
Eswatini, officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and also known by its former official name Swaziland and formerly the Kingdom of Swaziland, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its north, west, south, and southeast. At no more than 200 km (120 mi) north to south and 130 km (81 mi) east to west, Eswatini is one of the smallest countries in Africa; despite this, its climate and topography are diverse, ranging from a cool and mountainous highveld to a hot and dry lowveld.

Artifacts indicating human activity dating back to the early Stone Age have been found in the Kingdom of Eswatini. The earliest known inhabitants of the region were Khoisan hunter-gatherers. Later, the population became predominantly Nguni during and after the great Bantu migrations. People speaking languages ancestral to the current Sotho and Nguni languages began settling no later than the 11th century. The country now derives its name from a later king named Mswati II. Mswati II was the greatest of the fighting kings of Eswatini, and he greatly extended the area of the country to twice its current size. The people of Eswatini largely belong to a number of clans that can be categorized as Emakhandzambili, Bemdzabu, and Emafikamuva, depending on when and how they settled in Eswatini.

Mpumalanga is a province of South Africa. The name means "East", or literally "The Place Where the Sun Rises" in the Nguni languages. Mpumalanga lies in eastern South Africa, bordering Eswatini and Mozambique. It shares borders with the South African provinces of Limpopo to the north, Gauteng to the west, the Free State to the southwest, and KwaZulu-Natal to the south. The capital is Mbombela.

Hhohho is a region of Eswatini, located in the north western part of the country. Hhohho was named after the capital of King Mswati II, who expanded the Swazi territory to the north and west, taking in the districts of Barberton, Nelspruit, Carolina and Piet Retief. These areas were later acquired by what was the Province of Transvaal and today they form part of the Mpumalanga Province of South Africa. It has an area of 3,625.17 km², a population of 320,651 (2017), and is divided into 14 tinkhundla. The administrative center is the national capital of Mbabane. It borders Lubombo Region on the southeast and Manzini Region in the southwest.

Mbombela, formerly Nelspruit, is a city in northeastern South Africa. It is the capital of the Mpumalanga province. Located on the Crocodile River, The city lies about 110 km (68 mi) by road west of the Mozambique border, 330 km (210 mi) east of Johannesburg and 82 km (51 mi) north of the Eswatini border. The city was one of the host cities of the 2010 FIFA World Cup.

The Swazi or Swati are a Bantu ethnic group native to Southern Africa, inhabiting Eswatini, a sovereign kingdom in Southern Africa, and South Africa's Mpumalanga province. EmaSwati are part of the Nguni-language speaking peoples whose origins can be traced through archaeology to East Africa where similar traditions, beliefs and cultural practices are found.
Ngwane V was the King of Swaziland from 1895 until his death on 10 December 1899. Ngwane was born the son of Mbandzeni and his mother was Labotsibeni Mdluli. He ascended to the throne after a short regency of Queen Mother Tibati Nkambule. He was only 16 years old when he became king. His royal capital was at Zombodze while the Queen Mother's residence was at Lobamba. Ngwane became the king after the Swaziland convention of 1894. This had led to the classification of Swaziland as a protected state of the South African Republic which was then led by President Paul Kruger. During this time Swaziland had a partial Dutch administration in parallel to Ngwane's administration. The Dutch or European for European interests and Ngwane as head and authority of the Swazi nation. An annual payment was made to Ngwane and Labotsibeni while they were in office from taxes collected and from contributions from concessionaires and taxes. Ngwane's rule was short. In 1899 the Anglo-Boer war began, and brought to an end the Dutch or Boer partial administration of Swaziland and hence gave way to independence. However Mahlokohla died on 10 December of that year while dancing incwala. This was hid from the nation until the ceremony was over. Ngwane was succeeded by his four-month-old son Nkhotfotjeni and his wife Lomawa Ndwandwe. His mother Labotsibeni who had been very influential during his reign continued as queen regent until Sobhuza was crowned in 1921. Ngwane's reign gave way to a stable territory surrounded by conflicting states. Today Mahlokohla is named for one of the main streets, Mahlokohla Street in Swaziland's capital Mbabane.
King Mswati II, also known as Mswati and Mavuso III, was the king of Eswatini between 1840 and 1868. He was also the eponym of Eswatini. Mswati is considered to be one of the greatest fighting kings of Eswatini.

Dullstroom, also known as Emnothweni, is a small town in Mpumalanga province, South Africa. The town lies 35 kilometres north of Belfast and some 53 kilometres south-west of Lydenburg on the R540 road.

Hazyview is a sub-tropical farming town in Mpumalanga, South Africa, renowned for its large banana and macadamia nut industries, contributing about 20% of South Africa's bananas and 30% of macadamia output. Bordering the Kruger National Park, the town's name is derived from the shimmering haze that occurs during the heat of summer. Most of the province of Mpumalanga's private game reserves are found just east of Hazyview.

Malalane, alternatively rendered Malelane, is a farming town in Mpumalanga, South Africa situated on the N4 national highway. The farms in the region produce sugarcane, subtropical fruit and winter vegetables. The town was proclaimed in 1949 after which it was named. The origin of the name is disputed but was corrupted from the Swazi. Either the expression "eMlalani" which means place of the palms, or the expression "lala" which means to sleep is accepted origins of the name. The town started as the first rest-stop between Lourenço Marques and Pretoria. As of July 2007 the town was officially renamed from "Malelane" to "Malalane" as part of the government's renaming scheme by the South African Geographical Names Council.

Lobamba is a city in Eswatini, and is one of the two capitals, serving as the legislative, traditional, spiritual, seat of government of the Parliament of Eswatini, and Ludzidzini Royal Village, the residence of Queen Ntfombi, the Queen Mother.
Mbandzeni was the King of Swaziland from 1872 until 1889. Ingwenyama Mbandzeni was the son of Mswati II and Nandzi Nkambule. His mother the wife of King Mswati had died when he was still very young.

iNgwenyama is the title of the male monarch of Eswatini. In English, the title is sometimes translated as King of Eswatini. The iNgwenyama reigns together with the Ndlovukazi, a spiritual leadership position held by the iNgwenyama's mother or another female royal of high status.

Christianity is the predominant religion in Eswatini, with Protestantism being its largest denomination.

Sekhukhune I was the paramount King of the Marota, more commonly known as the Bapedi, from 21 September 1861 until his assassination on 13 August 1882 by his rival and half-brother, Mampuru II. As the Pedi paramount leader he was faced with political challenges from Voortrekkers, the independent South African Republic, the British Empire, and considerable social change caused by Christian missionaries.

Bushbuckridge Municipality is a local municipality within the Ehlanzeni District Municipality, in the Mpumalanga province of South Africa. Commercial farming, which consists of pine and bluegum plantations, tobacco, cotton, sub-tropical fruits and vegetables is practised in the municipality's countryside. The municipality includes the southern part of the Kruger National Park. Bushbuckridge is the largest local municipality in Mpumalanga in terms of land size.

Matsulu is a township in the Mbombela Local Municipality under the Ehlanzeni District Municipality in the Mpumalanga province of South Africa. It lies between Kruger National Park and the N4 national road 41 km east of Nelspruit (Mbombela) CBD, 3 km before the Kaapmuiden train station. It is also surrounded by the Nsikazi River & Crocodile River.
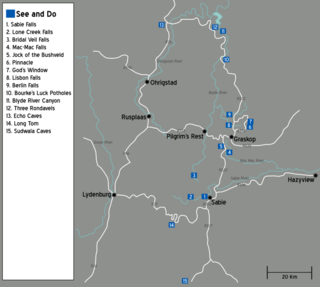
The Panorama Route is a scenic road in South Africa connecting several cultural and natural points of interest. The route, steeped in the history of South Africa, is in Mpumalanga province, centred around the Blyde River Canyon, the world's third largest canyon. It features numerous waterfalls, one of the largest afforested areas in South Africa, and several natural landmarks. The route starts at the foot of the Long Tom Pass just outside Lydenburg, following the natural descent from the Great Escarpment to the Lowveld, and ending at the border of the Mpumalanga and Limpopo provinces near the Echo Caves.

The Echo Caves in Limpopo, South Africa, are set in Precambrian dolomite rock, which was first laid down about 3800 million years ago, when Africa was still part of Gondwana. The caves are considered some of the oldest in the world. The Echo Caves are situated on the farm Klipfonteingrot, some 92 km north of the similar Sudwala Caves.





















