Socialism is a political, social, and economic philosophy encompassing a range of economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It includes the political theories and movements associated with such systems. Social ownership can be public, collective, or cooperative. While no single definition encapsulates the many types of socialism, social ownership is the one common element. Socialisms vary based on the role of markets and planning in resource allocation, on the structure of management in organizations, and from below or from above approaches, with some socialists favouring a party, state, or technocratic-driven approach. Socialists disagree on whether government, particularly existing government, is the correct vehicle for change.
State capitalism is an economic system in which the state undertakes business and commercial economic activity and where the means of production are nationalized as state-owned enterprises. The definition can also include the state dominance of corporatized government agencies or of public companies such as publicly listed corporations in which the state has controlling shares.
A mixed economy is variously defined as an economic system blending elements of a market economy with elements of a planned economy, markets with state interventionism, or private enterprise with public enterprise. Common to all mixed economies is a combination of free-market principles and principles of socialism. While there is no single definition of a mixed economy, one definition is about a mixture of markets with state interventionism, referring specifically to a capitalist market economy with strong regulatory oversight and extensive interventions into markets. Another is that of active collaboration of capitalist and socialist visions. Yet another definition is apolitical in nature, strictly referring to an economy containing a mixture of private enterprise with public enterprise. Alternatively, a mixed economy can refer to a reformist transitionary phase to a socialist economy that allows a substantial role for private enterprise and contracting within a dominant economic framework of public ownership. This can extend to a Soviet-type planned economy that has been reformed to incorporate a greater role for markets in the allocation of factors of production.
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from collective or cooperative property, which is owned by a group of non-governmental entities. The distinction between private and personal property varies depending on political philosophy, with socialist perspectives making a hard distinction between the two. As a legal concept, private property is defined and enforced by a country's political system.

State ownership, also called government ownership and public ownership, is the ownership of an industry, asset, or enterprise by the state or a public body representing a community as opposed to an individual or private party. Public ownership specifically refers to industries selling goods and services to consumers and differs from public goods and government services financed out of a government's general budget. Public ownership can take place at the national, regional, local, or municipal levels of government; or can refer to non-governmental public ownership vested in autonomous public enterprises. Public ownership is one of the three major forms of property ownership, differentiated from private, collective/cooperative, and common ownership.
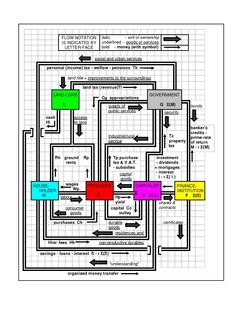
An economic system, or economic order, is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within a society or a given geographic area. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entities, decision-making processes and patterns of consumption that comprise the economic structure of a given community.

Marxism is a method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict as well as a dialectical perspective to view social transformation. It originates from the works of 19th-century German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. As Marxism has developed over time into various branches and schools of thought, currently no single, definitive Marxist theory exists.

The theory of state monopoly capitalism was initially a Marxist thesis popularised after World War II. Lenin had claimed in 1916 that World War I had transformed laissez-faire capitalism into monopoly capitalism, but he did not publish any extensive theory about the topic. The term refers to an environment where the state intervenes in the economy to protect larger monopolistic or oligopolistic businesses from threats. As conceived by Lenin in his pamphlet of the same name the theory aims to describe the final historical stage of capitalism, of which he believed the Imperialism of that time to be the highest expression.
The Socialist Party of Great Britain has weathered a number of internal disputes since its foundation in 1904, some of which have led to organisational breakaways.
Production for use is a phrase referring to the principle of economic organization and production taken as a defining criterion for a socialist economy. It is held in contrast to production for profit. This criterion is used to distinguish communism from capitalism, and is one of the fundamental defining characteristics of communism.
Eco-socialism is an ideology merging aspects of socialism with that of green politics, ecology and alter-globalization or anti-globalization. Eco-socialists generally believe that the expansion of the capitalist system is the cause of social exclusion, poverty, war and environmental degradation through globalization and imperialism, under the supervision of repressive states and transnational structures.

The socialist mode of production, also referred to as the communist mode of production, the lower-stage of communism or simply socialism as Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels used the terms communism and socialism interchangeably, is a specific historical phase of economic development and its corresponding set of social relations that emerge from capitalism in the schema of historical materialism within Marxist theory. The Marxist definition of socialism is that of an economic transition. In this transition, the sole criterion for production is use-value, therefore the law of value no longer directs economic activity. Marxist production for use is coordinated through conscious economic planning. Distribution of products is based on the principle of "to each according to his contribution". The social relations of socialism are characterized by the proletariat effectively controlling the means of production, either through cooperative enterprises or by public ownership or private artisanal tools and self-management. Surplus value goes to the working class and hence society as a whole.
Social ownership is the appropriation of the surplus product, produced by the means of production, to society as a whole. It is the defining characteristic of a socialist economic system. It can take the form of community ownership, state ownership, common ownership, employee ownership, cooperative ownership, and citizen ownership of equity. Traditionally, social ownership implied that capital and factor markets would cease to exist under the assumption that market exchanges within the production process would be made redundant if capital goods were owned and integrated by a single entity or network of entities representing society; but the articulation of models of market socialism where factor markets are utilized for allocating capital goods between socially owned enterprises broadened the definition to include autonomous entities within a market economy. Social ownership of the means of production is the common defining characteristic of all the various forms of socialism.
Socialist economics comprises the economic theories, practices and norms of hypothetical and existing socialist economic systems. A socialist economic system is characterized by social ownership and operation of the means of production that may take the form of autonomous cooperatives or direct public ownership wherein production is carried out directly for use rather than for profit. Socialist systems that utilize markets for allocating capital goods and factors of production among economic units are designated market socialism. When planning is utilized, the economic system is designated as a socialist planned economy. Non-market forms of socialism usually include a system of accounting based on calculation-in-kind to value resources and goods.
The World Socialist Movement (WSM) is an international organisation of socialist parties created in 1904 with the founding of the Socialist Party of Great Britain (SPGB).

Orthodox Marxism is the body of Marxist thought that emerged after the death of Karl Marx (1818–1883) and which became the official philosophy of the majority of the socialist movement as represented in the Second International until the First World War in 1914. Orthodox Marxism aims to simplify, codify and systematize Marxist method and theory by clarifying the perceived ambiguities and contradictions of classical Marxism.
Ethical socialism is a political philosophy that appeals to socialism on ethical and moral grounds as opposed to consumeristic, economic, and egoistic grounds. It emphasizes the need for a morally conscious economy based upon the principles of altruism, cooperation, and social justice while opposing possessive individualism.
Reformism is a political doctrine advocating the reform of an existing system or institution instead of its abolition and replacement.
A socialist state, socialist republic, or socialist country, sometimes referred to as a workers' state or workers' republic, is a sovereign state constitutionally dedicated to the establishment of socialism. The term communist state is often used synonymously in the West specifically when referring to one-party socialist states governed by Marxist–Leninist Communist parties, despite these countries being officially socialist states in the process of building socialism. These countries never describe themselves as communist nor as having implemented a communist society. Additionally, a number of countries that are multi-party capitalist states make references to socialism in their constitutions, in most cases alluding to the building of a socialist society, naming socialism, claiming to be a socialist state, or including the term people's republic or socialist republic in their country's full name, although this does not necessarily reflect the structure and development paths of these countries' political and economic systems. Currently, these countries include Algeria, Bangladesh, Guyana, India, Nepal, Nicaragua, Sri Lanka and Tanzania.
The socialist calculation debate, sometimes known as the economic calculation debate, was a discourse on the subject of how a socialist economy would perform economic calculation given the absence of the law of value, money, financial prices for capital goods and private ownership of the means of production. More specifically, the debate was centered on the application of economic planning for the allocation of the means of production as a substitute for capital markets and whether or not such an arrangement would be superior to capitalism in terms of efficiency and productivity.


