
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, computer programming, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret biological data. The subsequent process of analyzing and interpreting data is often referred to as computational biology, though the distinction between the two terms is often disputed.

Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to infer properties of an underlying distribution of probability. Inferential statistical analysis infers properties of a population, for example by testing hypotheses and deriving estimates. It is assumed that the observed data set is sampled from a larger population.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to statistics:

Open educational resources (OER) are teaching, learning, and research materials intentionally created and licensed to be free for the end user to own, share, and in most cases, modify. The term "OER" describes publicly accessible materials and resources for any user to use, re-mix, improve, and redistribute under some licenses. These are designed to reduce accessibility barriers by implementing best practices in teaching and to be adapted for local unique contexts.
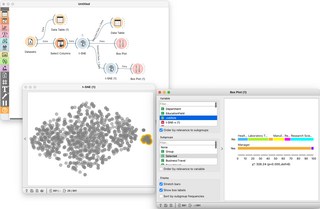
Orange is an open-source data visualization, machine learning and data mining toolkit. It features a visual programming front-end for exploratory qualitative data analysis and interactive data visualization.

ImageJ is a Java-based image processing program developed at the National Institutes of Health and the Laboratory for Optical and Computational Instrumentation. Its first version, ImageJ 1.x, is developed in the public domain, while ImageJ2 and the related projects SciJava, ImgLib2, and SCIFIO are licensed with a permissive BSD-2 license. ImageJ was designed with an open architecture that provides extensibility via Java plugins and recordable macros. Custom acquisition, analysis and processing plugins can be developed using ImageJ's built-in editor and a Java compiler. User-written plugins make it possible to solve many image processing and analysis problems, from three-dimensional live-cell imaging to radiological image processing, multiple imaging system data comparisons to automated hematology systems. ImageJ's plugin architecture and built-in development environment has made it a popular platform for teaching image processing.
Digital humanities (DH) is an area of scholarly activity at the intersection of computing or digital technologies and the disciplines of the humanities. It includes the systematic use of digital resources in the humanities, as well as the analysis of their application. DH can be defined as new ways of doing scholarship that involve collaborative, transdisciplinary, and computationally engaged research, teaching, and publishing. It brings digital tools and methods to the study of the humanities with the recognition that the printed word is no longer the main medium for knowledge production and distribution.
Open Source Physics, or OSP, is a project sponsored by the National Science Foundation and Davidson College, whose mission is to spread the use of open source code libraries that take care of a lot of the heavy lifting for physics: drawing and plotting, differential equation solvers, exporting to animated GIFs and movies, etc., tools, and compiled simulations for physics and other numerical simulations. The OSP collection provides curriculum resources that engage students in physics, computation, and computer modeling. The core library is in the Java programming language and licensed with GNU General Public License licenses. The site now serves over 10,000 visitors per month. The Open Source Physics Project is an extension of the Physlet Project.
A Biositemap is a way for a biomedical research institution of organisation to show how biological information is distributed throughout their Information Technology systems and networks. This information may be shared with other organisations and researchers.
KNIME, the Konstanz Information Miner, is a free and open-source data analytics, reporting and integration platform. KNIME integrates various components for machine learning and data mining through its modular data pipelining "Building Blocks of Analytics" concept. A graphical user interface and use of JDBC allows assembly of nodes blending different data sources, including preprocessing, for modeling, data analysis and visualization without, or with minimal, programming.

A motion chart is a dynamic bubble chart which allows efficient and interactive exploration and visualization of longitudinal multivariate data. Motion charts provide mechanisms for mapping ordinal, nominal and quantitative variables onto time, 2D coordinate axes, size, colors, glyphs and appearance characteristics, which facilitate the interactive display of multidimensional and temporal data.
MERLOT is an online repository and international consortium of institutions of higher education, industry partners, professional organizations, and individuals. MERLOT partners and members are devoted to identifying, peer reviewing, organizing, and making available existing online learning resources in a range of academic disciplines for use by higher education faculty and students.
The ViennaRNA Package is software, a set of standalone programs and libraries used for predicting and analysing RNA nucleic acid secondary structures. The source code for the package is released as free and open-source software and compiled binaries are available for the operating systems Linux, macOS, and Windows. The original paper has been cited over 2,000 times.

The first edition of the textbook Data Science and Predictive Analytics: Biomedical and Health Applications using R, authored by Ivo D. Dinov, was published in August 2018 by Springer. The second edition of the book was printed in 2023.
Dissemination of IT for the Promotion of Materials Science (DoITPoMS) is a web-based educational software resource designed to facilitate the teaching and learning of Materials science, at the tertiary level for free.

Ivaylo (Ivo) D. Dinov is a mathematical statistician, data scientist, and computational neuroscientist, who is the Henry Philip Tappan collegiate professor at the University of Michigan. He is a co-developer of the 5D spacekime model, a new technique for complex time (kime) representation, modeling, and analysis of repeated measurement longitudinal processes. Dinov is the author of the Data Science and Predictive Analytics (DSPA) book and has published significantly on a wide range of topics, including mathematical modeling, computational statistics, data science, neuroscience, applied statistics, and generative artificial intelligence models (GAIMs).









