
South Bend is a city in and the county seat of St. Joseph County, Indiana, United States, on the St. Joseph River near its southernmost bend, from which it derives its name. At the 2020 census, the city had a total of 103,453 residents and is the fourth-largest city in Indiana. Located just south of the border with Michigan, South Bend anchors the Michiana region and is 72 miles (116 km) east of downtown Chicago. The metropolitan area had a population of 324,501 in 2020, while its combined statistical area had 812,199.

The Monon Railroad, also known as the Chicago, Indianapolis, and Louisville Railway from 1897 to 1971, was an American railroad that operated almost entirely within the state of Indiana. The Monon was merged into the Louisville and Nashville Railroad in 1971, and much of the former Monon right of way is owned today by CSX Transportation. In 1970, it operated 540 miles (870 km) of road on 792 miles (1,275 km) of track; that year it reported 1320 million ton-miles of revenue freight and zero passenger-miles.
The Lake Shore and Michigan Southern Railway, established in 1833, and sometimes referred to as the Lake Shore, was a major part of the New York Central Railroad's Water Level Route from Buffalo, New York, to Chicago, Illinois, primarily along the south shore of Lake Erie and across northern Indiana. The line's trackage remains a major rail transportation corridor used by Amtrak passenger trains and several freight lines; in 1998, its ownership was split at Cleveland, Ohio, between CSX Transportation to the east and Norfolk Southern Railway in the west.

The Florida Central Railroad Company is one of several short line railroads run by Regional Rail, LLC. It runs from downtown Orlando northwest to Apopka and Tavares with a branch from Toronto to Ocoee and Winter Garden and branches from Tavares to Umatilla and Sorrento. The Florida Central connects with the Central Florida Rail Corridor in downtown Orlando, Florida and has trackage rights on the CFRC from there south to Taft Yard where they interchange with CSX Transportation. The railroad is based out of the Plymouth freight station.

The South Shore Line is an electrically powered interurban commuter rail line operated by the Northern Indiana Commuter Transportation District (NICTD) between Millennium Station in downtown Chicago, Illinois and the South Bend International Airport in South Bend, Indiana, United States. The name refers to both the physical line and the service operated over that route. The line was built in 1901–1908 by predecessors of the Chicago South Shore and South Bend Railroad, which continues to operate freight service. Passenger operation was assumed by the NICTD in 1989, who also purchased the track in 1990. The South Shore Line is one of the last surviving interurban trains in the United States. In 2023, the system had a ridership of 1,406,900, or about 6,300 per weekday as of the third quarter of 2024.

The Chicago South Shore and South Bend Railroad, also known as the South Shore Line, is a Class III freight railroad operating between Chicago, Illinois, and South Bend, Indiana. The railroad serves as a link between Class I railroads and local industries in northeast Illinois and northwest Indiana. It built the South Shore Line electric interurban and operated it until 1990, when the South Shore transferred its passenger operations to the Northern Indiana Commuter Transportation District. The freight railroad is owned by the Anacostia Rail Holdings Company.

The Watuppa Branch is a roughly six-mile freight railroad line in southeastern Massachusetts. The track originates at Mount Pleasant Junction, where it diverges from the New Bedford Secondary, and runs through Dartmouth before terminating in north Westport. The line is owned by the Massachusetts Department of Transportation and is operated by Massachusetts Coastal Railroad, which purchased operating rights from the previous operator, Bay Colony Railroad, in late 2023. The abandoned western portion of the right-of-way is used by the Quequechan River Rail Trail.

The Floridian was a train operated by Amtrak from 1971 to 1979 that ran between Chicago and Florida, with two branches south of Jacksonville terminating at Miami and St. Petersburg. For its Nashville to Montgomery segment, its route followed that of several former Louisville & Nashville Railroad (L&N) passenger trains, including the Pan-American and the Humming Bird. Originating in Chicago, the train served Lafayette and Bloomington, Indiana; Louisville and Bowling Green, Kentucky; Nashville, Tennessee; Decatur, Birmingham, Montgomery and Dothan, Alabama; and Thomasville, Valdosta and Waycross, Georgia.

The Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, Chicago and St. Louis Railroad, commonly called the Pan Handle Route, was a railroad that was part of the Pennsylvania Railroad system. Its common name came from its main line, which began at Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, crossed the Northern Panhandle of West Virginia, and continued west to Bradford, Ohio, where it split into a northern line to Chicago and a southern one through Indianapolis, Indiana, to East St. Louis, Illinois.

The Millstone and New Brunswick Railroad (M&NB) was chartered in the mid-19th century as a seven-mile long branch line from New Brunswick, New Jersey to East Millstone, New Jersey. Construction was completed and the line began operation on December 19, 1854. In 1871, under the order of the company's president Martin Howell, the M&NB signed a 999-year lease with the United Jersey Railroad Company, which would later become part of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) known as the "Millstone Branch." In 1915, the company was dissolved and became part of the United Jersey Railroad Company.

The Lake Shore Electric Railway (LSE) was an interurban electric railway that ran primarily between Cleveland and Toledo, Ohio by way of Sandusky and Fremont. Through arrangements with connecting interurban lines, it also offered service from Fremont to Fostoria and Lima, Ohio, and at Toledo to Detroit and Cincinnati.
The Indiana Railroad (IR) was the last of the typical Midwestern United States interurban lines. It was formed in 1930–31 by combining the operations of the five major interurban systems in central Indiana into one entity. The predecessor companies came under the control of Midland Utilities, owned by Samuel Insull. His plan was to modernize the profitable routes and abandon the unprofitable ones. With the onset of the Great Depression, the Insull empire collapsed and the Indiana Railroad was left with a decaying infrastructure and little hope of overcoming the growing competition of the automobile for passenger business and the truck for freight business. The IR faced bankruptcy in 1933, and Bowman Elder was designated as the receiver to run the company. Payments on bonded debt were suspended. Elder was able to keep the system virtually intact for four years, and IR operated about 600 miles (970 km) of interurban lines throughout Indiana during this period. During the late 1930s, the routes were abandoned one by one until a 1941 wreck with fatalities south of Indianapolis put an abrupt end to the Indiana Railroad's last passenger operations.

The Indiana Transportation Museum was a railroad museum that was formerly located in the Forest Park neighborhood of Noblesville, Indiana, United States. It owned a variety of preserved railroad equipment, some of which still operate today. ITM ceased operations in 2023 and the line is now owned and operated by the Nickel Plate Express.

The Butler Branch was a historic railroad line that operated in Indiana, USA. It ran between the city of Logansport on the Wabash River in north central Indiana and the namesake town of Butler near the Ohio border in northeastern Indiana.
The Columbus to Chicago Main Line was a rail line owned and operated by the Pennsylvania Railroad in the U.S. states of Ohio, Indiana, and Illinois. The line ran from Columbus, Ohio northwest via Logansport, Indiana to Chicago, Illinois. Junctions included the Columbus to Indianapolis Main Line via Bradford, which split at Bradford to reach the Pittsburgh to St. Louis Main Line at New Paris, Ohio; the Fort Wayne Branch at Ridgeville, Indiana; the Richmond Branch at Anoka, Indiana; and the South Bend Branch and I&F Branch at Logansport.
The Kankakee Belt Route is the nickname for the Illinois Division of the New York Central Railroad, which extended from South Bend, Indiana, through Kankakee, Illinois, and westward to Zearing, Illinois. This line was sometimes referred to as the "3 I Line", in reference to a corporate predecessor, the "Indiana, Illinois & Iowa Railroad". That portion of the line west of Kankakee to Moronts, Illinois, roughly parallels the Illinois River in Northern Illinois and was used, in large part, to transport corn toward eastern markets. See Kankakee Outwash Plain

The NJI&I was originally created by the Singer Sewing Machine Company in order to transport their products from South Bend, Indiana, to a connection with the Wabash Railroad in Pine, Indiana. The line began service in 1905 and officially operated on only 11.4 miles of track.
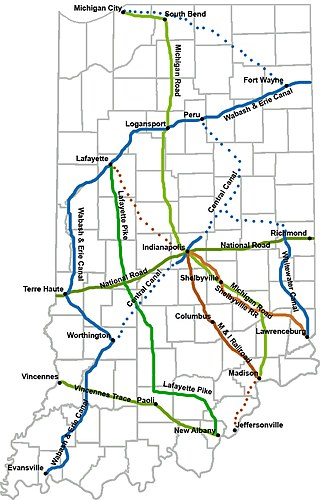
The Michigan Road was one of the earliest roads in Indiana. Roads in early Indiana were often roads in name only. In actuality they were sometimes little more than crude paths following old animal and Native American trails and filled with sinkholes, stumps, and deep, entrapping ruts. Hoosier leaders, however, recognized the importance of roads to the growth and economic health of the state, and the needed improvements. They encouraged construction of roads which would do for Indiana what the National Road was doing for the whole country.
Lydick is an unincorporated community in Warren Township, St. Joseph County, in the U.S. state of Indiana.

The Vandalia Railroad Company was incorporated January 1, 1905, by a merger of several lines in Indiana and Illinois that formed a 471-mile railroad consisting of lines mostly west of Indianapolis.














