25). "Son Preference and Its Consequences (A Review)". Gender and Behaviour. 3 (1): 269–280. doi:10.4314/gab.v3i1.23325. ISSN 1596-9231.
- 1 2 Lundberg, S. (2005-09-01). "Sons, Daughters, and Parental Behaviour". Oxford Review of Economic Policy. 21 (3): 340–356. doi:10.1093/oxrep/gri020. ISSN 0266-903X.
- ↑ Dahl, Gordon B.; Moretti, Enrico (October 2008). "The Demand for Sons". Review of Economic Studies. 75 (4): 1085–1120. doi:10.1111/j.1467-937X.2008.00514.x.
- ↑ Household socioeconomic status and sexual behaviour among Nigerian female youth, UC Isiugo-Abanihe, KA Oyediran - African Population Studies, 2004 - bioline.org.br - http://www.bioline.org.br/pdf?ep04005
- ↑ NWOKOCHA, EZEBUNWA E. (2007). "Male-Child Syndrome and the Agony of Motherhood Among the Igbo of Nigeria". International Journal of Sociology of the Family. 33 (1): 219–234. ISSN 0020-7667. JSTOR 23070771.
- ↑ Ezdi, Sehar; Baş, Ahmet Melik (2020). "Gender preferences and fertility: Investigating the case of Turkish immigrants in Germany". Demographic Research. 43: 59–96. doi: 10.4054/DemRes.2020.43.3 . ISSN 1435-9871. JSTOR 26967800. S2CID 221264434.
- ↑ Lin, Tin-chi (2009). "The decline of son preference and rise of gender indifference in Taiwan since 1990". Demographic Research. 20: 377–402. doi:10.4054/DemRes.2009.20.16. ISSN 1435-9871. JSTOR 26349320. PMC 3747565 . PMID 23970825.
- ↑ Duan, Huiqiong; Hicks, Daniel L. (2020-08-17). "New evidence on son preference among immigrant households in the United States". IZA Journal of Development and Migration. 11 (1): 20200014. doi: 10.2478/izajodm-2020-0014 . ISSN 2520-1786. S2CID 221257460.