Audio Interchange File Format (AIFF) is an audio file format standard used for storing sound data for personal computers and other electronic audio devices. The format was developed by Apple Inc. in 1988 based on Electronic Arts' Interchange File Format and is most commonly used on Apple Macintosh computer systems.

GarageBand is a line of digital audio workstations developed by Apple for macOS, iPadOS, and iOS devices that allows users to create music or podcasts. GarageBand was originally released for macOS in 2004 and brought to iOS in 2011. The app’s music and podcast creation system enables users to create multiple tracks with pre-made MIDI keyboards, pre-made loops, an array of various instrumental effects, and voice recordings.

Adobe Audition is a digital audio workstation developed by Adobe Inc. featuring both a multitrack, non-destructive mix/edit environment and a destructive-approach waveform editing view.

RealPlayer, formerly RealAudio Player, RealOne Player and RealPlayer G2, is a cross-platform media player app, developed by RealNetworks. The media player is compatible with numerous container file formats of the multimedia realm, including MP3, MP4, QuickTime File Format, Windows Media format, and the proprietary RealAudio and RealVideo formats. RealPlayer is also available for other operating systems; Linux, Unix, Palm OS, Windows Mobile, and Symbian versions have been released.
The Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC), also known as Apple Lossless, or Apple Lossless Encoder (ALE), is an audio coding format, and its reference audio codec implementation, developed by Apple Inc. for lossless data compression of digital music. After initially keeping it proprietary from its inception in 2004, in late 2011 Apple made the codec available open source and royalty-free. Traditionally, Apple has referred to the codec as Apple Lossless, though more recently it has begun to use the abbreviated term ALAC when referring to the codec.
A FourCC is a sequence of four bytes used to uniquely identify data formats. It originated from the OSType or ResType metadata system used in classic Mac OS and was adopted for the Amiga/Electronic Arts Interchange File Format and derivatives. The idea was later reused to identify compressed data types in QuickTime and DirectShow.
ReplayGain is a proposed technical standard published by David Robinson in 2001 to measure and normalize the perceived loudness of audio in computer audio formats such as MP3 and Ogg Vorbis. It allows media players to normalize loudness for individual tracks or albums. This avoids the common problem of having to manually adjust volume levels between tracks when playing audio files from albums that have been mastered at different loudness levels.

Logic Pro is a proprietary digital audio workstation (DAW) and MIDI sequencer software application for the macOS platform developed by Apple Inc. It was originally created in the early 1990s as Notator Logic, or Logic, by German software developer C-Lab which later went by Emagic. Apple acquired Emagic in 2002 and renamed Logic to Logic Pro. It is the second most popular DAW – after Ableton Live – according to a survey conducted in 2015.
Gapless playback is the uninterrupted playback of consecutive audio tracks, such that relative time distances in the original audio source are preserved over track boundaries on playback. For this to be useful, other artifacts at track boundaries should not be severed either. Gapless playback is common with compact discs, gramophone records, or tapes, but is not always available with other formats that employ compressed digital audio. The absence of gapless playback is a source of annoyance to listeners of music where tracks are meant to segue into each other, such as some classical music, progressive rock, concept albums, electronic music, and live recordings with audience noise between tracks.

Squeezebox is a family of network music players. The original device was the SliMP3, introduced in 2001 by Slim Devices. It had an Ethernet interface and played MP3 music files from a media server. The first Squeezebox was released two years later and was followed by several more models. Slim Devices was acquired by Logitech in 2006.

GoldWave is a commercial digital audio editing software product developed by GoldWave Inc, first released to the public in April 1993.
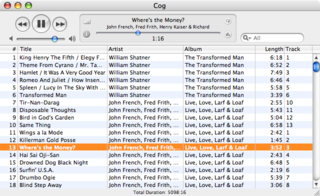
Cog is an open source audio player for macOS. The basic layout is a single-paned playlist interface with two retractable drawers, one for navigating the user's music folders and another for viewing audio file properties, like bitrate. Along with supporting most audio formats compatible with macOS's Core Audio API, Cog supports a wide array of other audio formats, along with their metadata, which are otherwise unsupported on macOS.
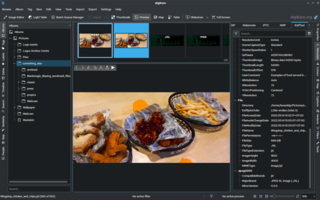
A tag editor is an app that can add, edit, or remove embedded metadata on multimedia file formats. Content creators, such as musicians, photographers, podcasters, and video producers, may need to properly label and manage their creations, adding such details as title, creator, date of creation, and copyright notice.

Mixxx is free and open-source software for DJing. It is cross-platform and supports most common music file formats. Mixxx can be controlled with MIDI and HID controllers and timecode vinyl records in addition to computer keyboards and mice.

GOM Player is a media player for Windows, developed by GOM & Company. With more than 100 million downloads, it is also known as the most used player in South Korea. Its main features include the ability to play some broken media files and find missing codecs using a codec finder service.
SoundEdit was the first popular GUI-based audio editor for digitized audio. It was one of the first significant audio applications for personal computers in general.

JUCE is an open-source cross-platform C++ application framework, used for the development of desktop and mobile applications. JUCE is used in particular for its GUI and plug-ins libraries. It is dual licensed under the GPLv3 and a commercial license.

Logic Studio is a discontinued professional music production suite by Apple Inc. The first version of Logic Studio was unveiled on September 12, 2007. It claims to be the largest collection of modeled instruments, sampler instruments, effect plug-ins, and audio loops ever put in a single application.









