
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way, where Earth is located. It has a total diameter of roughly 3 megaparsecs (10 million light-years; 9×1019 kilometres), and a total mass of the order of 2×1012 solar masses (4×1042 kg). It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape; the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about 800 kiloparsecs (3×10^6 ly; 2×1019 km) and are moving toward one another with a velocity of 123 km/s. The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies.

In the fields of Big Bang theory and cosmology, reionization is the process that caused electrically neutral atoms in the universe to reionize after the lapse of the "dark ages". Detecting and studying the reionization process is challenging but multiple avenues have been pursued. This reionization was driven by the formation of the first stars and galaxies.
The Milky Way has several smaller galaxies gravitationally bound to it, as part of the Milky Way subgroup, which is part of the local galaxy cluster, the Local Group.

The Dark Energy Survey (DES) is an astronomical survey designed to constrain the properties of dark energy. It uses images taken in the near-ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared to measure the expansion of the universe using Type Ia supernovae, baryon acoustic oscillations, the number of galaxy clusters, and weak gravitational lensing. The collaboration is composed of research institutions and universities from the United States, Australia, Brazil, the United Kingdom, Germany, Spain, and Switzerland. The collaboration is divided into several scientific working groups. The director of DES is Josh Frieman.

The Leo Cluster is a galaxy cluster about 330 million light-years distant in the constellation Leo, with at least 70 major galaxies. The galaxy known as NGC 3842 is the brightest member of this cluster. Along with the Coma Cluster, it is one of the two major clusters comprising the Coma Supercluster, which in turn is part of the CfA2 Great Wall, which is hundreds of millions light years long and is one of the largest known structures in the universe.

SMACS J0723.3–7327, commonly referred to as SMACS 0723, is a galaxy cluster about 4 billion light years from Earth, within the southern constellation of Volans. It is a patch of sky visible from the Southern Hemisphere on Earth and often observed by the Hubble Space Telescope and other telescopes in search of the deep past. It was the target of the first full-color image to be unveiled by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), imaged using NIRCam, with spectra included, showing objects lensed by the cluster with redshifts implying they are 13.1 billion years old. The cluster has been previously observed by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) as part of the Southern MAssive Cluster Survey (SMACS), as well as Planck and Chandra.

RX J1532.9+3021 is a galaxy cluster located in the constellation of Corona Borealis. It has a velocity of 103,539 ± 8 kilometers per second, equivalent to a Hubble distance of 1,527.1 ± 106.9 megaparsecs or 3.9 billion light years. It is classfied one of the massive and strongest X-ray bright cool clusters in the universe at redshift z = 0.362. The luminosity of the cluster is estimated to be 6 x 1045 ergs-1. According to a study published in 2013, a mini radio halo is seen surrounding the cluster.

ASW0009io9 (9io9) is a gravitationally lensed system of two galaxies. The nearer galaxy is approximately 2 billion light-years (610 Mpc) from Earth and is designated SDSS J020941.27+001558.4, while the lensed galaxy is 10 billion light-years (3.1 Gpc) distant and is designated ASW0009io9. It was discovered in January 2014 by a group of citizen scientists, while classifying images on the website Spacewarps.org. The discovery was announced on the BBC television programme Stargazing Live.

A tidal disruption event (TDE) is a transient astronomical source produced when a star passes so close to a supermassive black hole (SMBH) that it is pulled apart by the black hole's tidal force. The star undergoes spaghettification, producing a tidal stream of material that loops around the black hole. Some portion of the stellar material is captured into orbit, forming an accretion disk around the black hole, which emits electromagnetic radiation. In a small fraction of TDEs, a relativistic jet is also produced. As the material in the disk is gradually consumed by the black hole, the TDE fades over several months or years.

NGC 4424 is a spiral galaxy located in the equatorial constellation of Virgo. It was discovered February 27, 1865 by German astronomer Heinrich Louis d'Arrest. This galaxy is located at a distance of 13.5 million light years and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 442 km/s. It has a morphological class of SB(s)a, which normally indicates a spiral galaxy with a barred structure (SB), no inner ring feature (s), and tightly-wound spiral arms (a). The galactic plane is inclined at an angle of 62° to the line of sight from the Earth. It is a likely member of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies.
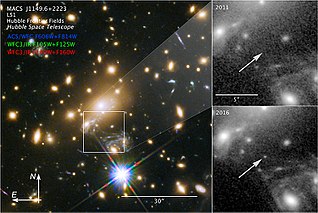
MACS J1149 Lensed Star 1, also known as Icarus, is a blue supergiant star observed through a gravitational lens. It is the seventh most distant individual star to have been detected so far, at approximately 14 billion light-years from Earth. Light from the star was emitted 4.4 billion years after the Big Bang. According to co-discoverer Patrick Kelly, the star is at least a hundred times more distant than the next-farthest non-supernova star observed, SDSS J1229+1122, and is the first magnified individual star seen.

NGC 5728 is an active barred spiral galaxy located 146 million light years away in the southern constellation of Libra. It was discovered on May 7, 1787 by William Herschel. The designation comes from the New General Catalogue of J. L. E. Dreyer, published in 1888. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 13.40 and spans an angle of 3.4 arcminutes. The galaxy shows a red shift of 0.00935 and has a heliocentric radial velocity of 2,803 km/s. It has an estimated mass of 72 billion times the mass of the Sun and stretches around 30 kpc across.

SMACS J0723.3–7327, commonly referred to as SMACS 0723, is a galaxy cluster about 4 billion light years from Earth, within the southern constellation of Volans. It is a patch of sky visible from the Southern Hemisphere on Earth and often observed by the Hubble Space Telescope and other telescopes in search of the deep past. It was the target of the first full-color image to be unveiled by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), imaged using NIRCam, with spectra included, showing objects lensed by the cluster with redshifts implying they are 13.1 billion years old. The cluster has been previously observed by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) as part of the Southern MAssive Cluster Survey (SMACS), as well as Planck and Chandra.

Godzilla is a variable star in the Sunburst galaxy at redshift z = 2.37, observed through the gravitational lens PSZ1 G311.65-18.48. It was originally identified in the NW arc as a possible transient event in images taken with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST).
SN H0pe (pronounced: Supernova Hope) is a Type Ia supernova discovered in 2023, at a redshift of z=1.78. It is a supernova discovered in a gravitationally lensed subject system, being itself a triply lensed object. Its name, H0pe, comes from its proposed utility in determination of the Hubble Constant (H0) that would allow determination of H0 in the distant universe and compare it with local determinations; and hopefully resolve Hubble tension, the difference in such determinations with local Type Ia supernovae and those based on the very distant Cosmic Microwave Background. The supernova exploded when the universe was 3.5 billion years old, rather than at today's date of 13.8 billion years old. The supernova progenitor was a white dwarf star, the progenitor of all Type Ia supernovae. The gravitational lens is galaxy cluster PLCK G165.7+67.0 (at a redshift of z=0.35), which lensed the supernova and its host galaxy.

Abell 68 is massive and rich galaxy cluster located in the constellation of Pisces with a projected co-moving distance of approximately 1124.6 Mpc or 3.668 billion light-years away from Earth. The cluster is especially notable for its gravitational lensing and was first discovered by George O. Abell in 1958.













