Related Research Articles
Rimau-rimau is a two-player abstract strategy board game that belongs to the hunt game family. This family includes games like Bagh-Chal, Main Tapal Empat, Aadu puli attam, Catch the Hare, Sua Ghin Gnua, the Fox games, Buga-shadara, and many more. Rimau-rimau is the plural of rimau which is an abbreviation of the word harimau which means "tiger" in the Malay language. Therefore, rimau-rimau means "tigers". The several hunters attempting to surround and immobilize the tigers are called orang-orang which is the plural of orang which means "man". Therefore, orang-orang means "men" and there are twenty-two or twenty-four of them depending on which version of the game is played. The game originates from Malaysia.
Main tapal empat is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Malaysia. It is a hunt game, and specifically a tiger hunt game since it uses an Alquerque board. The tigers can move as many spaces in a straight line as a clear path allows. Most hunt games have tigers, leopards, or foxes moving only one space at a time. In effect, the tigers in this game have the movement capability of the queen in chess.

Adugo is a two-player abstract strategy game that comes from the Bororo tribe on the Pantanal region of Brazil.
Dash-guti is a two-player abstract strategy board game from India, specifically from Central Provinces, United Provinces, Karwi Subdivision where it is called Kowwu Dunki which is the same name given to another similar game called Lau kata kati, and it was described by H.J.R. Murray in A History of Board-Games Other Than Chess (1952). The game is related to Draughts and even more so to Alquerque. Pieces are captured by leaping over them. Dash-guti consists of a Lau kata kati board, but with the addition of two line segments connected to the vertex but exterior to both triangles. Dash-guti belongs to a specific category of games called Indian War-games, and the other games in this category are Lau kata kati, Egara-guti, Pretwa, Gol-skuish. All Indian War-games have one important thing in common, and that is that all the pieces are laid out on the grid patterned board, with only one vacant point in the centre. This forces the first move to be played on the central point, and captured by the other player's piece.
Hare games are two-player abstract strategy board games that were popular in medieval northern Europe up until the 19th century. In this game, a hare is trying to get past three dogs who are trying to surround it and trap it. The three dogs are represented by three pieces which normally start on one end of the board, and the hare is represented by one piece that usually starts in the middle of the board or is dropped on any vacant point in the beginning of the game.

Komikan is a two-player abstract strategy board game of the Mapuches from Chile and Argentina. The same game is also played by the Incas under the name Taptana, Komina, Comina, Cumi, Puma, or Inca Chess. In modern Quechua, the language of the ethnolinguistic group that are the descendants of the Incas, Taptana means "chess". It is known by the Aymaras, a neighboring ethnolinguistic group to the Quechuan people, as kumisiña. Throughout South America the game is known as El león y las ovejas which literally means "the lion and the sheep". The lion is actually a puma as there are no lions native to the Americas. The Mapuches also call it El Leoncito. J. I. Molina, in 1787, described it as ‘el artificioso juego del ajedrez, al cual dan el nombre de comican’ which translates to "the ingenious game of chess to which they give the name comican". Komikan may actually be the same game as Adugo as played by the Bororó people of Brazil. in 1898, Stewart Culin, the famed anthropologist, named a game played in Peru as Solitario. The same name was also used by the game historian, Murray, in 1952. The game may also be known in Peru as Kukuli. Komikan is a hunt game, and specifically a tiger hunt game since it uses an expanded Alquerque board. Like all hunt games, there are two unequal forces at play. In Komikan, one player has only a single piece, usually called a "puma" or "jaguar", or "kom ikelu", or "leon", which can move one space at a time or capture the other player's pieces by hopping over them. The other player has twelve pieces, or perros or perritos which is Spanish for "dogs" and "little dogs" respectively, that can only move one space at a time, but not capture, and attempts only to surround and immobilize the puma or jaguar. Pieces must move and/or capture following the pattern on the board. The expanded Alquerque board consist of an Alquerque board and a triangular patterned board attached on one of its side.
Rimau is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Malaysia. It is a hunt game, and specifically a tiger hunt game since it uses an expanded Alquerque board. The one tiger is being hunted by 24 men. The tiger attempts to eat the men, and the men attempt to trap the tiger. An interesting feature in this game is that the tiger can capture a line of men in a single leap. There must be an odd number of men in the line, and they must be adjacent to one another. In most hunt games, the tiger, leopard, or fox is only able to capture one prey in a leap.

Buga-shadara, also known as Bouge Shodre, is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Tuva, a republic in Siberia, Russia. It is a hunt game where one player plays the deers. There are two deers usually represented as the black pieces. The boars are also referred black in the referenced article "Buga-shadara a folk game from Tuva". The other player has 24 white pieces with dogs associated to them. The board consist of an Alquerque board flanked on two of its opposite sides by a square patterned board. Because the board is in part an Alquerque board, this makes Buga-shadara a tiger hunt game. What makes Buga-shadara unique among tiger games are the expansion boards on the two opposite sides of the Alquerque board. They are square, whereas most are triangle-like. The word "shadara" resembles the word "shahdara". The "shah" part "is a title given to the emperors/kings and lords of Iran .". There is a place called Shahdara Bagh in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan, and it's thought that the word "Shahdara can be translated as "the way of kings". Shah translates as "king" and dara translates as the way of kings." The referenced article associates the boars as kings. Perhaps the boars or deers are kings, and have to find a way or have a way with the white pieces or dogs.
Sher-bakar is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Punjab, India. It is a hunt game. It uses an Alquerque board, and therefore, Sher-bakar is specifically a tiger hunt game. There are two tigers attempting to elude and capture as many of the other player's pieces which in other hunt games in this part of the world is often referred to as a goat, cows, lamb, or men. An interesting and uncommon feature in this game is that the goats, cows, lamb, or men are piled up on four points of the board at the beginning of the game. Piling up pieces is an unusual feature in hunt games or any board game in general. The only other hunt game that uses this feature is Bagh bandi, a game closely related to Sher-bakar. Hereinforth, the white pieces will be referred to as goats.
Bagh bandi is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Lower Bengal, India. It is a hunt game. It uses an Alquerque board, and therefore, Bagh bandi is specifically a tiger hunt game. There are two tigers attempting to elude and capture as many goats while the goats are attempting to surround and trap the tigers.
Liberian Queah is a two-player abstract strategy game from Liberia. It is specifically from the Queah tribe. The game is played on a slanted or diagonal square board with only 13 spaces. Pieces move "orthogonally" along these slanted or diagonal square boards. Another unique feature is that each player must have four pieces on the board. Each player's captured piece is resupplied at the beginning of their next turn with a piece from their reserve.
Catch the Hare is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Europe, and perhaps specifically from Spain. It is a hunt game, and since it uses a standard Alquerque board from the game Alquerque de Doze, it is specifically a tiger hunt game. In some variants, some or all of the diagonal lines are missing which makes it difficult to classify as a tiger game in general. One hare is going up against ten to twelve opponents(hunters or hounds). The hare is the "tiger" in this hunt game which is prey and predator at the same time. The hare can capture the opponents by leaping over them. The opponents attempt to surround and trap the hare.
Kharbaga is a two-player abstract strategy game from North Africa. In a way, it is a miniature version of Zamma; however, there are more diagonal lines per square on the board as compared to Zamma. The game is considered part of the Zamma family. The game is also similar to Alquerque and draughts. The board is essentially an Alquerque board with twice the number of diagonal lines or segments allowing for greater freedom of movement. The initial setup is also similar to Alquerque, where every space on the board is filled with each player's pieces except for the middle point of the board. Moreover, each player's pieces are also set up on each player's half of the board. The game specifically resembles draughts in that pieces must move in the forward directions until they are crowned "Mullah" which is the equivalent of the King in draughts. The Mullah can move in any direction.
High Jump is a two-player strategy board game from Somalia. It is related to draughts and Alquerque as pieces hop over one another for capture; however, pieces move and capture orthogonally and not diagonally. Moreover, the game is played on a 5×5 square board. A feature of High Jump is that the central square offers a kind of sanctuary; a piece occupying the central square cannot be hopped over and captured. The same board is used in the game Seega.
Awithlaknannai Mosona is a two-player strategy board game from the Zuni Native American Indian tribe of New Mexico, United States. It is unknown how old the game is. The game was described by Stewart Culin in his book "Games of the North American Indians Volume 2: Games of Skill" (1907). In this book, it was named Awithlaknan Mosona. Awithlaknannai Mosona resembles another Zuni board game called Kolowis Awithlaknannai with few minor differences. The former having a smaller board, and depending upon the variant, it also has less lines joining the intersection points. The rules are the same. Awithlaknannai Mosona belongs to the draughts and Alquerque family of games as pieces hop over one another when capturing. It is actually more related to Alquerque, since the board is made up of intersection points and lines connecting them. It is thought that the Spanish had brought Alquerque to the American Southwest, and Awithlaknannai Mosona may have been an evolution from Alquerque. However, in Stewart Culin's 1907 book, the Zunis claim that they had adopted a hunt game from Mexico similar to Catch the Hare and the Fox games of Europe, and transformed it into Awithlaknannai Mosona. In these games, one player has more pieces over the other, however, the other player's piece has more powers. The Zuni's equalized the numbers of pieces and their powers, and also may have transformed the board making its length far exceed its width. Diagonal lines also replaced orthogonal lines altogether. However, the hunt game from Mexico may have used an Alquerque board even though the game mechanics of their new game, Awithlaknannai Mosona, were completely different.
Indian and jackrabbits is a two-player abstract strategy board game from the Tiwa tribe of Taos, New Mexico. A similar game with a slightly different board is also played by the Tohono O'odham tribe of Arizona. From the outset, these games look like hunt games similar to Catch the Hare, the Fox games of Europe, and the tiger and leopard games of Asia, because they use very similar boards, and the game mechanics are the same, and the number of pieces each player controls is different. However, they are not the same games, because the goals are completely different. The goal of the one Indian is to capture just one of the twelve jackrabbits. The goal of the jackrabbits is to move themselves safely onto the other side of the board mirroring their initial positions.
Tiger and buffaloes is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Myanmar. It belongs to the hunt game family. The board is a 4x4 square grid, where pieces are placed on the intersection points and move along the lines. It is one of the smallest hunt games. Three tigers are going up against eleven buffaloes. The tigers attempt to capture as many of the buffaloes by the short leap as in draughts or Alquerque. The buffaloes attempt to hem in the tigers.
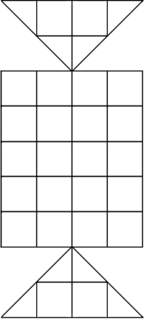
Astar is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Kyrgyzstan. It is a game similar to draughts and Alquerque as players hop over one another's pieces when capturing. However, unlike draughts and Alquerqe, Astar is played on 5x6 square grid with two triangular boards attached on two opposite sides of the grid. The board somewhat resembles those of Kotu Ellima, Sixteen Soldiers, and Peralikatuma, all of which are games related to Astar. However, these three games use an expanded Alquerque board with a 5x5 square grid with diagonal lines. Astar uses a 5x6 grid with no diagonal lines.

Chesquerque is a chess variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a board equaling four Alquerque boards combined, and like Alquerque, pieces move along marked lines (9×9) to the points of intersection. All the standard chess pieces are present, plus one additional pawn and one archbishop fairy piece per side. The pieces move in ways specially adapted to the Alquerque-gridded board.
References
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
This article includes a list of general references, but it remains largely unverified because it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(January 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
- 1 2 Murray, H.J.R. (2012). A History of Chess: The Original 1913 Edition. New York, NY: First Skyhorse Publishing edition. p. 136. ISBN 978-1-63220-293-2 . Retrieved 14 July 2016.
- 1 2 Culin, Stewart (1898). Chess and Playing-Cards: Catalogue of Games and Implements for Divination Exhited by the United States National Museum in Connection with the Department of Archaeology and Paleontology of the University of Pennsylvania at the Cotton States and International Exposition, Atlanta, Georgia 1895. Washington: Government Printing Office. p. 876. Retrieved 13 July 2016.
- ↑ Bell, Robert Charles (1979). Board and Table Games from Many Civilizations, Volumes 1-2 (Corrected ed.). New York: Dover Publications, Inc. p. 42. ISBN 0-486-23855-5 . Retrieved 13 July 2016.