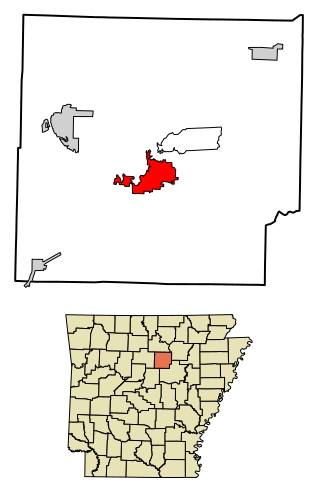
Heber Springs is a city in and the county seat of Cleburne County, Arkansas, United States. The population was 7,165 at the 2010 census.
The Little Red River is a 102-mile-long (164 km) river in White, Van Buren, Searcy, Stone and Cleburne counties of north-central Arkansas.

Sugarloaf is a ski area and resort located on Sugarloaf Mountain in Carrabassett Valley, western Maine. It is the second largest ski resort east of the Mississippi in terms of skiable area and snowmaking percentage (95%); its continuous vertical drop of 2,820 feet (860 m) is the second longest in New England. Sugarloaf recorded a total of 352,000 skier visits in the 2005–2006 season, ranking it second among Maine resorts and 11th in New England.

Pinnacle Mountain State Park is a 2,356-acre state park located in Pulaski County, Arkansas just outside of Little Rock. The main attraction is Pinnacle Mountain, an iconic landmark surrounded by the bottomlands of the Big Maumelle and Little Maumelle rivers.

Sugarloaf Mountain is a small mountain and park about 10 miles (16 km) south of Frederick, Maryland. The closest village is Barnesville, located just over one mile from the foot of the mountain. The peak of this relatively low mountain is approximately 800 feet higher than the surrounding farmland. It is visible from many parts of northern Montgomery County and southern Frederick County, notably from I-270 north of the town of Germantown. Because of its geological and natural history interest, it was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1969. It is a notable example of an admission-free, privately owned scenic park.

Greers Ferry Lake is the reservoir formed by Greers Ferry Dam, a United States Army Corps of Engineers dam in Northern Arkansas. It is located about 60 miles (100 km) north of Little Rock.

Ringwood State Park is a 4,444 acres (17.98 km2) state park in Passaic County in northeastern New Jersey, USA. The Park is located in the heart of the Ramapo Mountains in Ringwood. Its forests are part of the Northeastern coastal forests ecoregion.

Kittatinny Valley State Park is located in Andover Township and extends into Andover Borough, New Jersey. Features include Glacial lakes, limestone outcroppings, former railroads, and a small airport. Lake Aeroflex and Gardner's Pond form part of the headwaters of the Pequest River and are excellent for fishing and boating. The park is home to a variety of wildlife such as whitetail deer, wild turkeys, a variety of songbirds, beavers, muskrats, and squirrels. The park is operated and maintained by the New Jersey Division of Parks and Forestry.

Douthat State Park is a state park located in the Allegheny Mountains in Virginia. It is in Bath County and Alleghany County. The park is 4,545 acres (18 km2) total with a 50-acre (20 ha) lake, the second-largest Virginia state park after Pocahontas State Park. It is one of the original Virginia state parks built in the 1930s by the Civilian Conservation Corps.

Cleburne State Park is a 528-acre (2.14 km2) Texas state park in Johnson County, Texas operated by the Texas Parks and Wildlife Department. The park includes the 116-acre (0.47 km2), spring-fed Cedar Lake that was created by construction of an earthen dam by the Civilian Conservation Corps.

Sugarloaf Ridge State Park is a state park in Northern California, United States. Located in the Mayacamas Mountains north of Kenwood, the park straddles the boundary between Sonoma and Napa counties. The park contains the 2,729-foot (832 m) Bald Mountain and the headwaters of Sonoma Creek including a 25-foot (8 m) tall seasonal waterfall. The park is also home to the volunteer-run Robert Ferguson Observatory. Camping, picnicking, horseback riding, mountain biking, stargazing, fishing and hiking are common attractions of Sugarloaf. The park boasts 25 miles of trails with trails ranging from less than a mile to 8.8 miles, and elevation gains reaching 2,500 feet.

The Louisiana Purchase Historic State Park, located in eastern Arkansas, commemorates the initial point from which the lands acquired through the Louisiana Purchase were subsequently surveyed. The park encompasses 37.5 acres (15.2 ha) of forested wetlands, a landform which is regionally in decline due to agricultural development practices that include draining such areas. On the survey point is a 6-foot (1.8 m) marker erected in 1926 by the L'Anguille Chapter of the Daughters of the American Revolution It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places and designated as a National Historic Landmark.
Brushy Creek State Recreation Area is a state park in Webster County, Iowa in the United States. With an area encompassing over 6,000 acres (24 km2), the facility is one of Iowa's largest public outdoor recreation areas.

Waterloo State Recreation Area is the third-largest park in Michigan, encompassing over 21,000 acres (85 km2) of forest, lakes and wetlands. Located in northeast Jackson County and parts of Washtenaw County, the park is the largest in the Lower Peninsula of Michigan and features 4 campgrounds, 11 lakes, a nature center, and over 50 miles (80 km) of trails - some for horses, bicycles, hiking and cross-country skiing. Waterloo SRA includes the Black Spruce Bog Natural Area, a National Natural Landmark and borders the 11,000-acre (45 km2) Pinckney Recreation Area on the east and the 950-acre (3.8 km2) Phyllis Haehnle Memorial Audubon Sanctuary to the west. The land preserved by the park is not all contiguous and numerous private landholdings and roads run through the park area. The area is characterized by moraines, kettle lakes, swamps and bogs left by retreating glaciers after the last ice age. The park was created by the federal government during the Great Depression and is long-term leased to the state.

Highway 110 is a designation for three east–west state highways in north central Arkansas. One segment of 16.71 miles (26.89 km) runs east from US Highway 65 (US 65) at Botkinburg to Highway 9/Highway 16 near Shirley. A second route of 3.15 miles (5.07 km) begins at Highway 16/Highway 92 in Greers Ferry and runs east to the lake shore of Greers Ferry Lake. A third segment of 20.43 miles (32.88 km) begins at the Sugar Maple Dr/Old Tr intersection outside Heber Springs and runs east to Highway 16 in Pangburn.

Highway 337 is a designation for two state highways in the Ozarks. One segment connects Sugar Loaf Mountain Use Area to Highway 92, and the second connects Highway 5/Highway 25 and Highway 16 southeast of Heber Springs. Both routes are maintained by the Arkansas Department of Transportation (ArDOT).

Hobbs State Park – Conservation Area is a 12,056-acre (4,879 ha) Arkansas state park in Benton, Carroll, and Madison Counties, Arkansas in the United States. The park was bought in 1979 through a huge financial effort from Northwest Arkansas banks. Hobbs State Park – Conservation Area is located almost entirely in the Springfield Plateau subdivision of the Ozark Plateau. The park, located just south of Beaver Lake, is open for year-round recreation, including 32.9 miles (52.9 km) of hiking, mountain bike and equestrian trails. Hobbs State Park – Conservation Area also has several picnic areas, a shooting range, and primitive camping sites.

Arkansas Highway 210 is a designation for two east–west state highways in Cleburne County, Arkansas. One segment of 0.82 miles (1.32 km) runs in Heber Springs from Greers Ferry Lake east to Heber Springs Road as Case Ford Road. A second segment begins at Highway 110 and runs northeast as Industrial Park Rd.

Heber Springs Municipal Airport is a public-use airport located 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) northeast of the central business district of Heber Springs, in Cleburne County, Arkansas, United States. It is owned by the City of Heber Springs.

Mount Magazine State Park is a 2,234-acre park located in Logan County, Arkansas. Inhabited since the 1850s, Mount Magazine first became part of the Ouachita National Forest in 1938, was re-designated as part of the Ozark National Forest in 1941, and became a state park after a 22-year conversion process from the U.S. Forest Service to the Arkansas Department of Parks and Tourism. Mount Magazine State Park is the highest in Arkansas. The park contains Mossback Ridge, including the peak of Mount Magazine which contains The Lodge at Mount Magazine, cabins, trails, and a hang gliding area.























