Fehmarn is an island in the Baltic Sea, off the eastern coast of Germany's northernmost state of Schleswig-Holstein. It is Germany's third-largest island, after Rügen and Usedom. Fehmarn is separated from the German peninsula of Wagria in Holsatia by the Fehmarn Sound, and from the southern Danish island of Lolland by the Fehmarn Belt. It is connected to the Holsatian mainland by the Fehmarn Sound Bridge. The island belongs to the district of Ostholstein. The closest larger towns on the mainland are Heiligenhafen and Oldenburg in Holstein. Right opposite of Fehmarn, on the tip of the Wagrian Peninsula, is Großenbrode.

Hiddensee is a car-free island in the Baltic Sea, located west of Germany's largest island, Rügen, on the German coast.

Storkyrkan, also called Stockholms domkyrka and Sankt Nikolai kyrka, is the oldest church in Stockholm. Storkyrkan lies in the centre of Stockholm in Gamla stan, between Stockholm Palace and Stortorget, the old main square of Stockholm. It was consecrated to Saint Nicholas in 1306 but construction of the church probably started in the 13th century. Inside, Storkyrkan still maintains much of its late medieval appearance in the form of a hall church with a vaulted ceiling supported by brick pillars. The exterior of the church is however uniformly Baroque in appearance, the result of extensive changes made in the 18th century. The church played an important role during the Reformation in Sweden as the place where Mass was celebrated in Swedish for the first time. It currently serves as the seat of the Bishop of Stockholm within the Church of Sweden since the creation of the Diocese of Stockholm in 1942.

Saint Fin Barre's Cathedral is a Gothic Revival three-spire Church of Ireland cathedral in the city of Cork. It is located on the south bank of the River Lee and dedicated to Finbarr of Cork, patron saint of the city. Formerly the sole cathedral of the Diocese of Cork, it is now one of three co-cathedrals in the United Dioceses of Cork, Cloyne and Ross in the ecclesiastical province of Dublin. Christian use of the site dates back 7th-century AD when, according to local lore, Finbarr of Cork founded a monastery. The original building survived until the 12th century, when it either fell into disuse or was destroyed during the Norman invasion of Ireland. Around 1536, during the Protestant Reformation, the cathedral became part of the established church, later known as the Church of Ireland. The previous building was constructed in the 1730s, but was widely regarded as plain and featureless.

Saint Petersburg Mining University, is Russia's oldest technical university, and one of the oldest technical colleges in Europe. It was founded on October 21, 1773, by Empress Catherine the Great, who realised an idea proposed by Peter the Great and Mikhail Lomonosov for training engineers for the mining and metals industries. Having a strong engineering profession was seen by many Russian rulers as a vital means of maintaining Russia's status as a great power. As historian Alfred J. Rieber wrote, "The marriage of technology and central state power had a natural attraction for Peter the Great and his successors, particularly Paul I, Alexander I, and Nicholas I". All three had had a military education and seen the achievements of the engineers of revolutionary and imperial France, who had reconstructed the great highways, unified the waterways and erected buildings throughout Europe in a more lasting tribute to the French than all of Napoleon's victories.

The Church of St. Nicholas was a Gothic Revival cathedral that was formerly one of the five Lutheran Hauptkirchen in the city of Hamburg, Germany. The original chapel, a wooden building, was completed in 1195. It was replaced by a brick church in the 14th century, which was eventually destroyed by fire in 1842. The church was completely rebuilt by 1874, and was the tallest building in the world from 1874 to 1876. It was designed by the English architect George Gilbert Scott.

Westerland is a seaside resort and a former municipality located on the German North Sea island of Sylt. Since 1 January 2009, Westerland has been part of the municipality Gemeinde Sylt. Westerland is part of the Nordfriesland district in Schleswig-Holstein. It is the largest resort on the island, the local transportation hub and the centre of Sylt's tourist industry.

St Nicholas Church in Thames Ditton, Surrey, England, is a Grade I listed Anglican parish church that has parts that date back to the 12th century.

The Church of St. Nicholas, Bradfield is situated in the small village of High Bradfield, which is located 6 miles (10 km) north west of the centre of the city of Sheffield in South Yorkshire, England. It is one of only five Grade One Listed buildings in Sheffield. The church is situated 260 metres (850 ft) above sea level, overlooking the Peak District National Park.

St. Michael's Church is an Anglican church in Brighton, England, dating from the mid-Victorian era. Located on Victoria Road in the Montpelier area, to the east of Montpelier Road, it is one of the largest churches in the city of Brighton and Hove. The church is a Grade I listed building.

St. Nicholas Church is a medieval church building in Tallinn (Reval), Estonia. It was dedicated to Saint Nicholas, the patron of the fishermen and sailors. Originally built in the 13th century, it was partially destroyed in the Soviet bombing of Tallinn in World War II. The building itself has since been restored, however, as a church without own congregation, it has not been used for regular religious activities since World War II. At present it houses the Niguliste Museum, a branch of the Art Museum of Estonia, focusing mainly on ecclesiastical art from the Middle Ages onward. It is also used as a concert hall.
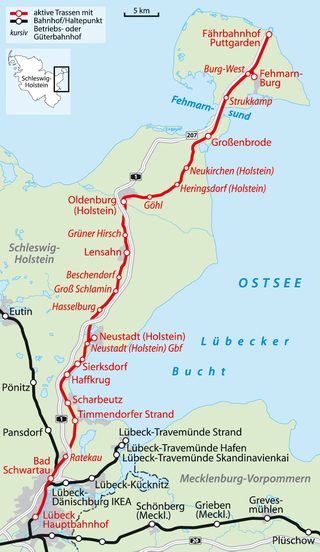
The Lübeck–Puttgarden railway is part of the international Vogelfluglinie between Germany and Denmark and connects Lübeck with Puttgarden on the Baltic Sea island of Fehmarn in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. The line is now closed north of Neustadt for the construction of the Fehmarn Belt Fixed Link.

St. Nicholas Church in Potsdam is a Lutheran church under the Evangelical Church in Berlin, Brandenburg and Silesian Upper Lusatia of the Evangelical Church in Germany on the Old Market Square in Potsdam. The central plan building in the Classicist style and dedicated to Saint Nicholas was built to plans by Karl Friedrich Schinkel in the years 1830 to 1837. The tambour of the 77-metre-high church that towers above the roofs of the city was built later, from 1843 to 1850. Its construction was taken over by Ludwig Persius and, from 1845, Friedrich August Stüler.

The Church of St Nicholas, Charlwood, is the parish church of Charlwood, Surrey, England. With a 12th-century tower and nave section and examples of 13th to 15th century art, fixtures and architecture, it is a Grade I listed building.

Saint Thomas's Church is a historic Roman Catholic church in St. Helier, Jersey. It is the largest church in the Channel Islands, and first opened its doors in 1887.

St Nicholas Church is an active Anglican parish church in the diocese of Chester on Newport Avenue, in Wallasey, in Wirral, England. It was designed by J. F. Doyle and built in 1910–11. The church is located near Wallasey Golf Club and is known as the Harrison Memorial Church or the Golfers' Church. It is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade II listed building.

Villach Friary is a Franciscan friary, responsible for the parish of St. Nicholas in Villach, Carinthia, Austria.

Lyngsjö Church is a medieval church in Lyngsjö, in the province of Skåne, Sweden. The well-preserved medieval church contains an unusual, Romanesque antependium of gilt copper of unknown origin.

St. Nikolai is the name of a Protestant parish and its church in Kiel, the capital of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is the town's oldest building, at the Alter Markt. It was dedicated to Saint Nicholas. In the 19th century, it was remodeled in Gothic Revival style. Destroyed in World War II, it was rebuilt with a simpler contemporary interior. It features notable artworks such as a bronze baptismal font from 1340, an altar from 1460, a triumphal cross from 1490, a wood-carved pulpit from 1705, and outside a bronze by Ernst Barlach from 1928.

St Walpurgis' Church in the upper part of the village of Großengottern in Thuringia, Germany, is a Late Gothic church building dating from the 15th century. Today, it is a Lutheran parish church. St Walpurgis' Church is known for its large Baroque organ by the significant organ builder Tobias H. G. Trost.