
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 species of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of Chlamydomonas is that it contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of Chlamydomonas are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains.
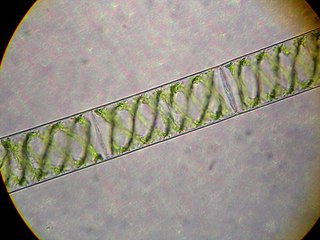
Spirogyra is a genus of filamentous charophyte green algae of the order Zygnematales, named for the helical or spiral arrangement of the chloroplasts that is characteristic of the genus. Spirogyra species, of which there are more than 500, are commonly found in freshwater habitats. Spirogyra measures approximately 10 to 150 micrometres in width and may grow to several centimetres in length.

The Zygnemataceae are a family of filamentous or unicellular, uniseriate (unbranched) green algae. The filaments are septated and reproduction is by conjugation; Spirogyra is commonly used in schools to demonstrate this kind of reproduction. The family is notable for its diversely shaped chloroplasts, such as stellate in Zygnema, helical in Spirogyra, and flat in Mougeotia. The Zygnemataceae are cosmopolitan, but though all generally occur in the same types of habitats, Mougeotia, Spirogyra, and Zygnema are by far the most common; in one study across North America, 95% of the Zygnemataceae collected were in these three genera. Classification and identification is primarily by the morphology of the conjugation, which is somewhat rare to find in natural populations of permanent water bodies; when in the vegetative state, the rarer genera resemble the three most common, and are often mistaken for them and catalogued as such. Conjugation can be induced in low-nitrogen culture. While they occupy many habitats, in North America all are found solely in freshwater or subaerial habitats. Species typically exist as floating mats in stagnant water in ditches and ponds, but some also grow in moving water, attaching themselves to a substrate by rhizoid-like projections of the basal cells of the filament. The mat species rise to the surface in early spring, grow rapidly through the summer, disappearing by late summer. Members of the Zygnemataceae, such as Spirogyra, fall prey to parasites, especially chytrids. Most genera previously assigned to Mesotaeniaceae as well as the Desmidiales actually emerged in the Zygnematacae.

AlgaeBase is a global species database of information on all groups of algae, both marine and freshwater, as well as sea-grass.
Struvea is a genus of green macroalgae in the family Boodleaceae.
Genicularina is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Gonatozygaceae.

Zygnematophyceae is a class of green algae in the paraphylum streptophyte algae, also referred to as Charophyta, consisting of more than 4000 described species. The Zygnematophyceae are the sister clade of the Embryophyta.
Jean Pierre Étienne Vaucher was a Swiss Protestant pastor and botanist who was a native of the Republic of Geneva.

Chaetophora elegans is the type species in the algae genus Chaetophora.

Galaxaura is a genus of thalloid red algae.

Klebsormidium is a genus of filamentous charophyte green algae comprising 20 species. The name was proposed in 1972 to resolve confusion in application and status of Hormidium and was given for the German botanist Georg Albrecht Klebs.
Gongolaria elegans is a species of brown algae in the family Sargassaceae endemic to the Mediterranean.

Martensia is a genus of red algae, containing the following species:
Chondracanthus elegans is a red algae species in the genus Chondracanthus. The name elegans is Latin for 'elegant.'

Rivularia is a genus of cyanobacteria of the family Rivulariaceae.
Cyanonephron elegans is a freshwater species of cyanobacteria in the family Synechococcaceae. It is described in the Netherlands, Siberia, Russia and Queensland, Australia.
Gongolaria is a genus of brown algae in the family Sargassaceae. It was formerly included in Cystoseira, but was recently found not to be closely related to it.









