Related Research Articles

The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is the part of the brain responsible for cognition.

Adult neurogenesis is the process in which neurons are generated from neural stem cells in the adult. This process differs from prenatal neurogenesis.
In vertebrates, a neuroblast or primitive nerve cell is a postmitotic cell that does not divide further, and which will develop into a neuron after a migration phase. In invertebrates such as Drosophila, neuroblasts are neural progenitor cells which divide asymmetrically to produce a neuroblast, and a daughter cell of varying potency depending on the type of neuroblast. Vertebrate neuroblasts differentiate from radial glial cells and are committed to becoming neurons. Neural stem cells, which only divide symmetrically to produce more neural stem cells, transition gradually into radial glial cells. Radial glial cells, also called radial glial progenitor cells, divide asymmetrically to produce a neuroblast and another radial glial cell that will re-enter the cell cycle.
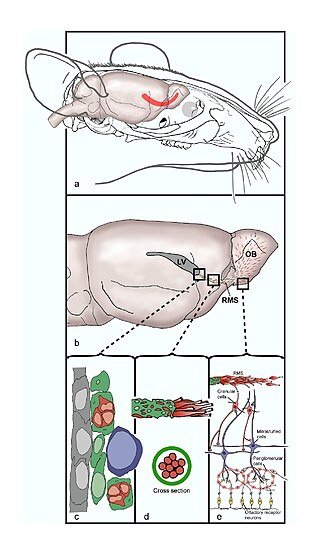
The rostral migratory stream (RMS) is a specialized migratory route found in the brain of some animals along which neuronal precursors that originated in the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the brain migrate to reach the main olfactory bulb (OB). The importance of the RMS lies in its ability to refine and even change an animal's sensitivity to smells, which explains its importance and larger size in the rodent brain as compared to the human brain, as our olfactory sense is not as developed. This pathway has been studied in the rodent, rabbit, and both the squirrel monkey and rhesus monkey. When the neurons reach the OB they differentiate into GABAergic interneurons as they are integrated into either the granule cell layer or periglomerular layer.

Gray matter heterotopia is a neurological disorder caused by gray matter being located in an atypical location in the brain.
Neuroepithelial cells, or neuroectodermal cells, form the wall of the closed neural tube in early embryonic development. The neuroepithelial cells span the thickness of the tube's wall, connecting with the pial surface and with the ventricular or lumenal surface. They are joined at the lumen of the tube by junctional complexes, where they form a pseudostratified layer of epithelium called neuroepithelium.
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are self-renewing, multipotent cells that firstly generate the radial glial progenitor cells that generate the neurons and glia of the nervous system of all animals during embryonic development. Some neural progenitor stem cells persist in highly restricted regions in the adult vertebrate brain and continue to produce neurons throughout life. Differences in the size of the central nervous system are among the most important distinctions between the species and thus mutations in the genes that regulate the size of the neural stem cell compartment are among the most important drivers of vertebrate evolution.

Radial glial cells, or radial glial progenitor cells (RGPs), are bipolar-shaped progenitor cells that are responsible for producing all of the neurons in the cerebral cortex. RGPs also produce certain lineages of glia, including astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Their cell bodies (somata) reside in the embryonic ventricular zone, which lies next to the developing ventricular system.
Neuropoiesis is the process by which neural stem cells differentiate to form mature neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes in the adult mammal. This process is also referred to as adult neurogenesis.

The subventricular zone (SVZ) is a region situated on the outside wall of each lateral ventricle of the vertebrate brain. It is present in both the embryonic and adult brain. In embryonic life, the SVZ refers to a secondary proliferative zone containing neural progenitor cells, which divide to produce neurons in the process of neurogenesis. The primary neural stem cells of the brain and spinal cord, termed radial glial cells, instead reside in the ventricular zone (VZ).

The subgranular zone (SGZ) is a brain region in the hippocampus where adult neurogenesis occurs. The other major site of adult neurogenesis is the subventricular zone (SVZ) in the brain.

The ganglionic eminence (GE) is a transitory structure in the development of the nervous system that guides cell and axon migration. It is present in the embryonic and fetal stages of neural development found between the thalamus and caudate nucleus.

The rhombic lip is a posterior section of the developing metencephalon which can be recognized transiently within the vertebrate embryo. It extends posteriorly from the roof of the fourth ventricle to dorsal neuroepithelial cells. The rhombic lip can be divided into eight structural units based on rhombomeres 1-8 (r1-r8), which can be recognized at early stages of hindbrain development. Producing granule cells and five brainstem nuclei, the rhombic lip plays an important role in developing a complex cerebellar neural system.

Eomesodermin also known as T-box brain protein 2 (Tbr2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EOMES gene.
Endogenous regeneration in the brain is the ability of cells to engage in the repair and regeneration process. While the brain has a limited capacity for regeneration, endogenous neural stem cells, as well as numerous pro-regenerative molecules, can participate in replacing and repairing damaged or diseased neurons and glial cells. Another benefit that can be achieved by using endogenous regeneration could be avoiding an immune response from the host.
The development of the cerebral cortex, known as corticogenesis is the process during which the cerebral cortex of the brain is formed as part of the development of the nervous system of mammals including its development in humans. The cortex is the outer layer of the brain and is composed of up to six layers. Neurons formed in the ventricular zone migrate to their final locations in one of the six layers of the cortex. The process occurs from embryonic day 10 to 17 in mice and between gestational weeks seven to 18 in humans.
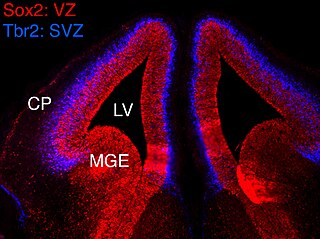
In vertebrates, the ventricular zone (VZ) is a transient embryonic layer of tissue containing neural stem cells, principally radial glial cells, of the central nervous system (CNS). The VZ is so named because it lines the ventricular system, which contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The embryonic ventricular system contains growth factors and other nutrients needed for the proper function of neural stem cells. Neurogenesis, or the generation of neurons, occurs in the VZ during embryonic and fetal development as a function of the Notch pathway, and the newborn neurons must migrate substantial distances to their final destination in the developing brain or spinal cord where they will establish neural circuits. A secondary proliferative zone, the subventricular zone (SVZ), lies adjacent to the VZ. In the embryonic cerebral cortex, the SVZ contains intermediate neuronal progenitors that continue to divide into post-mitotic neurons. Through the process of neurogenesis, the parent neural stem cell pool is depleted and the VZ disappears. The balance between the rates of stem cell proliferation and neurogenesis changes during development, and species from mouse to human show large differences in the number of cell cycles, cell cycle length, and other parameters, which is thought to give rise to the large diversity in brain size and structure.
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). This occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs), radial glial cells (RGCs), basal progenitors (BPs), intermediate neuronal precursors (INPs), subventricular zone astrocytes, and subgranular zone radial astrocytes, among others.

The Radial Unit Hypothesis (RUH) is a conceptual theory of cerebral cortex development, first described by Pasko Rakic. The RUH states that the cerebral cortex develops during embryogenesis as an array of interacting cortical columns, or 'radial units', each of which originates from a transient stem cell layer called the ventricular zone, which contains neural stem cells known as radial glial cells.
Intermediate progenitor cells (IPCs) are a type of progenitor cell in the developing cerebral cortex. They are multipolar cells produced by radial glial cells who have undergone asymmetric division. IPCs can produce neuron cells via neurogenesis and are responsible for ensuring the proper quantity of cortical neurons are produced. In mammals, neural stem cells are the primary progenitors during embryogenesis whereas intermediate progenitor cells are the secondary progenitors.
References
- ↑ Kase, Yoshitaka; Shimazaki, Takuya; Okano, Hideyuki (2020-06-18). "Current understanding of adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: how does adult neurogenesis decrease with age?". Inflammation and Regeneration. 40: 10. doi: 10.1186/s41232-020-00122-x . ISSN 1880-9693. PMC 7302355 . PMID 32566044.
- ↑ Falcão, Ana Mendanha; Marques, Fernanda; Novais, Ashley; Sousa, Nuno; Palha, Joana A.; Sousa, João Carlos (2012-08-09). "The path from the choroid plexus to the subventricular zone: go with the flow!". Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 6: 34. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2012.00034 . ISSN 1662-5102. PMC 3414909 . PMID 22907990.
- ↑ Kazanis, Ilias (2009). "The subependymal zone neurogenic niche: a beating heart in the centre of the brain". Brain. 132 (11): 2909–2921. doi:10.1093/brain/awp237. PMC 2768664 . PMID 19773354.
- ↑ Page 424 in: Neil Vasan; Le, Tao; Bhushan, Vikas (2010). First Aid for the USMLE Step 1, 2010 (First Aid USMLE) . McGraw-Hill Medical. ISBN 978-0-07-163340-6.