Tick-borne diseases, which afflict humans and other animals, are caused by infectious agents transmitted by tick bites. Tick-borne illnesses are caused by infection with a variety of pathogens, including rickettsia and other types of bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. Because individual ticks can harbor more than one disease-causing agent, patients can be infected with more than one pathogen at the same time, compounding the difficulty in diagnosis and treatment. As of 2016, 16 tick-borne diseases of humans are known.

Dermacentor variabilis, also known as the American dog tick or wood tick, is a species of tick that is known to carry bacteria responsible for several diseases in humans, including Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia. It is one of the most well-known hard ticks. Diseases are spread when it sucks blood from the host, which could take several days for the host to experience some symptoms.

Quercus variabilis, the Chinese cork oak, is a species of oak in the section Quercus sect. Cerris, native to a wide area of eastern Asia in southern, central, and eastern China, Taiwan, Japan, and Korea.

The grey bunting is a species of bird in the family Emberizidae.

Gap junction beta-3 protein (GJB3), also known as connexin 31 (Cx31) — is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GJB3 gene.

Gap junction beta-4 protein (GJB4), also known as connexin 30.3 (Cx30.3) — is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GJB4 gene.
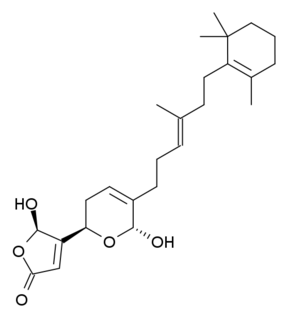
Manoalide is a calcium channel blocker. It has antibiotic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects and is found in some sponges, including the West Pacific species Luffariella variabilis.

Erythrokeratodermia variabilis is a rare autosomal dominant disorder that usually presents at birth or during the first year of life. To date, it is thought to be caused by mutations in genes encoding for connexin channels proteins in the epidermis, leading to the misregulation of homeostasis in keratinocytes.

Dolomena variabilis, common name : the Variable Conch, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Strombidae, the true conchs.
Anabaena variabilis is a species of filamentous cyanobacterium. This species of the genus Anabaena and the domain Eubacteria is capable of photosynthesis. This species is also known to be heterotrophic in that it may grow without light in the presence of fructose. It also can convert atmospheric dinitrogen to ammonia via nitrogen fixation.

Apophysomyces variabilis is an emerging fungal pathogen that can cause serious and sometimes fatal infection in humans. This fungus is a soil-dwelling saprobe with tropical to subtropical distribution. It is a zygomycete that causes mucormycosis, an infection in humans brought about by fungi in the order Mucorales. Infectious cases have been reported globally in locations including the Americas, Southeast Asia, India, and Australia. Apophysomyces variabilis infections are not transmissible from person to person.

Sternotomis variabilis, the Lesser Jewel Longhorn Beetle, is a species of flat-faced longhorn beetles belonging to the family Cerambycidae.
Tragocephalini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the Lamiinae subfamily. It was described by Thomson in 1857.
Spilotragus is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:

Gnorimus variabilis, also known as the variable chafer, is a species of scarab beetle belonging to the subfamily Cetoniinae, the flower chafers. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758. The species is native to Europe and is usually found in oak and beech woods or parkland.
Spilotragus crucifer is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Per Olof Christopher Aurivillius in 1908. It is known from Somalia and Kenya.
Spilotragus clarkei is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1976.
Spilotragus ornatus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Charles Joseph Gahan in 1898.
Spilotragus xanthus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Jordan in 1903. It is known from Mozambique and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Canis mosbachensis, sometimes known as the Mosbach wolf, is an extinct small wolf that once inhabited Eurasia from the Middle Pleistocene era to the Late Pleistocene. It is widely accepted as the ancestor of Canis lupus, the gray wolf.











