
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon, and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). The sulfur and carbon act as fuels while the saltpeter is an oxidizer. Gunpowder has been widely used as a propellant in firearms, artillery, rocketry, and pyrotechnics, including use as a blasting agent for explosives in quarrying, mining, building pipelines, tunnels, and roads.

A shell, in a military context, is a projectile whose payload contains an explosive, incendiary, or other chemical filling. Originally it was called a bombshell, but "shell" has come to be unambiguous in a military context. Modern usage sometimes includes large solid kinetic projectiles, which are more properly termed shot. Solid shot may contain a pyrotechnic compound if a tracer or spotting charge is used.

A smoke screen is smoke released to mask the movement or location of military units such as infantry, tanks, aircraft, or ships.

Early thermal weapons, which used heat or burning action to destroy or damage enemy personnel, fortifications or territories, were employed in warfare during the classical and medieval periods.
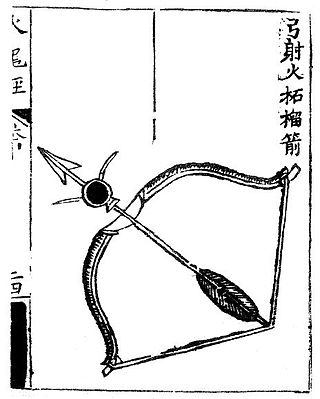
Fire arrows were one of the earliest forms of weaponized gunpowder, being used from the 9th century onward. Not to be confused with earlier incendiary arrow projectiles, the fire arrow was a gunpowder weapon which receives its name from the translated Chinese term huǒjiàn (火箭), which literally means fire arrow. In China a 'fire arrow' referred to a gunpowder projectile consisting of a bag of incendiary gunpowder attached to the shaft of an arrow. Fire arrows are the predecessors of fire lances, the first firearm.

The Battle of Caishi was a major naval engagement of the Jin–Song Wars of China that took place on November 26–27, 1161. It ended with a decisive Song victory, aided by their use of gunpowder weapons.

Royal Naval Dockyard, Halifax was a Royal Navy base in Halifax, Nova Scotia. Established in 1759, the Halifax Yard served as the headquarters for the Royal Navy's North American Station for sixty years, starting with the Seven Years' War. The Royal Navy continued to operate the station until it was closed in 1905. The station was sold to Canada in 1907 becoming His Majesty's Canadian Dockyard, a function it still serves today as part of CFB Halifax.

The Battle of Tangdao (唐岛之战) was a naval engagement that took place in 1161 between the Jurchen Jin and the Southern Song Dynasty of China on the East China Sea. The conflict was part of the Jin-Song wars, and was fought near Tangdao Island. It was an attempt by the Jin to invade and conquer the Southern Song Dynasty, yet resulted in failure and defeat for the Jurchens. The Jin Dynasty navy was set on fire by firearms and Fire Arrows, suffering heavy losses. For this battle, the commander of the Song Dynasty squadron, Li Bao, faced the opposing commander Zheng Jia, the admiral of the Jin Dynasty. On the fate of Zheng Jia, the historical text of the Jin Shi states:
Zheng Jia did not know the sea routes well, nor much about the management of ships, and he did not believe. But all of a sudden they appeared, and finding us quite unready they hurled incendiary gunpowder projectiles on to our ships. So seeing all his ships going up in flames, and having no means of escape, Zheng Jia jumped into the sea and drowned.

The Huolongjing, also known as Huoqitu, is a Chinese military treatise compiled and edited by Jiao Yu and Liu Bowen of the early Ming dynasty (1368–1683) during the 14th-century. The Huolongjing is primarily based on the text known as Huolong Shenqi Tufa, which no longer exists.

The Wujing Zongyao, sometimes rendered in English as the Complete Essentials for the Military Classics, is a Chinese military compendium written from around 1040 to 1044.

Gunpowder is the first explosive to have been developed. Popularly listed as one of the "Four Great Inventions" of China, it was invented during the late Tang dynasty while the earliest recorded chemical formula for gunpowder dates to the Song dynasty. Knowledge of gunpowder spread rapidly throughout Asia and Europe, possibly as a result of the Mongol conquests during the 13th century, with written formulas for it appearing in the Middle East between 1240 and 1280 in a treatise by Hasan al-Rammah, and in Europe by 1267 in the Opus Majus by Roger Bacon. It was employed in warfare to some effect from at least the 10th century in weapons such as fire arrows, bombs, and the fire lance before the appearance of the gun in the 13th century. While the fire lance was eventually supplanted by the gun, other gunpowder weapons such as rockets and fire arrows continued to see use in China, Korea, India, and this eventually led to its use in the Middle East, Europe, and Africa. Bombs too never ceased to develop and continued to progress into the modern day as grenades, mines, and other explosive implements. Gunpowder has also been used for non-military purposes such as fireworks for entertainment, or in explosives for mining and tunneling.

His Majesty's Naval Base, Devonport is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy and is the sole nuclear repair and refuelling facility for the Royal Navy. The largest naval base in Western Europe, HMNB Devonport is located in Devonport, in the west of the city of Plymouth, England.
William Mounsey CB was a British officer of the Royal Navy. He served during the American Revolutionary, the French Revolutionary and the Napoleonic Wars, rising to the rank of Captain.
John Pratt, pen name John Winton was an English author and obituarist, following a career in the Royal Navy in which he rose to Lieutenant-Commander. He was born in London and served in the Korean War and during the Suez Crisis. Whilst still in the Navy, he wrote the comic novel We Joined the Navy, featuring the character of "The Artful Bodger". Several other novels, and a number of non-fiction works on naval subjects, followed, including a biography of Admiral John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe. Pratt also served for 14 years as an obituarist for The Daily Telegraph.

Admiral Sir William Robert Kennedy was a Royal Navy officer who served as Commander-in-Chief, The Nore.
Gunpowder weapons in the Song dynasty included fire arrows, gunpowder lit flamethrowers, soft shell bombs, hard shell iron bombs, fire lances, and possibly early cannons known as "eruptors". The eruptors, such as the "multiple bullets magazine eruptors", consisting of a tube of bronze or cast iron that was filled with about 100 lead balls, and the "flying-cloud thunderclap eruptor", were early cast-iron proto-cannons that did not include single shots that occluded the barrel. The use of proto-cannon, and other gunpowder weapons, enabled the Song dynasty to ward off its generally militarily superior enemies—the Khitan led Liao, Tangut led Western Xia, and Jurchen led Jin—until its final collapse under the onslaught of the Mongol forces of Kublai Khan and his Yuan dynasty in the late 13th century.

The Battle of Canton was fought between British and Chinese forces at the city of Canton (Guangzhou), Guangdong province, China on 23 October to 5 November 1856 during the Second Opium War.
This is a timeline of the history of gunpowder and related topics such as weapons, warfare, and industrial applications. The timeline covers the history of gunpowder from the first hints of its origin as a Taoist alchemical product in China until its replacement by smokeless powder in the late 19th century.
This is an overview of Chinese siege weapons.













