
Victoria Island is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth-largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi) in area, it is Canada's second-largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,010 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,200 sq mi]). The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. The population of 2,168 is divided among 2 settlements, the larger of which is in Nunavut and the other of which is in the Northwest Territories.
Naukati Bay is a census-designated place (CDP) in the Prince of Wales-Hyder Census Area of the Unorganized Borough of the U.S. state of Alaska. The population was 113 at the 2010 census, down from 135 in 2000.

The Dixon Entrance is a strait about 80 kilometers (50 mi) long and wide in the Pacific Ocean at the Canada–United States border, between the U.S. state of Alaska and the province of British Columbia in Canada. The Dixon Entrance is part of the Inside Passage shipping route. It forms part of the maritime boundary between the U.S. and Canada, although the location of that boundary here is disputed.

Clarence Strait, originally Duke of Clarence Strait, is a strait in southeastern Alaska, in the United States in the Alexander Archipelago. The strait separates Prince of Wales Island, on the west side, from Revillagigedo Island and Annette Island, on the east side. Clarence Strait is 126 miles (203 km) long, extending from Dixon Entrance to Sumner Strait. Moira Sound is on the west side of the strait.
Evans Island is an island in the Prince William Sound of southern Alaska. It lies just east of Bainbridge Island across the Prince of Wales Passage. Elrington Island lies to its south, Latouche Island to its southeast, and Knight Island to its northeast. Although Evans Island had been inhabited up to the time of the Russian exploration of Alaska, the island had no modern-day inhabitants until 1984, when a group of residents and former residents of the original Alutiq village of Chenega, on Chenega Island, decided to build the village of Chenega Bay on Crab Bay on Evans Island. Old Chenega had been destroyed and one-third of its residents had been killed by the tsunami from the 1964 Alaska earthquake. The new community of Chenega is coextensive with Evans Island, which has a land area of 74.605 km2 and a population of 86 persons as of the 2000 census.
Etolin Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, United States at 56°05′52″N132°21′37″W. It is between Prince of Wales Island, to its west, and the Alaska mainland, to its east. It is southwest of Wrangell Island. It was first charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition. He only charted its southwest and east coasts, not realizing it was an island. It was originally named Duke of York Island but was renamed by the United States after the Alaska Purchase. It is named after Adolf Etolin, governor of the Russian American colonies from 1840 to 1845.

Russell Island is an uninhabited island of the Arctic Archipelago in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the Parry Channel, separated from the northern tip of Prince of Wales Island by the narrow Baring Channel. The western third of the island is separated from the other two thirds by a narrow lake and its outlet. At the northern end of the lake there is an isthmus just 1.1 km (0.68 mi) wide and this joins the two parts of the island. With a total area of 940 km2 (360 sq mi), it is the largest island offshore of Prince of Wales Island.

England comprises most of the central and southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain, in addition to a number of small islands of which the largest is the Isle of Wight. England is bordered to the north by Scotland and to the west by Wales. It is closer to continental Europe than any other part of mainland Britain, divided from France only by a 33 km (21 mi) sea gap, the English Channel. The 50 km (31 mi) Channel Tunnel, near Folkestone, directly links England to mainland Europe. The English/French border is halfway along the tunnel.

Dall Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago off the southeast coast of Alaska, just west of Prince of Wales Island and north of Canadian waters. Its peak elevation is 2,443 feet above sea level. Its land area is 254.0 square miles (657.9 km2), making it the 28th largest island in the United States. Dall is used economically for fishing and limestone quarrying.

Zarembo Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, United States. It lies directly south of Mitkof Island and northwest of Etolin Island. To the northwest is Kupreanof Island and to the southwest is Prince of Wales Island. It has a land area of 183.14 square miles, making it the 34th largest island in the United States. It has no permanent resident population. It was first charted in 1793 by Laurenz Hartmann, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition. He only charted its north, west, and south coasts, not realizing it was an island. The island is named after Dionysius Zarembo, a Polish employee of the Russian American Company and explorer of Alaska. Usually known as Dionysius Zarembo, he was captain of the Russian-American Company ship Chichagof during the foundation of the Redoubt San Dionisio, named for his name-saint, a fortification at present-day Wrangell which was established to forestall encroachment on the Stikine region by the Hudson's Bay Company.

Kosciusko Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, United States. It lies near the northwest corner of Prince of Wales Island, just across the El Capitan Passage from the larger island.
Suemez Island is located in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, United States. It resides in the west-central coast of Prince of Wales Island. The northern tip of Dall Island lies to its southeast, while Baker Island lies to its northwest. Suemez Island has a land area of 151.713 km2 and was unpopulated at the 2000 census.
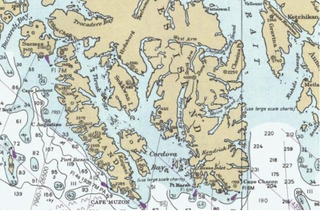
Long Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, United States. It lies across the Kaigani Strait from the southern portion of Dall Island and west of the southern part of Prince of Wales Island. Directly to its north is Sukkwan Island. Long Island forms part of the western boundary of Cordova Bay, and has a land area of 116.136 km2 and was unpopulated at the 2000 census.
Heceta Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, United States. It lies just off the west coast of Prince of Wales Island. Kosciusko Island lies to its north, while Tuxekan Island lies to its northeast. Directly to its south are the Maurelle Islands group, while further south are Noyes Island, Lulu Island, and San Fernando Island. The island's area is 181.0 km2.
Baker Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, United States. It lies off the central west coast of Prince of Wales Island. Its closest significant island neighbors are Noyes Island to its northwest, Lulu Island directly to its north, and Suemez Island across Bucareli Bay to its southeast. The smaller San Juan Bautista Island and St. Ignace Island separate it from Prince of Wales Island and its nearest community, Craig. The island has a land area of 44.44 square miles (115.1 km2) and is uninhabited.
Karta River Wilderness is a U. S. wilderness area within the Tongass National Forest, centrally located on Prince of Wales Island. It is 8 miles (13 km) north of Hollis, Alaska just east of the Kasaan Peninsula and may be accessed by a quick 10-minute plane ride or 30-minute boat ride. The wilderness was established by Congress in 1990, as part of the Tongass Timber Reform Act.

Cordova Bay is a bay in the Alexander Archipelago of southeast Alaska. It opens onto Dixon Entrance to the south, between Cape Muzon on Dall Island and Point Marsh. The name Puerto Cordova y Cordova was given by the Spanish explorer Lieutenant Don Jacinto Caamaño in 1792, in honor of Admiral Luis de Córdova y Córdova. The name was published by George Vancouver in 1798.
The South Prince of Wales Wilderness is a wilderness area on Prince of Wales Island, Alaska, protecting 90,968 acres of undeveloped Pacific temperate rainforest, much of which is old-growth. Managed by the United States Forest Service as part of the Tongass National Forest, the wilderness area was designated in a provision of the 1980 Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act. This wilderness contains 75 or more islands that range from a few to over 500 acres in size. The South Prince of Wales Wilderness sees tidal bores, tidal surges, fierce winds, and heavy storms regularly.

Kasaan Peninsula lies between Clarence Strait and Kasaan Bay in the U.S. state of Alaska. It forms a cut out from the eastern coast of Prince of Wales Island on the south, and by Tolstoi Bay and Thome Bay on the north. A low mountain range forms the backbone of the peninsula, with altitudes ranging from 1,500–2,000 feet (460–610 m). The southern and western shore line is abrupt and almost unbroken, and has practically no shelter from southeasterly storms which sweep up Kasaan Bay. The northeastern coast of the peninsula also rises abruptly from the water, but is broken by a number of indentations, some of which form small harbors. The first discovery of copper deposits in the Ketchikan district was made by the Russians on the southern side of Kasaan Peninsula. Kasaan is the largest settlement on the peninsula.
Moira Sound is a branching inlet on the east side of the southern end of Prince of Wales Island in U.S. state of Alaska. It is situated within the Tongass National Forest.










