
Armour-piercing ammunition (AP) is a type of projectile designed to penetrate either body armour or vehicle armour.

The 8.8 cm KwK 36 was an 88-millimetre (3.5 in) tank gun used by the German Army during World War II. This was the primary armament of the PzKpfw VI Tiger I tank. It was developed and built by Krupp.

The Panzerfaust was a development family of single-shot man-portable anti-tank systems developed by Nazi Germany during World War II. The weapons were the first single-use light anti-tank weapons based on a pre-loaded disposable launch tube, a weapon configuration which is still used today.

The 15 cm sIG 33 was the standard German heavy infantry gun used in the Second World War. It was the largest weapon ever classified as an infantry gun by any nation.

The RP-3 was a British air to ground rocket projectile introduced during the Second World War. The "3 inch" designation referred to the nominal diameter of the rocket motor tube. The use of a 60-pound (27 kg) warhead gave rise to the alternative name of the "60-pound rocket". Though primarily an air-to-ground weapon, it saw limited use in other roles. They were generally used by British fighter-bomber aircraft against targets such as tanks, trains, motor transport and buildings, as well as by Coastal Command and Royal Navy aircraft against U-boats and ships.

The 7.5 cm KwK 40(7.5 cm Kampfwagenkanone 40) was a German 75 mm Second World War era vehicle-mounted gun, used as the primary armament of the German Panzer IV medium tank and the Sturmgeschütz III and Sturmgeschütz IV tank destroyers/assault guns.

The 5 cm KwK 38 L/42(5 cm Kampfwagenkanone 38 L/42) was a German 50 mm calibre cannon used as the main armament of variants of the German Sd.Kfz. 141 Panzerkampfwagen III medium tank during the Second World War..

The 5 cm KwK 39 L/60(5 cm Kampfwagenkanone 39 L/60) was a German 50 mm calibre tank gun used during the Second World War, primarily as the main armament of later models of the German Panzer III tank from December 1941 onwards. It was produced when the well-armoured T-34 and KV-1 tanks were encountered in ever increasing numbers on the Eastern Front, although it was only partially successful in its role. It was later superseded by the 7.5 cm KwK 40 L/43.

The 2 inch medium trench mortar, also known as the 2-inch howitzer, and nicknamed the "toffee apple" or "plum pudding" mortar, was a British smooth bore muzzle loading (SBML) medium trench mortar in use in World War I from mid-1915 to mid-1917. The designation "2-inch" refers to the mortar barrel, into which only the 22-inch bomb shaft but not the bomb itself was inserted; the spherical bomb itself was actually 9 inches (230 mm) in diameter and weighed 42 lb (19 kg), hence this weapon is more comparable to a standard mortar of approximately 5-6 inch bore.

The 8.8 cm Raketenwerfer 43 Puppchen was an 88 mm calibre reusable anti-tank rocket launcher developed by Nazi Germany during World War II.

The Royal Ordnance L11A5, officially designated Gun 120 mm Tk L11, is a 120 mm L/55 rifled tank gun design. It was the first of NATO's 120 mm main battle tank guns which became the standard calibre for Western tanks in the later period of the Cold War. By 2005, a total of 3,012 L11 guns were produced. List price was US $227,000 (1990).

The 2A28 Grom is the main armament of the BMP-1 and BMD-1 infantry fighting vehicles. It is a 73 mm low pressure smoothbore semi-automatic gun with a wedge breech block. Development of the 2A28 Grom was directly linked to that of the SPG-9 recoilless gun; both fired projectiles similar to rocket-propelled grenades.

The Stielgranate 41 was a German shaped charge, fin-stabilized shell, used with the 3.7 cm Pak 36 anti-tank gun to give it better anti-tank performance.

The 30 cm Wurfkörper 42 Spreng was an unguided spin-stabilized artillery rocket developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.

The Gewehr-Granatpatrone 40 or GGP/40 for short was a shaped charge rifle grenade used by German forces during the Second World War. It was originally developed for Luftwaffe Fallschirmjäger units to provide them with a light and portable anti-tank weapon.
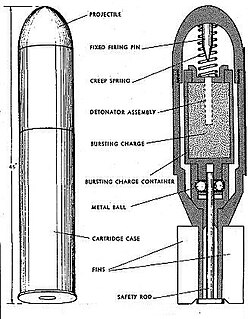
The Wurfgranate Patrone 326 was a small grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Wurfgranate Patrone 326 was designed to be fired from a Leuchtpistole or flare gun in English.

The AB 250-2(Abwurfbehälter) was a cluster bomb used by the Luftwaffe during World War II.
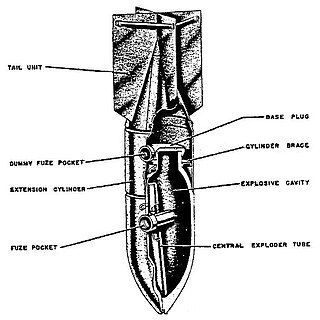
The SD 250 or thick walled explosive bomb in English was a fragmentation bomb used by the Luftwaffe during World War II.
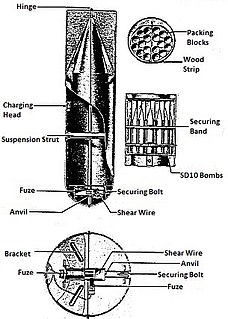
The AB 500-1(Abwurfbehälter) was a cluster bomb used by the Luftwaffe during World War II.

The 24 cm schwerer LadungsWerfer Ehrhardt shortened to 24 cm sLW Ehrhardt,('24 cm heavy charge thrower Ehrhardt' in English) was a heavy mortar used by the Imperial German Army during the First World War.




















