
Dimocarpus longan, commonly known as the longan, is a tropical tree species that produces edible fruit. It is one of the better-known tropical members of the soapberry family Sapindaceae, to which the lychee and rambutan also belong. The fruit of the longan is similar to that of the lychee, but less aromatic in taste. It is native to tropical Asia and China.

Lychee is a monotypic taxon and the sole member in the genus Litchi in the soapberry family, Sapindaceae.

An aril, also called an arillus, is a specialized outgrowth from a seed that partly or completely covers the seed. An arillode or false aril is sometimes distinguished: whereas an aril grows from the attachment point of the seed to the ovary, an arillode forms from a different point on the seed coat. The term "aril" is sometimes applied to any fleshy appendage of the seed in flowering plants, such as the mace of the nutmeg seed. Arils and arillodes are often edible enticements that encourage animals to transport the seed, thereby assisting in seed dispersal. Pseudarils are aril-like structures commonly found on the pyrenes of Burseraceae species that develop from the mesocarp of the ovary. The fleshy, edible pericarp splits neatly in two halves, then falling away or being eaten to reveal a brightly coloured pseudaril around the black seed.

Nephelium is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the family Sapindaceae, native to southeastern Asia.

Chashan is a town under the direct administration of the prefecture-level city of Dongguan, Guangdong Province, China. It is located 11.5 kilometres (7.1 mi) northeast of the prefecture-level city centre.

Girdling, also called ring-barking, is the complete removal of the bark from around the entire circumference of either a branch or trunk of a woody plant. Girdling results in the death of the area above the girdle over time. A branch completely girdled will fail and when the main trunk of a tree is girdled, the entire tree will die, if it cannot regrow from above to bridge the wound. Human practices of girdling include forestry, horticulture, and vandalism. Foresters use the practice of girdling to thin forests. Animals such as rodents will girdle trees by feeding on outer bark, often during winter under snow. Girdling can also be caused by herbivorous mammals feeding on plant bark and by birds and insects, both of which can effectively girdle a tree by boring rows of adjacent holes.

Hypoglycin A is a naturally occurring amino acid derivative found in the unripened fruit of the Ackee tree and in the seeds of the box elder tree. It is toxic if ingested, and is the causative agent of Jamaican vomiting sickness. A 2017 Lancet report established a link between the consumption of unripened lychees resulting in hypoglycaemia and death from acute toxic encephalopathy.
Burichang, also known as Burichong, is an upazila of Comilla District in the Division of Chittagong, Bangladesh.
Raiganj is an upazila of Sirajganj District in the Rajshahi Division of Bangladesh.

Isotenes miserana is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in the Northern Territory, Queensland, New South Wales and Victoria. This species has been introduced to New Zealand.
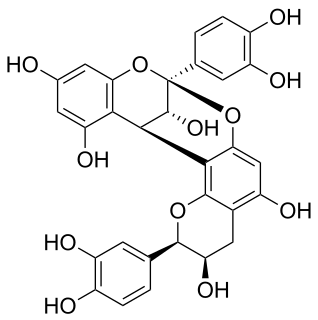
Procyanidin A2 is an A type proanthocyanidin.

Yangxi County is a coastal county in the southwest of Guangdong Province, China, facing the South China Sea to the south. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Yangjiang. The county has a total area of 1,271 km2 (491 sq mi), and 126.6 km (78.7 mi) of coastline.
L. chinensis may refer to:
Adoxophyes privatana, the appleleaf-curling moth, is a moth of the family Tortricidae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1863. It is native to south-east Asia, where it has been recorded from Taiwan, Hong Kong, Hainan in China, Nepal, India, Sri-Lanka, Thailand, Vietnam, western Malaysia, Singapore, Sumatra, Java, Borneo, the Philippines and the Chagos Archipelago. It is an accidental introduction in Great Britain.
The cocoa pod borer is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Saudi Arabia, China, India, Thailand, Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam, Australia, New Britain, the Philippines, Samoa, the Solomon Islands, Sri Lanka, Taiwan and Vanuatu.
The litchi fruit borer or the litchi stem-end borer is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is present in China, India, Nepal, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam.
Tengraha is a village in Minapur Block in Muzaffarpur district of Bihar, India. It belongs to Tirhut Division. It is located 26 km north of the Muzaffarpur district headquarters, 8 km from Minapur, and 91 km from the state capital, Patna. It is surrounded by Gandak and Bagmati rivers. Most of the people in this village are farmers. This village, as well as the rest of Muzaffarpur district, is famous for its Lichee trees, which grow litchis fruit. Tengrari has a small shopping market. Balua Bazar is near Tengrari, which has a shopping market and Rishabh Vastralaya.

Methylene cyclopropyl acetic acid (MCPA) is found in lychee seeds and also a toxic metabolite in mammalian digestion after ingestion of hypoglycin.

Colaba Woods is a garden in the Colaba area of Mumbai, India.
Arene lychee is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Areneidae. It was described from Canopus Bank, a seamount located in northeastern Brazil, and named after its resemblance to the fruit of the Asian soapberry tree, Litchi chinenis.











