Immunoglobulin G is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG antibody has two paratopes.

Histopathology refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments.
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD), including neuromyelitis optica (NMO), are autoimmune diseases characterized by acute inflammation of the optic nerve and the spinal cord (myelitis). Episodes of ON and myelitis can be simultaneous or successive. A relapsing disease course is common, especially in untreated patients. In more than 80% of cases, NMO is caused by immunoglobulin G autoantibodies to aquaporin 4 (anti-AQP4), the most abundant water channel protein in the central nervous system. A subset of anti-AQP4-negative cases is associated with antibodies against myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (anti-MOG). Rarely, NMO may occur in the context of other autoimmune diseases or infectious diseases. In some cases, the etiology remains unknown.

Parotitis is an inflammation of one or both parotid glands, the major salivary glands located on either side of the face, in humans. The parotid gland is the salivary gland most commonly affected by inflammation.

Trichobilharzia regenti is a neuropathogenic parasitic flatworm of birds which also causes cercarial dermatitis in humans. The species was originally described in 1998 in the Czech Republic and afterwards it was detected also in other European countries, e.g. Denmark, Germany, France, Iceland, Poland, Switzerland, or Russia, and even in Iran. For its unique neurotropic behaviour in vertebrate hosts, the host-parasite interactions are extensively studied in terms of molecular biology, biochemistry and immunology.

Benign lymphoepithelial lesion or Mikulicz' disease is a type of benign enlargement of the parotid and/or lacrimal glands. This pathologic state is sometimes, but not always, associated with Sjögren's syndrome.
Autoimmune Pancreatitis (AIP) is an increasingly recognized type of chronic pancreatitis that can be difficult to distinguish from pancreatic carcinoma but which responds to treatment with corticosteroids, particularly prednisone. Although autoimmune pancreatitis is quite rare, it constitutes an important clinical problem for both patients and their clinicians: the disease commonly presents itself as a tumorous mass which is diagnostically indistinguishable from pancreatic cancer, a disease that is much more common in addition to being very dangerous. Hence, some patients undergo pancreatic surgery, which is associated to substantial mortality and morbidity, out of the fear by patients and clinicians to undertreat a malignancy. However, surgery is not a good treatment for this condition as AIP responds well to immunosuppressive treatment. There are two categories of AIP: Type 1 and Type 2, each with distinct clinical profiles.
Riedel's thyroiditis, is a chronic form of thyroiditis. It is now believed that Riedel's thyroiditis is one manifestation of a systemic disease that can affect many organ systems called IgG4-related disease. It is often a multi-organ disease affecting pancreas, liver, kidney, salivary and orbital tissues and retroperitoneum. The hallmarks of the disease are fibrosis and infiltration by IgG4 secreting plasma cells.
Aortitis is the inflammation of the aortic wall. The disorder is potentially life-threatening and rare. It is reported that there are only 1–3 new cases of aortitis per year per million people in the United States and Europe. Aortitis is most common in people 10 to 40 years of age.

Kimura's disease is a benign rare chronic inflammatory disorder. Its primary symptoms are subdermal lesions in the head or neck or painless unilateral inflammation of cervical lymph nodes.

Multifocal fibrosclerosis and idiopathic fibrosclerosis are disorders of unknown aetiology, characterised by fibrous lesions (co-)occurring at a variety of sites. Known manifestations include retroperitoneal fibrosis, mediastinal fibrosis and Riedel's thyroiditis.

IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), formerly known as IgG4-related systemic disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by tissue infiltration with lymphocytes and IgG4-secreting plasma cells, various degrees of fibrosis (scarring) and a usually prompt response to oral steroids. In approximately 51–70% of people with this disease, serum IgG4 concentrations are elevated during an acute phase.
Plasma cell granulomas (PCGs) are uncommon, non-neoplastic lesions of unknown etiology and are considered an entity of IgG4-related diseases.

Salivary gland diseases (SGDs) are multiple and varied in cause. There are three paired major salivary glands in humans – the parotid glands, the submandibular glands, and the sublingual glands. In addition there are about 800-1000 minor salivary glands in the mucosa of the mouth. The parotid gland is located in front of each ear, and secretes mostly serous saliva via the parotid duct into the mouth, usually opening roughly opposite the maxillary second molar. The submandibular gland is located medial to the angle of the mandible, and it drains its mixture of serous and mucous saliva via the submandibular duct into the mouth, usually opening in a punctum located in the floor of mouth. The sublingual gland is located below the tongue, on the floor of the mouth. It drains its mostly mucous saliva into the mouth via about 8-20 ducts which open along the plica sublingualis.
Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis is a chronic (long-lasting) inflammatory condition affecting the salivary gland. Relatively rare in occurrence, this condition is benign, but presents as hard, indurated and enlarged masses that are clinically indistinguishable from salivary gland neoplasms or tumors. It is now regarded as a manifestation of IgG4-related disease.
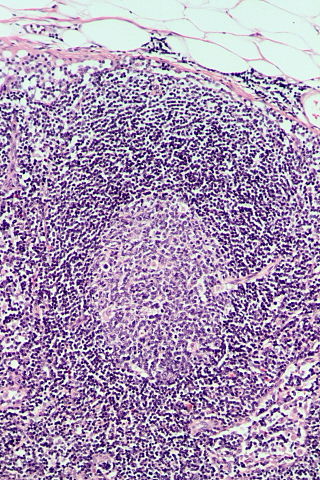
Follicular hyperplasia (FH) is a type of lymphoid hyperplasia and is classified as a lymphadenopathy, which means a disease of the lymph nodes. It is caused by a stimulation of the B cell compartment and by abnormal cell growth of secondary follicles. This typically occurs in the cortex without disrupting the lymph node capsule. The follicles are pathologically polymorphous, are often contrasting and varying in size and shape. Follicular hyperplasia is distinguished from follicular lymphoma in its polyclonality and lack of bcl-2 protein expression, whereas follicular lymphoma is monoclonal, and expresses bcl-2.

IgG4-related prostatitis is prostate involvement in men with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), which is an emerging fibroinflammatory disease entity which is characterised (i) by a tendency to mass forming lesions in multiple sites of the body and (ii) by usually a prompt response to steroid therapy.

IgG4-related ophthalmic disease (IgG4-ROD) is the recommended term to describe orbital manifestations of the systemic condition IgG4-related disease, which is characterised by infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells and subsequent fibrosis in involved structures. It can involve one or more of the orbital structures.
IgG4-related skin disease is the recommended name for skin manifestations in IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). Multiple different skin manifestations have been described.

A cartwheeel pattern pattern is a histopathologic architectural pattern. Microscopically, cartwheel arrangements appear to have center points that radiate cells or connective tissue outward. Cartwheel patterns may be irregular and, at lower magnification, can cause tissue to appear tangled into clumps.











