
The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.
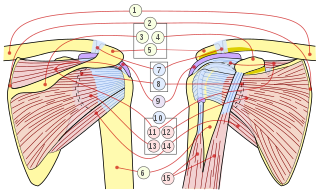
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are:

The axillary nerve or the circumflex nerve is a nerve of the human body, that originates from the brachial plexus at the level of the axilla (armpit) and carries nerve fibers from C5 and C6. The axillary nerve travels through the quadrangular space with the posterior circumflex humeral artery and vein to innervate the deltoid and teres minor.

The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula, and the humerus as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons.

The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle appears to be made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part
- posterior or scapular part
- intermediate or acromial part

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the arm, forearm and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects.

A synovial bursa, usually simply bursa, is a small fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane with an inner capillary layer of viscous synovial fluid. It provides a cushion between bones and tendons and/or muscles around a joint. This helps to reduce friction between the bones and allows free movement. Bursae are found around most major joints of the body.

In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspinatus is to externally rotate the humerus and stabilize the shoulder joint.

The shoulder joint is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus. Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body.

The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the shoulder-joint.

The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of the clavicle, scapula, and coracoid. Some mammalian species have only the scapula.

The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a bone part of the shoulder. The word glenoid is pronounced or and is from Greek: gléne, "socket", reflecting the shoulder joint's ball-and-socket form. It is a shallow, pyriform articular surface, which is located on the lateral angle of the scapula. It is directed laterally and forward and articulates with the head of the humerus; it is broader below than above and its vertical diameter is the longest.

The coracohumeral ligament is a broad ligament of the shoulder. It attaches to the coracoid process at one end, and to the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus at the other. It strengthens the upper part of the joint capsule of the shoulder joint.
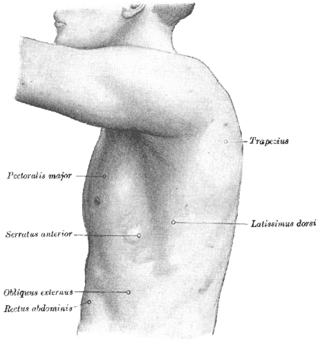
A winged scapula is a skeletal medical condition in which the shoulder blade protrudes from a person's back in an abnormal position.

Shoulder replacement is a surgical procedure in which all or part of the glenohumeral joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant. Such joint replacement surgery generally is conducted to relieve arthritis pain or fix severe physical joint damage.

The subacromial bursa is the synovial cavity located just below the acromion, which communicates with the subdeltoid bursa in most individuals, forming the so-called subacromial-subdeltoid bursa (SSB).

The capsule of the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint is the articular capsule of the shoulder. It completely surrounds the joint. It is attached above to the circumference of the glenoid cavity beyond the glenoidal labrum, and below to the anatomical neck of the humerus, approaching nearer to the articular cartilage above than in the rest of its extent.
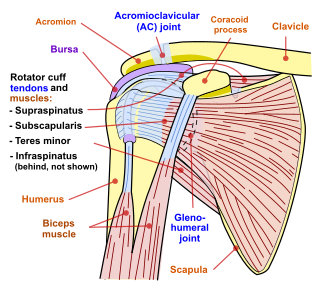
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a syndrome involving tendonitis of the rotator cuff muscles as they pass through the subacromial space, the passage beneath the acromion. It is particularly associated with tendonitis of the supraspinatus muscle. This can result in pain, weakness, and loss of movement at the shoulder.
A shoulder examination is a portion of a physical examination used to identify potential pathology involving the shoulder. It should be conducted with both shoulders exposed to assess for asymmetry and muscle wasting.

















