The slide rule is a mechanical analog computer, which is used primarily for multiplication and division, and for functions such as exponents, roots, logarithms, and trigonometry. It is not typically designed for addition or subtraction, which is usually performed using other methods. Maximum accuracy for standard linear slide rules is about three decimal significant digits, while scientific notation is used to keep track of the order of magnitude of results.

Straightedge and compass construction, also known as ruler-and-compass construction or classical construction, is the construction of lengths, angles, and other geometric figures using only an idealized ruler and a pair of compasses.

A ruler, sometimes called a rule or line gauge, is a device used in geometry and technical drawing, as well as the engineering and construction industries, to measure distances or draw straight lines.

HO or H0 is a rail transport modelling scale using a 1:87 scale. It is the most popular scale of model railway in the world. The rails are spaced 16.5 millimetres (0.650 in) apart for modelling 1,435 mm standard gauge tracks and trains in HO.

A hand plane is a tool for shaping wood using muscle power to force the cutting blade over the wood surface. Some rotary power planers are motorized power tools used for the same types of larger tasks, but are unsuitable for fine-scale planing, where a miniature hand plane is used.
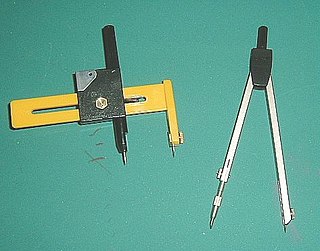
A compass, more accurately known as a pair of compasses, is a technical drawing instrument that can be used for inscribing circles or arcs. As dividers, it can also be used as a tool to step out distances, in particular, on maps. Compasses can be used for mathematics, drafting, navigation and other purposes.

A tape measure or measuring tape is a flexible ruler used to measure size or distance.

A combination square is a multi-purpose measuring and marking tool used in metalworking, woodworking, and stonemasonry. It is composed of a rule and one or more interchangeable heads that can be attached to the rule. Other names for the tool include adjustable square, combo square, and sliding square.

A try square or try-square is a woodworking tool used for marking and checking 90° angles on pieces of wood. Though woodworkers use many different types of square, the try square is considered one of the essential tools for woodworking.

The steel square is a tool used in carpentry. Carpenters use various tools to lay out structures that are square, many of which are made of steel, but the name steel square refers to a specific long-armed square that has additional uses for measurement, especially of various angles. It consists of a long, wider arm and a shorter, narrower arm, which meet at an angle of 90 degrees. Today the steel square is more commonly referred to as the framing square or carpenter's square, and such squares are no longer invariably made of steel ; they can also be made of aluminum or polymers, which are light and resistant to rust.

A backsaw is any hand saw which has a stiffening rib on the edge opposite the cutting edge, enabling better control and more precise cutting than with other types of saws. Backsaws are normally used in woodworking for precise work, such as cutting dovetails, mitres, or tenons in cabinetry and joinery. Because of the stiffening rib, backsaws are limited in the depth to which they can cut. Backsaws usually have relatively closely spaced teeth, often with little or no set.
Marking out or layout means the process of transferring a design or pattern to a workpiece, as the first step in the manufacturing process. It is performed in many industries or hobbies although in the repetition industries the machine's initial setup is designed to remove the need to mark out every individual piece.

Pitchnut is a wooden tabletop game of French Canadian origins, similar to carrom, crokinole and pichenotte, with mechanics that lie somewhere between pocket billiards and air hockey. Unlike with other wooden board games, there are no records of pitchnut being mass-produced; all existing boards are handmade. Pitchnut is not a patented game. It is in the public domain. The name Pitchnut is a registered trademark by Lee Larcheveque, who coined and trademarked the name. In French-speaking areas of Canada, the game is called pichenotte, which is French for 'flick'. There are several other disk-flicking games which are also referred to as 'pichenotte' by French speakers. Many modern boards are in use, made mostly by Lee Larcheveque, and before him, by Achille Scalabrini, in Sainte-Edwidge-de-Clifton, Quebec, Canada. The game is common on the farming villages near Coaticook, Quebec, Canada and in Amherst, Massachusetts, United States.

Wooden toy trains are toy trains that run on a wooden track system with grooves to guide the wheels of the rolling stock. While the trains, tracks and scenery accessories are made mainly of wood, the engines and cars connect to each other using metal hooks or small magnets, and some use plastic wheels mounted on metal axles. Some trains are made to resemble anthropomorphical, fictional, and prototypical railroad equipment.

Baker Street Mill is a grade II listed smock mill at Baker Street, Orsett, Essex, England which has been part adapted to residential use on its lower two floors only.

Drafting tools may be used for measurement and layout of drawings, or to improve the consistency and speed of creation of standard drawing elements. Tools such as pens and pencils mark the drawing medium. Other tools such as straight edges, assist the operator in drawing straight lines, or assist the operator in drawing complicated shapes repeatedly. Various scales and the protractor are used to measure the lengths of lines and angles, allowing accurate scale drawing to be carried out. The compass is used to draw arcs and circles. A drawing board was used to hold the drawing media in place; later boards included drafting machines that sped the layout of straight lines and angles. Tools such as templates and lettering guides assisted in the drawing of repetitive elements such as circles, ellipses, schematic symbols and text. Other auxiliary tools were used for special drawing purposes or for functions related to the preparation and revision of drawings. The tools used for manual technical drawing have been displaced by the advent of computer-aided drawing, drafting and design (CADD).

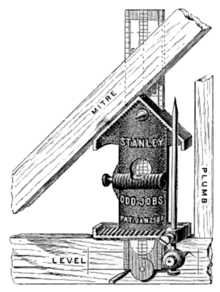
Stanley Hand Tools is a brand of hand tools. It is a division of Stanley Black & Decker, following the merger of The Stanley Works with Black & Decker in March 2010.

A speed square, also called a rafter square, rafter angle square, and triangle square, is a multi-purpose triangular carpenters' tool use for marking out. Its functions include many of those of a combination square, try square, and framing square. Carpenters use it to make basic measurements and mark lines on dimensional lumber, and as a saw guide for short 45 and 90 degree cuts.

A square is a tool used for marking and referencing a 90° angle, though mitre squares are used for 45° angles. Squares see common use in woodworking, metalworking, construction and technical drawing. Some squares incorporate a scale for measuring distances or for calculating angles.