
Bausch + Lomb is an American-Canadian eye health products company based in Vaughan, Ontario, Canada. It is one of the world's largest suppliers of contact lenses, lens care products, pharmaceuticals, intraocular lenses, and other eye surgery products. The company was founded in Rochester, New York, in 1853 by optician John Bausch and cabinet maker turned financial backer Henry Lomb. Until its sale in 2013, Bausch + Lomb was one of the oldest continually operating companies in the United States.

Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes when viewing distant objects. Most binoculars are sized to be held using both hands, although sizes vary widely from opera glasses to large pedestal-mounted military models.

A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.

An artillery observer,artillery spotter, or forward observer (FO) is a soldier responsible for directing artillery and mortar fire support onto a target. An artillery observer usually accompanies a tank or infantry unit. Spotters ensure that indirect fire hits targets which those at a fire support base cannot see.

A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by sending a laser pulse in a narrow beam towards the object and measuring the time taken by the pulse to be reflected off the target and returned to the sender. Due to the high speed of light, this technique is not appropriate for high precision sub-millimeter measurements, where triangulation and other techniques are often used. It is a type of scannerless lidar.

A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a human gunner firing a weapon, but attempts to do so faster and more accurately.

Gun laying is the process of aiming an artillery piece or turret, such as a gun, howitzer, or mortar, on land, in air, or at sea, against surface or aerial targets. It may be laying for direct fire, where the gun is aimed similarly to a rifle, or indirect fire, where firing data is calculated and applied to the sights. The term includes automated aiming using, for example, radar-derived target data and computer-controlled guns.

A keratometer, also known as an ophthalmometer, is a diagnostic instrument for measuring the curvature of the anterior surface of the cornea, particularly for assessing the extent and axis of astigmatism. It was invented by the German physiologist Hermann von Helmholtz in 1851, although an earlier model was developed in 1796 by Jesse Ramsden and Everard Home.

A height finder is a ground-based aircraft altitude measuring device. Early height finders were optical range finder devices combined with simple mechanical computers, while later systems migrated to radar devices. The unique vertical oscillating motion of height finder radars led to them also being known as nodding radar. Devices combining both optics and radar were deployed by the U.S. Military.
Base end stations were used by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps as part of fire control systems for locating the positions of attacking ships and controlling the firing of seacoast guns, mortars, or mines to defend against them. A British equivalent was the position finding cell.

A rangefinder is a device used to measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, such as photography, the military, and space travel. They were especially useful for finding the range of a target, such as in naval gunnery and anti-aircraft artillery. The word telemeter is derived from Ancient Greek τῆλε (têle) 'distant, far away', and μέτρον (métron) 'something used to measure'.

A director, also called an auxiliary predictor, is a mechanical or electronic computer that continuously calculates trigonometric firing solutions for use against a moving target, and transmits targeting data to direct the weapon firing crew.

A coincidence rangefinder or coincidence telemeter is a type of rangefinder that uses mechanical and optical principles to allow an operator to determine the distance to a visible object. There are subtypes split-image telemeter, inverted image, or double-image telemeter with different principles how two images in a single ocular are compared. Coincidence rangefinders were important elements of fire control systems for long-range naval guns and land-based coastal artillery circa 1890–1960. They were also used in rangefinder cameras.

Ship gun fire-control systems (GFCS) are analogue fire-control systems that were used aboard naval warships prior to modern electronic computerized systems, to control targeting of guns against surface ships, aircraft, and shore targets, with either optical or radar sighting. Most US ships that are destroyers or larger employed gun fire-control systems for 5-inch (127 mm) and larger guns, up to battleships, such as Iowa class.

In the U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps, the term fire control system was used to refer to the personnel, facilities, technology and procedures that were used to observe designated targets, estimate their positions, calculate firing data for guns directed to hit those targets, and assess the effectiveness of such fire, making corrections where necessary.

The 14-inch M1920 railway gun was the last model railway gun to be deployed by the United States Army. It was an upgrade of the US Navy 14"/50 caliber railway gun. Only four were deployed; two in the Harbor Defenses of Los Angeles and two in the Panama Canal Zone, where they could be shifted between the harbor defenses of Cristobal (Atlantic) or Balboa (Pacific).
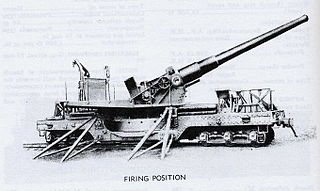
The 8-inch Navy gun Mk.VI M3A2 on railway mount M1A1 was a World War II improved replacement for the World War I-era 8-inch M1888 gun and was used by the US Army's Coast Artillery Corps in US harbor defenses. The guns were also mounted in fixed emplacements on the barbette carriage M1A1. These guns were US Navy surplus 8"/45 caliber guns from battleships scrapped under the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty. Mark VI was the Navy designation. The Army designation for this gun was "8-inch Navy gun Mk.VI M3A2".

The depression range finder (DRF) was a fire control device used to determine the target's position by observing range and bearing and to calculate firing solutions when gun laying in coastal artillery. It was the main component of a vertical base rangefinding system. It was necessitated by the introduction of rifled artillery from the mid-19th century onwards, which had much greater ranges than the old smoothbore weapons and were consequently more difficult to aim accurately. The DRF was invented by Captain H.S.S. Watkin of the Royal Artillery in the 1870s and was adopted in 1881. It could provide both range and bearing information on a target. The device's inventor also developed a family of similar devices, among them the position finder, which used two telescopes as a horizontal base rangefinding system, around the same time; some of these were called electric position finders. Some position finders retained a depression range finding capability; some of these were called depression position finders. Watkin's family of devices were deployed in position finding cells, a type of fire control tower, often in configurations that allowed both horizontal base and vertical base rangefinding. Watkin's system included automatic electrical updating of range and bearing dials near the guns as the position finders were manipulated, and a system of remotely firing the guns electrically from the position finding cell. The improved system was trialled in 1885 and widely deployed in the 1890s. Functionally equivalent devices were developed for the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps and its predecessors, called depression position finders or azimuth instruments depending on function, adopted in 1896 and deployed widely beginning in the early 1900s as the Endicott program of modern coastal defences was built. These devices were also used by both countries to control submarine (underwater) minefields.

A macroscope or photomacroscope in its camera-equipped version is a type of optical microscope developed and named by Swiss microscope manufacturers Wild Heerbrugg and later, after that company's merger with Leica in 1987, by Leica Microsystems of Germany, optimised for high quality macro photography and/or viewing using a single objective lens and light path, rather than stereoscopic viewing of specimens, at magnifications up to around x40. The Wild, subsequently Leica "macroscope" line was in production from approximately 1976–2003; it was succeeded by the Leica Z6 and Z16 offerings, which continued an equivalent functionality, but without the "macroscope" designation. The macroscope remains a useful, if somewhat specialised, instrument for examination of relevant specimens in various laboratories today.






















