North Carolina is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and South Carolina to the south, and Tennessee to the west. In the 2020 census, the state had a population of 10,439,388. Raleigh is the state's capital and Charlotte is its largest city. The Charlotte metropolitan area, with a population of 2,595,027 in 2020, is the most-populous metropolitan area in North Carolina, the 21st-most populous in the United States, and the largest banking center in the nation after New York City. The Raleigh-Durham-Cary combined statistical area is the second-largest metropolitan area in the state and 32nd-most populous in the United States, with a population of 2,043,867 in 2020, and is home to the largest research park in the United States, Research Triangle Park.

The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west.

Tidewater refers to the north Atlantic Plain region of the United States.

The United States Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit is a federal court located in Richmond, Virginia, with appellate jurisdiction over the district courts in the following districts:

The Eastern United States, often abbreviated as simply The East or The East Coast, is a region of the United States located east of the Mississippi River. It includes 26 states and the national capital of Washington, D.C. As of 2011, the region had an estimated population exceeding 179 million, representing over 58 percent of the total U.S. population.

The New River is a river which flows through the U.S. states of North Carolina, Virginia, and West Virginia before joining with the Gauley River to form the Kanawha River at the town of Gauley Bridge, West Virginia. Part of the Ohio River watershed, it is about 360 miles (580 km) long.
Circuit courts are court systems in several common law jurisdictions. The core concept of circuit courts requires judges to travel to different locales to ensure wide visibility and understanding of cases in a region. More generally, the term may also refer to a court that merely holds trials and other proceedings at a series of multiple locations in some kind of rotation.

The Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, also called the Ridge and Valley Province or the Valley and Ridge Appalachians, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division and are also a belt within the Appalachian Mountains extending from southeastern New York in the north through northwestern New Jersey, westward into Pennsylvania through the Lehigh Valley, and southward into Maryland, West Virginia, Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, Georgia, and Alabama. They form a broad arc between the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Appalachian Plateau physiographic province. They are characterized by long, even ridges, with long, continuous valleys in between.

The Solid South or the Southern bloc was the electoral voting bloc of the states of the Southern United States for issues that were regarded as particularly important to the interests of Democrats in those states. The Southern bloc existed especially between the end of Reconstruction in 1877 and the passage of the Civil Rights Act in 1964. During this period, the Democratic Party overwhelmingly controlled southern state legislatures, and most local, state and federal officeholders in the South were Democrats. During the late 1800s and early 1900s, Southern Democrats disenfranchised blacks in all Southern states, along with a few non-Southern states doing the same as well. This resulted essentially in a one-party system, in which a candidate's victory in Democratic primary elections was tantamount to election to the office itself. White primaries were another means that the Democrats used to consolidate their political power, excluding blacks from voting in primaries.

The Southeastern United States, also referred to as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical region of the United States. It is located broadly on the eastern portion of the southern United States and the southern portion of the Eastern United States. It comprises at least a core of states on the lower East Coast of the United States and eastern Gulf Coast. Expansively, it reaches as far north as West Virginia and Maryland, and stretches as far west as Arkansas and Louisiana. There is no official U.S. government definition of the region, though various agencies and departments use different definitions.

Law reports or reporters are series of books that contain judicial opinions from a selection of case law decided by courts. When a particular judicial opinion is referenced, the law report series in which the opinion is printed will determine the case citation format.

Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an ethnographic classification for Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now part of the Southeastern United States and the northeastern border of Mexico, that share common cultural traits. This classification is a part of the Eastern Woodlands. The concept of a southeastern cultural region was developed by anthropologists, beginning with Otis Mason and Frank Boas in 1887. The boundaries of the region are defined more by shared cultural traits than by geographic distinctions. Because the cultures gradually instead of abruptly shift into Plains, Prairie, or Northeastern Woodlands cultures, scholars do not always agree on the exact limits of the Southeastern Woodland culture region. Shawnee, Powhatan, Waco, Tawakoni, Tonkawa, Karankawa, Quapaw, and Mosopelea are usually seen as marginally southeastern and their traditional lands represent the borders of the cultural region.

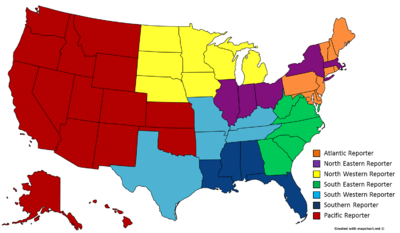
The North Eastern Reporter, North Eastern Reporter Second and North Eastern Reporter Third are United States regional case law reporters. It is part of the National Reporter System created by John B. West for West Publishing Company, which is now part of Thomson West.

The North Western Reporter and North Western Reporter, Second Series are United States regional case law reporters. It is part of the National Reporter System created by John B. West for West Publishing Company, which is now part of Thomson West.

The South Western Reporter, South Western Reporter Second, and South Western Reporter Third are United States regional case law reporters. It is part of the National Reporter System created by John B. West for West Publishing Company, which is now part of Thomson Reuters.

U.S. Route 15 is a part of the U.S. Highway System that runs from Walterboro, South Carolina to Painted Post, New York. In Virginia, the U.S. Highway runs 230.37 miles (370.74 km) from the North Carolina state line near Clarksville north to the Maryland state line at the Potomac River near Lucketts. US 15 is a major north–south highway through the Piedmont of Virginia, connecting Clarksville and Farmville in Southside Virginia with Culpeper, Warrenton, and Leesburg in Northern Virginia.

The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, economics, demographics, and settlement patterns.
This is an incomplete list of historic properties and districts at United States colleges and universities that are listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP). This includes National Historic Landmarks (NHLs) and other National Register of Historic Places listings. It includes listings at current and former educational institutions.

The Charlotte metropolitan area, sometimes referred to as Metrolina, is a metropolitan area of the U.S. states of North and South Carolina, within and surrounding the city of Charlotte. The metropolitan area also includes the cities of Gastonia, Concord, Huntersville, and Rock Hill as well as the large suburban area in the counties surrounding Mecklenburg County, which is at the center of the metro area. Located in the Piedmont, it is the largest metropolitan area in the Carolinas, and the fourth largest in the Southeastern United States. The Charlotte metropolitan area is one of the fastest growing metropolitan areas in the United States.