Related Research Articles

Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colourless and odourless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant chemical species in air. Because of the volatility of nitrogen compounds, nitrogen is relatively rare in the solid parts of the Earth.
Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
In chemistry, a nitride is a chemical compound of nitrogen. Nitrides can be inorganic or organic, ionic or covalent. The nitride anion, N3- ion, is very elusive but compounds of nitride are numerous, although rarely naturally occurring. Some nitrides have a found applications, such as wear-resistant coatings (e.g., titanium nitride, TiN), hard ceramic materials (e.g., silicon nitride, Si3N4), and semiconductors (e.g., gallium nitride, GaN). The development of GaN-based light emitting diodes was recognized by the 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics. Metal nitrido complexes are also common.
Sulfur oxide refers to many types of sulfur and oxygen containing compounds such as SO, SO2, SO3, S7O2, S6O2, S2O2, etc.

Tetrasulfur tetranitride is an inorganic compound with the formula S4N4. This vivid orange, opaque, crystalline explosive is the most important binary sulfur nitride, which are compounds that contain only the elements sulfur and nitrogen. It is a precursor to many S-N compounds and has attracted wide interest for its unusual structure and bonding.

Sulfur dichloride is the chemical compound with the formula SCl2. This cherry-red liquid is the simplest sulfur chloride and one of the most common, and it is used as a precursor to organosulfur compounds. It is a highly corrosive and toxic substance, and it reacts on contact with water to form chlorine-containing acids.

Disulfur decafluoride is a chemical compound with the formula S2F10. It was discovered in 1934 by Denbigh and Whytlaw-Gray. Each sulfur atom of the S2F10 molecule is octahedral, and surrounded by five fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom. The two sulfur atoms are connected by a single bond. In the S2F10 molecule, the oxidation state of each sulfur atoms is +5, but their valency is 6. S2F10 is highly toxic, with toxicity four times that of phosgene.

Disulfur dichloride is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the formula S2Cl2. It is an amber oily liquid.
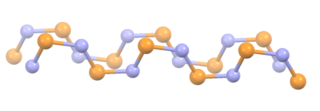
Polythiazyl, (SN)x, is an electrically conductive, gold- or bronze-colored polymer with metallic luster. It was the first conductive inorganic polymer discovered and was also found to be a superconductor at very low temperatures. It is a fibrous solid, described as "lustrous golden on the faces and dark blue-black", depending on the orientation of the sample. It is air stable and insoluble in all solvents.
The chemical element nitrogen is one of the most abundant elements in the universe and can form many compounds. It can take several oxidation states; but the most common oxidation states are -3 and +3. Nitrogen can form nitride and nitrate ions. It also forms a part of nitric acid and nitrate salts. Nitrogen compounds also have an important role in organic chemistry, as nitrogen is part of proteins, amino acids and adenosine triphosphate.

Selenium compounds are compounds containing the element selenium (Se). Among these compounds, selenium has various oxidation states, the most common ones being −2, +4, and +6. Selenium compounds exist in nature in the form of various minerals, such as clausthalite, guanajuatite, tiemannite, crookesite etc., and can also coexist with sulfide minerals such as pyrite and chalcopyrite. For many mammals, selenium compounds are essential. For example, selenomethionine and selenocysteine are selenium-containing amino acids present in the human body. Selenomethionine participates in the synthesis of selenoproteins. The reduction potential and pKa (5.47) of selenocysteine are lower than those of cysteine, making some proteins have antioxidant activity. Selenium compounds have important applications in semiconductors, glass and ceramic industries, medicine, metallurgy and other fields.
Uranium compounds are compounds formed by the element uranium (U). Although uranium is a radioactive actinide, its compounds are well studied due to its long half-life and its applications. It usually forms in the +4 and +6 oxidation states, although it can also form in other oxidation states.

Uranium nitrides is any of a family of several ceramic materials: uranium mononitride (UN), uranium sesquinitride (U2N3) and uranium dinitride (UN2). The word nitride refers to the −3 oxidation state of the nitrogen bound to the uranium.

The lower sulfur oxides are a group of inorganic compounds with the formula SmOn, where 2m > n. These species are often unstable and thus rarely encountered in everyday life. They are significant intermediates in the combustion of elemental sulfur. Some well characterized examples include sulfur monoxide (SO), its dimer S2O2, and a series of cyclic sulfur oxides, SnOx (x = 1, 2), based on cyclic Sn rings.

Disulfur dinitride is the chemical compound with the formula S2N2.
Sulfur fluoride may refer to any of the following sulfur fluorides:
Sulfur mononitride is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula SN. It is the sulfur analogue of and isoelectronic to the radical nitric oxide, NO. It was initially detected in 1975, in outer space in giant molecular clouds and later the coma of comets. This spurred further laboratory studies of the compound. Synthetically, it is produced by electric discharge in mixtures of nitrogen and sulfur compounds, or combustion in the gas phase and by photolysis in solution.

Disulfur monoxide or sulfur suboxide is an inorganic compound with the formula S2O, one of the lower sulfur oxides. It is a colourless gas and condenses to give a roughly dark red coloured solid that is unstable at room temperature.

Disulfur dioxide, dimeric sulfur monoxide or SO dimer is an oxide of sulfur with the formula S2O2. The solid is unstable with a lifetime of a few seconds at room temperature.
Phosphorus nitride refers to several chemical compounds of phosphorus and nitrogen:
References
- ↑ Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) Inorganic Chemistry, Elsevier ISBN 0-12-352651-5