
The Spanish Navy or officially, the Armada, is the maritime branch of the Spanish Armed Forces and one of the oldest active naval forces in the world. The Spanish Navy was responsible for a number of major historic achievements in navigation, the most famous being the discovery of America and the first global circumnavigation by Elcano. For several centuries, it played a crucial logistical role in the expansion and consolidation of the Spanish Empire, and defended a vast trade network across the Atlantic Ocean between the Americas and Europe, and the Manila Galleon across the Pacific Ocean between the Philippines and the Americas.

HMS Superb was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, and the fourth vessel to bear the name. She was launched on 19 March 1798 from Northfleet, and was eventually broken up in 1826. Superb is mostly associated with Richard Goodwin Keats who commanded her as captain from 1801 until his promotion in 1806. Keats famously spent only one night out of the ship during four and a half years out of a home port. She also served as his flagship from early 1808 until she was paid off in 1809.

Charles-Alexandre Léon Durand, Comte de Linois was a French admiral who served in the French Navy during the reign of Napoleon Bonaparte. He commanded the combined Franco-Spanish fleet during the Algeciras Campaign in 1801, winning the First Battle of Algeciras before losing the Second Battle of Algeciras. He then led an unsuccessful campaign against British trade in the Indian Ocean and South China Sea in 1803, being defeated by a harmless fleet of the East India Company during the Battle of Pulo Aura and ending his cruise and sea-going career being bested in battle by John Warren in the action of 13 March 1806. Following the Bourbon restoration, Linois was appointed Governor of Guadeloupe. He supported Napoleon during the Hundred Days and so, on his return to France, he was forced to resign and was court martialled. Although acquitted, he was placed in retirement and never served again.

Federico Carlos Gravina y Nápoli, born Federico Carlo Gravina Cruyllas was a Sicilian-Spanish admiral in the service of the Spanish Empire, during the American Revolution and Napoleonic Wars. He died of wounds sustained during the Battle of Trafalgar. Explorer Jacinto Caamaño named the Gravina Island in Alaska in his honor.
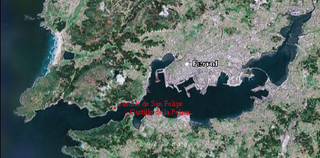
The Ferrol Expedition took place on 25 and 26 August 1800, and was an unsuccessful British attempt to capture Ferrol from Spain. Ferrol was a major Spanish naval base with a shipyard for shipbuilding and dry dock for repairs.

Neptuno was an 80-gun Neptuno-class ship of the line of the Spanish Navy. She was built in 1795 and took part in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. She fought with the Franco-Spanish fleet in the battle of Trafalgar, and was wrecked in its aftermath.

The Algeciras campaign, or Battles of Algeciras, was a brief naval campaign fought between a combined French and Spanish Navy force and a British Royal Navy force during 4–13 July 1801. A French squadron, seeking to join the Spanish fleet and a number of French ships of the line at the Spanish Atlantic base of Cadiz, sailed from Toulon on 13 June under Contre-amiral Charles Linois. Rounding the British naval base of Gibraltar on the southern coast of Spain on 4 July, Linois learned that a British squadron under Rear-Admiral Sir James Saumarez was on station off Cadiz. Seeking to avoid battle with Saumarez's much larger force, Linois anchored in the Spanish port of Algeciras, close to Gibraltar. Saumarez discovered Linois there on 6 July and attacked at 08:30, his ships hampered by light winds and Linois's strong defensive position.

The Algeciras campaign was an attempt by a French naval squadron from Toulon under Contre-Admiral Charles Linois to join a French and Spanish fleet at Cadiz during June and July 1801 during the French Revolutionary Wars prior to a planned operation against either Egypt or Portugal. To reach Cadiz, the French squadron had to pass the British naval base at Gibraltar, which housed the squadron tasked with blockading Cadiz. The British squadron was commanded by Rear-Admiral Sir James Saumarez. After a successful voyage between Toulon and Gibraltar, in which a number of British vessels were captured, the squadron anchored at Algeciras, a fortified port city within sight of Gibraltar across Gibraltar Bay. On 6 July 1801, Saumarez attacked the anchored squadron, in the First Battle of Algeciras. Although severe damage was inflicted on all three French ships of the line, none could be successfully captured and the British were forced to withdraw without HMS Hannibal, which had grounded and was subsequently seized by the French.

The First Battle of Algeciras was a naval battle fought on 6 July 1801 between a squadron of British Royal Navy ships of the line and a smaller French Navy squadron at anchor in the fortified Spanish port of Algeciras in the Strait of Gibraltar. The British outnumbered their opponents, but the French position was protected by Spanish gun batteries and the complicated shoals that obscured the entrance to Algeciras Bay. The French squadron, under Contre-Amiral Charles Linois, had stopped at Algeciras en route to the major Spanish naval base at Cadiz, where they were to form a combined French and Spanish fleet for operations against Britain and its allies in the French Revolutionary Wars. The British, under Rear-Admiral Sir James Saumarez, sought to eliminate the French squadron before it could reach Cadiz and form a force powerful enough to overwhelm Saumarez and launch attacks against British forces in the Mediterranean Sea.

The Príncipe de Asturias was a Spanish three-deck 112-gun ship of the line, named after Ferdinand, eldest surviving son of Charles IV of Spain and heir apparent with the title Prince of Asturias. She served during the Napoleonic wars escorting convoys, and fought at different times against both the British and French navies. Her invocation name was Los Santos Reyes.

Santa Ana was a 112-gun three-decker ship of the line of the Spanish Navy, built to plans drawn by engineer Miguel de la Puente, following a specification issued by José Romero Fernández de Landa. Her actual constructor at Ferrol was Honorato Bouyón. She was the prototype and lead ship of the Santa Ana class, also known as los Meregildos, which were built during the following years at Ferrol and Havana and which formed the backbone of the Spanish Navy - the other ships were the Mejicano, Conde de Regla, Salvador del Mundo, Real Carlos, San Hermenegildo, Reina María Luisa and Príncipe de Asturias. Her dimensions were 213.4 Burgos feet long, 58 feet in the beam and a total tonnage of 2,112 tonnes.

The Second Battle of Algeciras was a naval battle fought on the night of 12 July 1801 between a squadron of British Royal Navy ships of the line and a larger squadron of ships from the Spanish Navy and French Navy in the Gut of Gibraltar.
Mexicano was a 112-gun three-decker ship of the line built at Havanna for the Spanish Navy in 1786 to plans by Romero Landa. One of the eight very large ships of the line of the Santa Ana class, also known as los Meregildos. Mexicano served in the Spanish Navy for three decades throughout the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, finally being sold at Ferrol in 1815. Although she was a formidable part of the Spanish battlefleet throughout these conflicts, the only major action Mexicano participated in was the Battle of Cape St Vincent in 1797.

San Hermenegildo was a 112-gun three-decker ship of the line built at Havanna for the Spanish Navy in 1789 to plans by Romero Landa, one of the eight very large ships of the line of the Santa Ana class, also known as los Meregildos. San Hermenegildo served in the Spanish Navy during the French Revolutionary Wars and was destroyed with heavy loss of life during the Second Battle of Algeciras.

The Reina Luisa was a 112-gun three-decker ship of the line built at Ferrol for the Spanish Navy in 1791 to plans by José Joaquín Romero Fernández de Landa. One of the eight very large ships of the line of the Santa Ana class, also known as Los Meregildos. The Reina Luisa served in the Spanish Navy for three decades throughout the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, finally being wrecked off Béjaïa in 1815. Although she was a formidable part of the Spanish battlefleet throughout these conflicts, she did not participate in any major operations.

Salvador del Mundo was a 112-gun three-decker ship of the line built at Ferrol for the Spanish Navy in 1787 to plans by Romero Landa, one of the eight very large ships of the line of the Santa Ana class, also known as los Meregildos. Salvador del Mundo served during the French Revolutionary Wars until its capture at the Battle of Cape St Vincent by a Royal Navy fleet on 14 February 1797. Salvador del Mundo remained in British hands throughout the Napoleonic Wars, serving as a harbour ship, until it was sold and broken up in 1815.

Purísima Concepción, was a Spanish first-rate ship of the line of the Kingdom of Spain's Armada Real in service between 1779 and 1810.

Enrique MacDonell, also spelled MacDonnell, was a Spanish admiral noted for his participation in several sea battles including the Battle of Trafalgar.
Joaquín Zarauz y de Santander (1756–1810) was a Spanish naval officer.
















