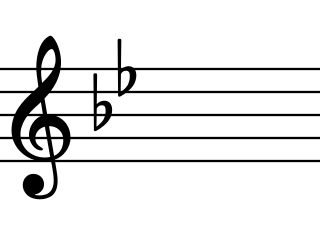Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known simply as depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of low mood that is present across most situations. It is often accompanied by low self-esteem, loss of interest in normally enjoyable activities, low energy, and pain without a clear cause. People may also occasionally have false beliefs or see or hear things that others cannot. Some people have periods of depression separated by years in which they are normal, while others nearly always have symptoms present. Major depressive disorder can negatively affect a person's personal life, work life, or education, as well as sleeping, eating habits, and general health. Between 2–8% of adults with major depression die by suicide, and about 50% of people who die by suicide had depression or another mood disorder.
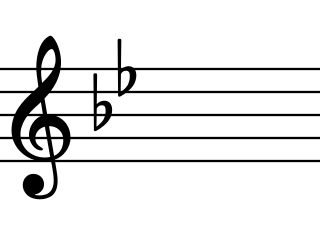
In musical notation, a key signature is a set of sharp, flat, and rarely, natural symbols placed together on the staff. Key signatures are generally written immediately after the clef at the beginning of a line of musical notation, although they can appear in other parts of a score, notably after a double barline.
In music theory, the term minor scale refers to three scale patterns – the natural minor scale, the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale – rather than just one as with the major scale.
In music theory, a scale is any set of musical notes ordered by fundamental frequency or pitch. A scale ordered by increasing pitch is an ascending scale, and a scale ordered by decreasing pitch is a descending scale. Some scales contain different pitches when ascending than when descending, for example, the melodic minor scale.
In music theory, an interval is the difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord.
Sonata form is a musical structure consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century.
The orbital period is the time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object, and applies in astronomy usually to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars.

A chord progression or harmonic progression is a succession of musical chords, which are two or more notes, typically sounded simultaneously. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from the common practice era of Classical music to the 21st century. Chord progressions are the foundation of Western popular music styles and traditional music. In these genres, chord progressions are the defining feature on which melody and rhythm are built.

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of pitches consisting of two or more notes that are heard as if sounding simultaneously.

In music, modulation is most commonly the act or process of changing from one key to another. This may or may not be accompanied by a change in key signature. Modulations articulate or create the structure or form of many pieces, as well as add interest. Treatment of a chord as the tonic for less than a phrase is considered tonicization.
Modulation is the essential part of the art. Without it there is little music, for a piece derives its true beauty not from the large number of fixed modes which it embraces but rather from the subtle fabric of its modulation.

In classical music from Western culture, a third is a musical interval encompassing three staff positions, and the major third is a third spanning four semitones. Along with the minor third, the major third is one of two commonly occurring thirds. It is qualified as major because it is the larger of the two: the major third spans four semitones, the minor third three. For example, the interval from C to E is a major third, as the note E lies four semitones above C, and there are three staff positions from C to E. Diminished and augmented thirds span the same number of staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones.
In Western music, the adjectives major and minor can describe a musical composition, movement, section, scale, key, chord, or interval.

Guitar tunings assign pitches to the open strings of guitars, including acoustic guitars, electric guitars, and classical guitars. Tunings are described by the particular pitches denoted by notes in Western music. By convention, the notes are ordered from lowest-pitched string to highest-pitched.

G major is a major scale based on G, with the pitches G, A, B, C, D, E, and F♯. Its key signature has one sharp, F♯. Its relative minor is E minor and its parallel minor is G minor.

A major is a major scale based on A, with the pitches A, B, C♯, D, E, F♯, and G♯. Its key signature has three sharps. Its relative minor is F-sharp minor and its parallel minor is A minor. The key of A major is the only key where a Neapolitan sixth chord on requires both a flat and a natural accidental.
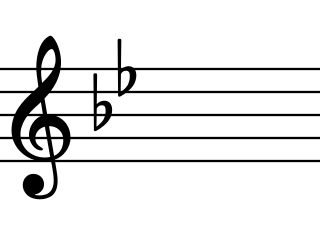
G minor is a minor scale based on G, consisting of the pitches G, A, B♭, C, D, E♭, and F. Its key signature has two flats. Its relative major is B-flat major and its parallel major is G major.

The G20 is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union. Founded in 1999 with the aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability, the G20 has expanded its agenda since 2008 and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers and foreign ministers, have periodically conferred at summits ever since. It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one organization.

In geometry, the major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter: a line segment that runs through the center and both foci, with ends at the widest points of the perimeter. The semi-major axis is one half of the major axis, and thus runs from the centre, through a focus, and to the perimeter. For the special case of a circle, the semi-major axis is the radius.

In music, the dominant is the fifth scale degree of the diatonic scale, called "dominant" because it is next in importance to the tonic, and a dominant chord is any chord built upon that pitch, using the notes of the same diatonic scale. The dominant is sung as so in solfege. The dominant function has the role of creating instability that requires the tonic for resolution.
In very much conventionally tonal music, harmonic analysis will reveal a broad prevalence of the primary harmonies: tonic, dominant, and subdominant, and especially the first two of these.
The scheme I-x-V-I symbolizes, though naturally in a very summarizing way, the harmonic course of any composition of the Classical period. This x, usually appearing as a progression of chords, as a whole series, constitutes, as it were, the actual "music" within the scheme, which through the annexed formula V-I, is made into a unit, a group, or even a whole piece.