
Wool is the textile fiber obtained from sheep and other animals, including cashmere and mohair from goats, qiviut from muskoxen, hide and fur clothing from bison, angora from rabbits, and other types of wool from camelids.

A textile is a flexible material consisting of a network of natural or artificial fibers. Yarn is produced by spinning raw fibres of wool, flax, cotton, hemp, or other materials to produce long strands. Textiles are formed by weaving, knitting, crocheting, knotting, tatting, felting, or braiding.
A metal matrix composite (MMC) is composite material with at least two constituent parts, one being a metal necessarily, the other material may be a different metal or another material, such as a ceramic or organic compound. When at least three materials are present, it is called a hybrid composite. An MMC is complementary to a cermet.

Glass fiber is a material consisting of numerous extremely fine fibers of glass.
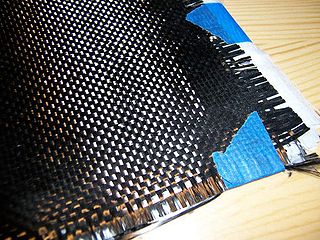
Carbon fibers or carbon fibres are fibers about 5–10 micrometres in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. Carbon fibers have several advantages including high stiffness, high tensile strength, low weight, high chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance and low thermal expansion. These properties have made carbon fiber very popular in aerospace, civil engineering, military, and motorsports, along with other competition sports. However, they are relatively expensive when compared with similar fibers, such as glass fibers or plastic fibers.

Mohair is a fabric or yarn made from the hair of the Angora goat. Both durable and resilient, mohair is notable for its high luster and sheen, and is often used in fiber blends to add these qualities to a textile. Mohair takes dye exceptionally well. It feels warm in winter as it has excellent insulating properties, while its moisture-wicking properties allow it to remain cool in summer. It is durable, naturally elastic, flame-resistant and crease-resistant. It is considered a luxury fiber, like cashmere, angora, and silk, and can be more expensive than most sheep's wool.
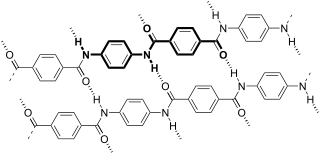
Aramid fibers are a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers. They are used in aerospace and military applications, for ballistic-rated body armor fabric and ballistic composites, in marine cordage, marine hull reinforcement, and as an asbestos substitute. The name is a portmanteau of "aromatic polyamide". The chain molecules in the fibers are highly oriented along the fiber axis. As a result, a higher proportion of the chemical bond contributes more to fiber strength than in many other synthetic fibers. Aramides have a very high melting point

Jute is a long, soft, shiny Bast fiber that can be spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced primarily from plants in the genus Corchorus, which was once classified with the family Tiliaceae. The primary source of the fiber is Corchorus olitorius, but it is considered inferior to Corchorus capsularis. "Jute" is the name of the plant or fiber used to make burlap, hessian or gunny cloth.

Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic engineering polymer that is used as an insulator in the electrical and electronics industries. It is a thermoplastic (semi-)crystalline polymer, and a type of polyester. PBT is resistant to solvents, shrinks very little during forming, is mechanically strong, heat-resistant up to 150 °C and can be treated with flame retardants to make it noncombustible. It was developed by Britain's Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI).

Nomex is a flame-resistant meta-aramid material developed in the early 1960s by DuPont and first marketed in 1967.

Metallic fibers are manufactured fibers composed of metal, metallic alloys, plastic-coated metal, metal-coated plastic, or a core completely covered by metal.
Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene is a subset of the thermoplastic polyethylene. Also known as high-modulus polyethylene, (HMPE), it has extremely long chains, with a molecular mass usually between 3.5 and 7.5 million amu. The longer chain serves to transfer load more effectively to the polymer backbone by strengthening intermolecular interactions. This results in a very tough material, with the highest impact strength of any thermoplastic presently made.
Olefin fiber is a synthetic fiber made from a polyolefin, such as polypropylene or polyethylene. It is used in wallpaper, carpeting, ropes, and vehicle interiors.
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) is concrete containing fibrous material which increases its structural integrity. It contains short discrete fibers that are uniformly distributed and randomly oriented. Fibers include steel fibers, glass fibers, synthetic fibers and natural fibers – each of which lend varying properties to the concrete. In addition, the character of fiber-reinforced concrete changes with varying concretes, fiber materials, geometries, distribution, orientation, and densities.
The manufacture of textiles is one of the oldest of human technologies. To make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fibre from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving, which turns yarn into cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. For decoration, the process of colouring yarn or the finished material is dyeing. For more information of the various steps, see textile manufacturing.
A technical textile is a textile product manufactured for non-aesthetic purposes, where function is the primary criterion. Technical textiles include textiles for automotive applications, medical textiles, geotextiles, agrotextiles, and protective clothing.
A conductive textile is a fabric which can conduct electricity. Conductive textiles can be made with metal strands woven into the construction of the textile or by conductive yarns which are conductive thanks to a metal-coating. There is also an interest in semiconducting textiles, made by impregnating normal textiles with carbon- or metal-based powders.

Alpaca fleece is the natural fiber harvested from an alpaca. There are two different types of alpaca fleece. the most common fleece type comes from a Huacaya. Huacaya fiber grows and looks similar to sheep wool in that the animal looks "fluffy". The second type of alpaca is Suri and makes up less than 10% of the South American alpaca population. Suri fiber is more similar to natural silk and hangs off the body in locks that have a dreadlock appearance. While both fibers can be used in the worsted milling process using light weight yarn or thread, Huacaya fiber can also be used in a woolen process and spun into various weight yarns. It is a soft, durable, luxurious and silky natural fiber.

Ripstop fabrics are woven fabrics, often made of nylon, using a special reinforcing technique that makes them resistant to tearing and ripping. During weaving, (thick) reinforcement yarns are interwoven at regular intervals in a crosshatch pattern. The intervals are typically 5 to 8 millimeters. Thin and lightweight ripstop fabrics have a 2-dimensional structure due to the thicker yarns being interwoven in thinner cloth. Older lightweight ripstop fabrics display the thicker interlocking thread patterns in the material quite prominently, but more modern weaving techniques make the ripstop threads less obvious. A similar effect can be achieved by weaving two or three fine yarns together at smaller intervals.

In textile manufacturing, finishing refers to the processes that convert the woven or knitted cloth into a usable material and more specifically to any process performed after dyeing the yarn or fabric to improve the look, performance, or "hand" (feel) of the finish textile or clothing. The precise meaning depends on context.












