Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini (Swaziland) and South Africa to the southwest. The sovereign state is separated from the Comoros, Mayotte and Madagascar by the Mozambique Channel to the east. The capital and largest city of Mozambique is Maputo.
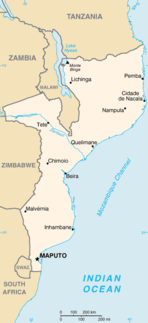
Modes of transport in Mozambique include rail, road, water, and air. There are rail links serving principal cities and connecting the country with Malawi, Zimbabwe and South Africa. There are over 30,000km of roads, but much of the network is unpaved.

Maputo, officially named Lourenço Marques until 1976, is the capital and most populous city of Mozambique. The city is named after chief Maputsu I of the Tembe clan, a subgroup of Tsonga people. Located near the southern end of the country, it is positioned within 120 km of the Eswatini and South Africa borders. The city has a population of 1,088,449 distributed over a land area of 347,69 km2. The Maputo metropolitan area includes the neighbouring city of Matola, and has a total population of 2,717,437. Maputo is a port city, with an economy centered on commerce. It is also noted for its vibrant cultural scene and distinctive, eclectic architecture.

The Cahora Bassa lake—in the Portuguese colonial era known as Cabora Bassa, from Nyungwe Kahoura-Bassa, meaning "finish the job"—is Africa's fourth-largest artificial lake, situated in the Tete Province in Mozambique. In Africa, only Lake Volta in Ghana, Lake Kariba, on the Zambezi upstream of Cahora Bassa, and Egypt's Lake Nasser are bigger in terms of surface water.
Mozambique refers to two separate styles of music.

Beira is the capital and largest city of Sofala Province, where the Pungwe River meets the Indian Ocean, in the central region of Mozambique. It is the fourth-largest city by population in Mozambique, after Maputo, Matola and Nampula. Beira had a population of 397,368 in 1997, which grew to 530,604 in 2019. A coastal city, it holds the regionally significant Port of Beira, which acts as a gateway for both the central interior portion of the country as well as the land-locked nations of Zimbabwe, Zambia and Malawi.

Cahora-Bassa is an HVDC power transmission system between the Cahora Bassa Hydroelectric Generation Station at the Cahora Bassa Dam in Mozambique, and Johannesburg, South Africa.

Xai-Xai is a city in the south of Mozambique. Until 1975, the city was named João Belo. It is the capital of Gaza Province. As of 2007 it has a population of 116,343.

The Island of Mozambique lies off northern Mozambique, between the Mozambique Channel and Mossuril Bay, and is part of Nampula Province. Prior to 1898, it was the capital of colonial Portuguese East Africa. With its rich history and sandy beaches, the Island of Mozambique is a UNESCO World Heritage site and one of Mozambique's fastest growing tourist destinations. It has a permanent population of approximately 14,000 people and is served by nearby Lumbo Airport on the Nampula mainland.

The national emblem of Mozambique was adopted in 1990 in the Constitution of Mozambique article 194. The article clearly states the design and meaning of the device. It shows a gear wheel, bordered by corn stalks and sugarcane. In the middle there is a red sun over a map of Mozambique in green, and blue waves, an AK-47 crossed with a hoe, and a book. The wreath is tied with a ribbon bearing the name of the country. The emblem is "socialist heraldry" style similar to those of the Soviet republics.

The Pink Map, more generally known in English-language known as the Rose-Coloured Map, was a document prepared in 1885 to represent Portugal's claim of sovereignty over a land corridor connecting their colonies of Angola and Mozambique during the "Scramble for Africa". The area claimed included almost all of what is currently Zimbabwe and large parts of modern Zambia and Malawi. In the first half of the 19th century, Portugal fully controlled only a few coastal towns in Angola and Mozambique. It also claimed suzerainty over other almost independent towns and nominally Portuguese subjects in the Zambezi valley, but could rarely enforce its claims; most of the territory now within Angola and Mozambique was entirely independent of any Portuguese control. Between 1840 and 1869, Portugal expanded the area it controlled but began to feel threatened by the activities of other powers.

The Mozambican War of Independence was an armed conflict between the guerrilla forces of the Mozambique Liberation Front or FRELIMO, and Portugal. The war officially started on September 25, 1964, and ended with a ceasefire on September 8, 1974, resulting in a negotiated independence in 1975.

Bazaruto Island Airport is an airport serving Bazaruto Island, Bazaruto Archipelago, Mozambique, and the Bazaruto National Park.

Indigo Bay Lodge Airport is an airport serving the former Indigo Bay Lodge on Bazaruto Island, Mozambique. The current facility is the Anantara Bazaruto Island Resort. The private facility has an airstrip and a helipad.

The Cahora Bassa Dam is located in Mozambique. It is one of the three major dams on the Zambezi river system, the others being the Kariba and the Itezhi-Tezhi, the latter on the Kafue River, a tributary of the Zambezi. The dam was finished in December 1974 after much political debate. This dam is used to convert the Zambezi River power into electricity by turning turbines. That energy is then sent to South African cities, farms, and mines. The Cahora Bassa dam forms Cahora Bassa Lake. The dam is jointly owned by Mozambique and Portugal. From independence till 2007, eighteen percent of the dam and lake was owned by Mozambique and eighty-two percent by Portugal. Portugal sold down its share to 15 percent in 2007. The Cahora Bassa dam is the largest hydroelectric power plant in southern Africa and the most efficient power generating station in Mozambique.
Hélder Pelembe is a Mozambican professional footballer who plays for Mozambican club UD Songo as a forward.

Songo Songo Airstrip is a private airstrip in eastern Tanzania on Songo Songo Island in Lindi Region.
Stélio Marcelino Ernesto, better known as Telinho is a Mozambican football winger who currently plays for Moçambola club UD Songo and the Mozambique national team.
Dr Solange Laura Macamo is Lecturer of Archaeology and Heritage Management in the Department of Archaeology and Anthropology, Eduardo Mondlane University, Mozambique. From 2010 to 2016 she was also the National Director for Cultural Heritage, Ministry of Culture and Tourism, Mozambique.