
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye. There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy, along with the emerging field of X-ray microscopy.

The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly invented in their present compound form in the 17th century. Basic optical microscopes can be very simple, although many complex designs aim to improve resolution and sample contrast.

In optics, any optical instrument or system – a microscope, telescope, or camera – has a principal limit to its resolution due to the physics of diffraction. An optical instrument is said to be diffraction-limited if it has reached this limit of resolution performance. Other factors may affect an optical system's performance, such as lens imperfections or aberrations, but these are caused by errors in the manufacture or calculation of a lens, whereas the diffraction limit is the maximum resolution possible for a theoretically perfect, or ideal, optical system.

Immunofluorescence(IF) is a light microscopy-based technique that allows detection and localization of a wide variety of target biomolecules within a cell or tissue at a quantitative level. The technique utilizes the binding specificity of antibodies and antigens. The specific region an antibody recognizes on an antigen is called an epitope. Several antibodies can recognize the same epitope but differ in their binding affinity. The antibody with the higher affinity for a specific epitope will surpass antibodies with a lower affinity for the same epitope.

A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. "Fluorescence microscope" refers to any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a simple set up like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image.

Confocal microscopy, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) or laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of using a spatial pinhole to block out-of-focus light in image formation. Capturing multiple two-dimensional images at different depths in a sample enables the reconstruction of three-dimensional structures within an object. This technique is used extensively in the scientific and industrial communities and typical applications are in life sciences, semiconductor inspection and materials science.
Super-resolution imaging (SR) is a class of techniques that enhance (increase) the resolution of an imaging system. In optical SR the diffraction limit of systems is transcended, while in geometrical SR the resolution of digital imaging sensors is enhanced.
RESOLFT, an acronym for REversible Saturable OpticaLFluorescence Transitions, denotes a group of optical fluorescence microscopy techniques with very high resolution. Using standard far field visible light optics a resolution far below the diffraction limit down to molecular scales can be obtained.

Ptychography is a computational method of microscopic imaging. It generates images by processing many coherent interference patterns that have been scattered from an object of interest. Its defining characteristic is translational invariance, which means that the interference patterns are generated by one constant function moving laterally by a known amount with respect to another constant function. The interference patterns occur some distance away from these two components, so that the scattered waves spread out and "fold" into one another as shown in the figure.

Vertico spatially modulated illumination (Vertico-SMI) is the fastest light microscope for the 3D analysis of complete cells in the nanometer range. It is based on two technologies developed in 1996, SMI and SPDM. The effective optical resolution of this optical nanoscope has reached the vicinity of 5 nm in 2D and 40 nm in 3D, greatly surpassing the λ/2 resolution limit applying to standard microscopy using transmission or reflection of natural light according to the Abbe resolution limit That limit had been determined by Ernst Abbe in 1873 and governs the achievable resolution limit of microscopes using conventional techniques.

Optical sectioning is the process by which a suitably designed microscope can produce clear images of focal planes deep within a thick sample. This is used to reduce the need for thin sectioning using instruments such as the microtome. Many different techniques for optical sectioning are used and several microscopy techniques are specifically designed to improve the quality of optical sectioning.
Super-resolution microscopy is a series of techniques in optical microscopy that allow such images to have resolutions higher than those imposed by the diffraction limit, which is due to the diffraction of light. Super-resolution imaging techniques rely on the near-field or on the far-field. Among techniques that rely on the latter are those that improve the resolution only modestly beyond the diffraction-limit, such as confocal microscopy with closed pinhole or aided by computational methods such as deconvolution or detector-based pixel reassignment, the 4Pi microscope, and structured-illumination microscopy technologies such as SIM and SMI.
Photo-activated localization microscopy and stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) are widefield fluorescence microscopy imaging methods that allow obtaining images with a resolution beyond the diffraction limit. The methods were proposed in 2006 in the wake of a general emergence of optical super-resolution microscopy methods, and were featured as Methods of the Year for 2008 by the Nature Methods journal. The development of PALM as a targeted biophysical imaging method was largely prompted by the discovery of new species and the engineering of mutants of fluorescent proteins displaying a controllable photochromism, such as photo-activatible GFP. However, the concomitant development of STORM, sharing the same fundamental principle, originally made use of paired cyanine dyes. One molecule of the pair, when excited near its absorption maximum, serves to reactivate the other molecule to the fluorescent state.
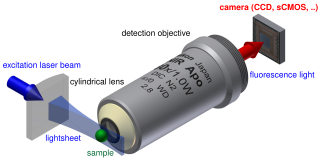
Light sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) is a fluorescence microscopy technique with an intermediate-to-high optical resolution, but good optical sectioning capabilities and high speed. In contrast to epifluorescence microscopy only a thin slice of the sample is illuminated perpendicularly to the direction of observation. For illumination, a laser light-sheet is used, i.e. a laser beam which is focused only in one direction. A second method uses a circular beam scanned in one direction to create the lightsheet. As only the actually observed section is illuminated, this method reduces the photodamage and stress induced on a living sample. Also the good optical sectioning capability reduces the background signal and thus creates images with higher contrast, comparable to confocal microscopy. Because light sheet fluorescence microscopy scans samples by using a plane of light instead of a point, it can acquire images at speeds 100 to 1,000 times faster than those offered by point-scanning methods.

Live-cell imaging is the study of living cells using time-lapse microscopy. It is used by scientists to obtain a better understanding of biological function through the study of cellular dynamics. Live-cell imaging was pioneered in the first decade of the 21st century. One of the first time-lapse microcinematographic films of cells ever made was made by Julius Ries, showing the fertilization and development of the sea urchin egg. Since then, several microscopy methods have been developed to study living cells in greater detail with less effort. A newer type of imaging using quantum dots have been used, as they are shown to be more stable. The development of holotomographic microscopy has disregarded phototoxicity and other staining-derived disadvantages by implementing digital staining based on cells’ refractive index.
Lattice light-sheet microscopy is a modified version of light sheet fluorescence microscopy that increases image acquisition speed while decreasing damage to cells caused by phototoxicity. This is achieved by using a structured light sheet to excite fluorescence in successive planes of a specimen, generating a time series of 3D images which can provide information about dynamic biological processes.
Wide-field multiphoton microscopy refers to an optical non-linear imaging technique tailored for ultrafast imaging in which a large area of the object is illuminated and imaged without the need for scanning. High intensities are required to induce non-linear optical processes such as two-photon fluorescence or second harmonic generation. In scanning multiphoton microscopes the high intensities are achieved by tightly focusing the light, and the image is obtained by beam scanning. In wide-field multiphoton microscopy the high intensities are best achieved using an optically amplified pulsed laser source to attain a large field of view (~100 μm). The image in this case is obtained as a single frame with a CCD without the need of scanning, making the technique particularly useful to visualize dynamic processes simultaneously across the object of interest. With wide-field multiphoton microscopy the frame rate can be increased up to a 1000-fold compared to multiphoton scanning microscopy. Wide-field multiphoton microscopes are not yet commercially available, but working prototypes exist in several optics laboratories.
Super-resolution dipole orientation mapping (SDOM) is a form of fluorescence polarization microscopy (FPM) that achieved super resolution through polarization demodulation. It was first described by Karl Zhanghao and others in 2016. Fluorescence polarization (FP) is related to the dipole orientation of chromophores, making fluorescence polarization microscopy possible to reveal structures and functions of tagged cellular organelles and biological macromolecules. In addition to fluorescence intensity, wavelength, and lifetime, the fourth dimension of fluorescence—polarization—can also provide intensity modulation without the restriction to specific fluorophores; its investigation in super-resolution microscopy is still in its infancy.
Super-resolution photoacoustic imaging is a set of techniques used to enhance spatial resolution in photoacoustic imaging. Specifically, these techniques primarily break the optical diffraction limit of the photoacoustic imaging system. It can be achieved in a variety of mechanisms, such as blind structured illumination, multi-speckle illumination, or photo-imprint photoacoustic microscopy in Figure 1.
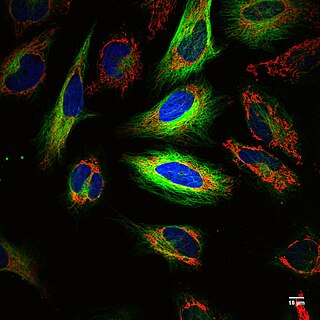
Fluorescence imaging is a type of non-invasive imaging technique that can help visualize biological processes taking place in a living organism. Images can be produced from a variety of methods including: microscopy, imaging probes, and spectroscopy.




















