
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of Lentivirus that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype. In most cases, HIV is a sexually transmitted infection and occurs by contact with or transfer of blood, pre-ejaculate, semen, and vaginal fluids. Research has shown that HIV is untransmittable through condomless sexual intercourse if the HIV-positive partner has a consistently undetectable viral load. Non-sexual transmission can occur from an infected mother to her infant during pregnancy, during childbirth by exposure to her blood or vaginal fluid, and through breast milk. Within these bodily fluids, HIV is present as both free virus particles and virus within infected immune cells.

A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome, the reverse of the usual pattern, thus retro (backwards). The new DNA is then incorporated into the host cell genome by an integrase enzyme, at which point the retroviral DNA is referred to as a provirus. The host cell then treats the viral DNA as part of its own genome, transcribing and translating the viral genes along with the cell's own genes, producing the proteins required to assemble new copies of the virus.

A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by certain viruses such as HIV and the hepatitis B virus to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. Contrary to a widely held belief, the process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, as transfers of information from RNA to DNA are explicitly held possible.

Virology is the study of viruses – submicroscopic, parasitic particles of genetic material contained in a protein coat – and virus-like agents. It focuses on the following aspects of viruses: their structure, classification and evolution, their ways to infect and exploit host cells for reproduction, their interaction with host organism physiology and immunity, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy. Virology is a subfield of microbiology.
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do not destroy their target pathogen; instead they inhibit its development.
Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) is a species of retrovirus that cause persistent infections in at least 45 species of African non-human primates. Based on analysis of strains found in four species of monkeys from Bioko Island, which was isolated from the mainland by rising sea levels about 11,000 years ago, it has been concluded that SIV has been present in monkeys and apes for at least 32,000 years, and probably much longer.
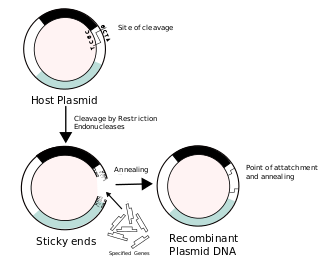
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome.
Gammaretrovirus is a genus in the retroviridae family. Example species are the murine leukemia virus and the feline leukemia virus. They cause various sarcomas, leukemias and immune deficiencies in mammals, reptiles and birds.
The genome and proteins of HIV have been the subject of extensive research since the discovery of the virus in 1983. "In the search for the causative agent, it was initially believed that the virus was a form of the Human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV), which was known at the time to affect the human immune system and cause certain leukemias. However, researchers at the Pasteur Institute in Paris isolated a previously unknown and genetically distinct retrovirus in patients with AIDS which was later named HIV." Each virion comprises a viral envelope and associated matrix enclosing a capsid, which itself encloses two copies of the single-stranded RNA genome and several enzymes. The discovery of the virus itself occurred two years following the report of the first major cases of AIDS-associated illnesses.

Yuan Chang is an American virologist and pathologist who co-discovered Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) and Merkel cell polyomavirus, two of the seven known human oncoviruses.
The murine leukemia viruses are retroviruses named for their ability to cause cancer in murine (mouse) hosts. Some MLVs may infect other vertebrates. MLVs include both exogenous and endogenous viruses. Replicating MLVs have a positive sense, single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) genome that replicates through a DNA intermediate via the process of reverse transcription.

A long terminal repeat (LTR) is a pair of identical sequences of DNA, several hundred base pairs long, which occur in eukaryotic genomes on either end of a series of genes or pseudogenes that form a retrotransposon or an endogenous retrovirus or a retroviral provirus. All retroviral genomes are flanked by LTRs, while there are some retrotransposons without LTRs. Typically, an element flanked by a pair of LTRs will encode a reverse transcriptase and an integrase, allowing the element to be copied and inserted at a different location of the genome. Copies of such an LTR-flanked element can often be found hundreds or thousands of times in a genome. LTR retrotransposons comprise about 8% of the human genome.

A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 6,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology.

A genetically modified virus is a virus that has been altered or generated using biotechnology methods, and remains capable of infection. Genetic modification involves the directed insertion, deletion, artificial synthesis or change of nucleotide bases in viral genomes. Genetically modified viruses are mostly generated by the insertion of foreign genes intro viral genomes for the purposes of biomedical, agricultural, bio-control, or technological objectives. The terms genetically modified virus and genetically engineered virus are used synonymously.
Protein music is a musical technique where music is composed by converting protein sequences or genes to musical notes. It is a theoretical method made by Joel Sternheimer, who is a physicist, composer and mathematician.
Mason-Pfizer monkey virus (M-PMV), formerly Simian retrovirus (SRV), is a species of retroviruses that usually infect and cause a fatal immune deficiency in Asian macaques. The ssRNA virus appears sporadically in mammary carcinoma of captive macaques at breeding facilities which expected as the natural host, but the prevalence of this virus in feral macaques remains unknown. M-PMV was transmitted naturally by virus-containing body fluids, via biting, scratching, grooming, and fighting. Cross contaminated instruments or equipment (fomite) can also spread this virus among animals.

William A. Haseltine is an American scientist, businessman, author, and philanthropist. He is known for his groundbreaking work on HIV/AIDS and the human genome. Haseltine was a professor at Harvard Medical School where he founded two research departments on cancer and HIV/AIDS. Haseltine is a founder of several biotechnology companies including Cambridge Biosciences, The Virus Research Institute, ProScript, LeukoSite, Dendreon, Diversa, X-VAX, and Demetrix. He was a founder chairman and CEO of Human Genome Sciences, a company that pioneered the application of genomics to drug discovery. He is the president of the Haseltine Foundation for Science and the Arts and is the founder, chairman, and president of ACCESS Health International, a not-for-profit organization dedicated to improving access to high-quality health worldwide. He was listed by Time Magazine as one of the world's 25 most influential business people in 2001 and one of the 100 most influential leaders in biotechnology by Scientific American in 2015.

Stephen C. Harrison is professor of biological chemistry and molecular pharmacology, professor of pediatrics, and director of the Center for Molecular and Cellular Dynamics of Harvard Medical School, head of the Laboratory of Molecular Medicine at Boston Children's Hospital, and investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Since antiretroviral therapy requires a lifelong treatment regimen, research to find more permanent cures for HIV infection is currently underway. It is possible to synthesize zinc finger nucleotides with zinc finger components that selectively bind to specific portions of DNA. Conceptually, targeting and editing could focus on host cellular co-receptors for HIV or on proviral HIV DNA.

Bette Korber is an American computational biologist focusing on the molecular biology and population genetics of the HIV virus that causes infection and eventually AIDS. She has contributed heavily to efforts to obtain an effective HIV vaccine. She created a database at Los Alamos National Laboratory that has enabled her to design novel mosaic HIV vaccines, one of which is currently in human testing in Africa. The database contains thousands of HIV genome sequences and related data.












