
Nepal measures about 880 kilometers (547 mi) along its Himalayan axis by 150 to 250 kilometers across. It has an area of 147,516 km2 (56,956 sq mi).
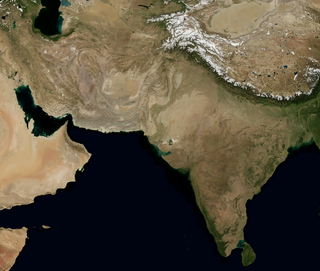
The Geography of Pakistan is a profound blend of landscapes varying from plains to deserts, forests, and plateaus ranging from the coastal areas of the Indian Ocean in the south to the mountains of the Karakoram, Hindukush, Himalayas ranges in the north. Pakistan geologically overlaps both with the Indian and the Eurasian tectonic plates where its Sindh and Punjab provinces lie on the north-western corner of the Indian plate while Balochistan and most of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa lie within the Eurasian plate which mainly comprises the Iranian Plateau.
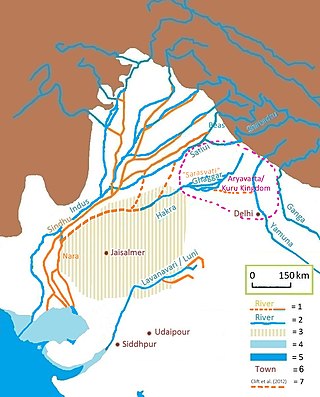
The Sarasvati River is a deified river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Vedic religion, appearing in all but the fourth book of the Rigveda.

The Himalayas, or Himalaya, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 peaks exceeding 7,200 m (23,600 ft) in elevation lie in the Himalayas.

The Oregon Trail was a 2,170-mile (3,490 km) east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what is now the state of Kansas and nearly all of what are now the states of Nebraska and Wyoming. The western half of the trail spanned most of the current states of Idaho and Oregon.

Black pepper is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit, which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit is a drupe (stonefruit) which is about 5 mm (0.20 in) in diameter, dark red, and contains a stone which encloses a single pepper seed. Peppercorns and the ground pepper derived from them may be described simply as pepper, or more precisely as black pepper, green pepper, or white pepper.

The Mojave River is an intermittent river in the eastern San Bernardino Mountains and the Mojave Desert in San Bernardino County, California, United States. Most of its flow is underground, while its surface channels remain dry most of the time, except for the headwaters and several bedrock gorges in the lower reaches.

The California Trail was an emigrant trail of about 1,600 mi (2,600 km) across the western half of the North American continent from Missouri River towns to what is now the state of California. After it was established, the first half of the California Trail followed the same corridor of networked river valley trails as the Oregon Trail and the Mormon Trail, namely the valleys of the Platte, North Platte, and Sweetwater rivers to Wyoming. The trail has several splits and cutoffs for alternative routes around major landforms and to different destinations, with a combined length of over 5,000 mi (8,000 km).

The National Security Guard (NSG), commonly known as Black Cats, is a counter-terrorism unit of India under the Ministry of Home Affairs. It was founded on 16 October 1984, following Operation Blue Star, for combating terrorist activities and protect states against internal disturbances. Formalised in the Parliament of India under the National Security Guard Act, 1986. It is one of the seven Central Armed Police Forces of India.

The Sutlej or Satluj River is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. The Sutlej River is also known as Satadru. It is the easternmost tributary of the Indus River. The Bhakra Dam is built around the river Sutlej to provide irrigation and other facilities to the states of Punjab, Rajasthan and Haryana.

NY Waterway, or New York Waterway, is a private transportation company running ferry and bus service in the Port of New York and New Jersey and in the Hudson Valley. The company utilizes public-private partnership with agencies such as the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, New Jersey Transit, New York City Department of Transportation, and Metropolitan Transportation Authority to provide service and maintain docking facilities.

Amarnath Temple is a Hindu shrine located in Anantnag district of Jammu and Kashmir, India. A cave situated at an altitude of 3,888 m (12,756 ft), about 168 km from Anantnag city, the district headquarters, 141 km (88 mi) from Srinagar, the summer capital of Jammu and Kashmir, reached through either Sonamarg or Pahalgam. The shrine represents an important part of Hinduism. The cave, located in Sind Valley, is surrounded by glaciers, snowy mountains and is covered with snow most of the year, except for a short period in the summer, when it is open to pilgrims. In 1989, pilgrims numbered between 12,000 and 30,000. In 2011, the numbers reached a peak, crossing 6.3 lakh (630,000) pilgrims. In 2018 pilgrims numbered 2.85 lakh (285,000). The annual pilgrimage has varied between 20 and 60 days.

The 2001–2002 India–Pakistan standoff was a military standoff between India and Pakistan that resulted in the massing of troops on both sides of the border and along the Line of Control (LoC) in the region of Kashmir. This was the second major military standoff between India and Pakistan following the successful detonation of nuclear devices by both countries in 1998, the first being the Kargil War of 1999.

Ichamati River, is a trans-boundary river which flows through India and Bangladesh and also forms the boundary between the two countries. The river is facing the problem of siltation leading to thin flow of water in the dry season and floods in the rainy season. Experts are handling the situation and remedial matters are being discussed between the governments of India and Bangladesh.

Pune Metro is a mass rapid transit system serving the city of Pune, India. The system comprises 3 lines with a combined length of 54.58 km (33.91 mi), of which 12 km (7.5 mi) on two lines are operational as of March 2022. The 16.59 km (10.31 mi) Purple line from PCMC Bhavan to Swargate runs on an elevated viaduct between PCMC Bhavan to Range Hills, from where it goes underground. The Aqua line runs from Vanaz to Ramwadi covering a distance of 14.66 km (9.11 mi) on an elevated viaduct. The 23.33 km (14.50 mi) elevated Line 3 will run from the Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park in Hinjawadi via Balewadi to Civil Court. All three lines will align at the Civil Court interchange station.

The Sahibi river, also called the Sabi River, is an ephemeral, rain-fed river flowing through Rajasthan, Haryana and Delhi states in India. It drains into Yamuna in Delhi, where its channeled course is also called the Najafgarh drain, which also serves as Najafgarh drain bird sanctuary. Sahibi is a seasonal river which is 300 km long and flows from Aravalli hills in Rajasthan to Haryana, of which 100 km is in Haryana.

The ghost pepper, also known as bhut jolokia, is an interspecific hybrid chili pepper cultivated in Northeast India. It is a hybrid of Capsicum chinense and Capsicum frutescens.
On January 2 2016, militants from Islamic separatist Kashmiri groups attacked the Indian Air Force's Pathankot Airbase, part of its Western Air Command.

Indian Army operations in Jammu and Kashmir include security operations such as Operation Rakshak, which began in 1990, Operation Sarp Vinash in 2003 and Operation Randori Behak in 2020. Other operations include humanitarian missions such as Operation Megh Rahat and operations with a social aim such as Operation Goodwill and Operation Calm Down. The Indian Army works in tandem with the other arms of the Indian Armed Forces and security forces in Jammu and Kashmir such as during Mission Sahayata or joint operations.
The Darbuk–Shyok–DBO Road, also called the Sub-Sector North Road, is a strategic all-weather road in eastern Ladakh in India, close to the Line of Actual Control with China. It connects Ladakh's capital city Leh, via the villages of Darbuk and Shyok at southern Shyok River Valley, with the Daulat Beg Oldi (DBO) post near the northern border. The 220-km long section between Shyok and DBO was constructed between 2000 and 2019 by India's Border Roads Organisation (BRO). The DS-DBO Road has reduced the travel time between Leh to DBO from 2 days to 6 hours. In January 2023, BRO announced that it is constructing the DSDBO tunnel on this route.

















