Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to obtain a desired amplification in the output force. The model for this is the law of the lever. Machine components designed to manage forces and movement in this way are called mechanisms. An ideal mechanism transmits power without adding to or subtracting from it. This means the ideal machine does not include a power source, is frictionless, and is constructed from rigid bodies that do not deflect or wear. The performance of a real system relative to this ideal is expressed in terms of efficiency factors that take into account departures from the ideal.

A tandem bicycle or twin is a form of bicycle designed to be ridden by more than one person. The term tandem refers to the seating arrangement, not the number of riders. Patents related to tandem bicycles date from the mid 1880s. Tandems can reach higher speeds than the same riders on single bicycles, and tandem bicycle racing exists. As with bicycles for single riders, there are many variations that have been developed over the years.

An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type of axle is referred to as a spindle.

A tricycle, sometimes abbreviated to trike, is a human-powered three-wheeled vehicle.

A bicycle brake reduces the speed of a bicycle or prevents the wheels from moving. The two main types are: rim brakes and disc brakes. Drum brakes are less common on bicycles.

The crankset or chainset is the component of a bicycle drivetrain that converts the reciprocating motion of the rider's legs into rotational motion used to drive the chain or belt, which in turn drives the rear wheel. It consists of one or more sprockets, also called chainrings or chainwheels attached to the cranks, arms, or crankarms to which the pedals attach. It is connected to the rider by the pedals, to the bicycle frame by the bottom bracket, and to the rear sprocket, cassette or freewheel via the chain.

A crank is an arm attached at a right angle to a rotating shaft by which circular motion is imparted to or received from the shaft. When combined with a connecting rod, it can be used to convert circular motion into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The arm may be a bent portion of the shaft, or a separate arm or disk attached to it. Attached to the end of the crank by a pivot is a rod, usually called a connecting rod (conrod).

The bottom bracket on a bicycle connects the crankset (chainset) to the bicycle and allows the crankset to rotate freely. It contains a spindle to which the crankset attaches, and the bearings that allow the spindle and crankset to rotate. The chainrings and pedals attach to the cranks. Bottom bracket bearings fit inside the bottom bracket shell, which connects the seat tube, down tube and chain stays as part of the bicycle frame.

A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission, or stick shift, is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission system, where gear changes require the driver to manually select the gears by operating a gear stick and clutch.
In mechanical engineering, an eccentric is a circular disk solidly fixed to a rotating axle with its centre offset from that of the axle.

A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft, propeller shaft, or Cardan shaft is a component for transmitting mechanical power, torque, and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them.

A swingarm, or "swinging arm" (UK), originally known as a swing fork or pivoted fork, is a single or double sided mechanical device which attaches the rear wheel of a motorcycle to its body, allowing it to pivot vertically. The main component of the rear suspension of most modern motorbikes and ATVs, it holds the rear axle firmly, while pivoting to absorb bumps and suspension loads induced by the rider, acceleration, and braking.

An elliptical trainer or cross-trainer is a stationary exercise machine used to stair climb, walk, or run without causing excessive pressure to the joints, hence decreasing the risk of impact injuries. For this reason, people with some injuries can use an elliptical to stay fit, as the low impact affects them little. Elliptical trainers offer a non-impact cardiovascular workout that can vary from light to high intensity based on the speed of the exercise and the resistance preference set by the user.
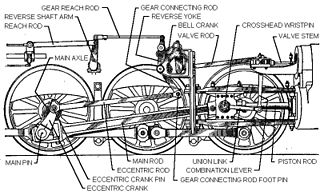
After about 1910, the Baker valve gear was the main competitor to Walschaerts valve gear for steam locomotives in the United States. Strictly speaking it was not a valve gear but a variable expansion mechanism adapted to the Walschaerts layout replacing the expansion link and sliding die block. The Baker arrangement used more pivot bearings or pin joints, but avoided the die slip inherent to the expansion link, with the aim of lessening wear and the need for service; it could also facilitate longer valve travel.

A rowbike is an example of a rowing cycle, hybrid fitness/transport machine that combines a bicycle, and a rowing machine. "Rowbike" is a trademark of the Rowbike company. The Rowbike was invented by Scott Olson, the creator of Rollerblade inline skates. "Rowling" is a combination of rowing and rolling, and is sometimes used in place of rowing when describing a Rowbike.

The Meillerwagen was a German World War II trailer used to transport a V-2 rocket from the 'transloading point' of the Technical Troop Area to the launching point, to erect the missile on the Brennstand, and to act as the service gantry for fuelling and launch preparation.

Bicycle drivetrain systems are used to transmit power on bicycles, tricycles, quadracycles, unicycles, or other human-powered vehicles from the riders to the drive wheels. Most also include some type of a mechanism to convert speed and torque via gear ratios.
This glossary of automotive terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related to automobiles, including their parts, operation, and manufacture, as well as automotive engineering, auto repair, and the automotive industry in general. For more specific terminology regarding the design and classification of various automobile styles, see Glossary of automotive design; for terms related to transportation by road, see Glossary of road transport terms; for competitive auto racing, see Glossary of motorsport terms.















