Related Research Articles

In vertebrate anatomy, ribs are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the thoracic cavity. They serve to protect the lungs, heart, and other vital organs of the thorax. In some animals, especially snakes, ribs may provide support and protection for the entire body.

In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck.

The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels and support the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the axial skeleton.

The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. It originates from the transverse processes of the four uppermost cervical vertebrae; it inserts onto the upper portion of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the cervical nerves C3-C4, and frequently also by the dorsal scapular nerve. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.

The omohyoid muscle is a muscle in the neck. It is one of the infrahyoid muscles. It consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. Its inferior belly is attached to the scapula; its superior belly is attached to the hyoid bone. Its intermediate tendon is anchored to the clavicle and first rib by a fascial sling. The omohyoid is innervated by the ansa cervicalis of the cervical plexus. It acts to depress the hyoid bone.
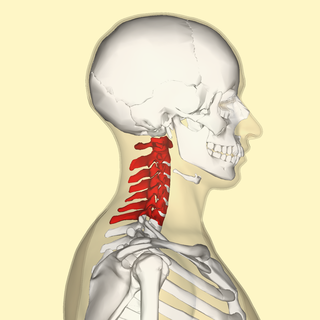
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae lie caudal of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine.

The abdominal external oblique muscle is the largest and outermost of the three flat abdominal muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen.

The thoracolumbar fascia is a complex, multilayer arrangement of fascial and aponeurotic layers forming a separation between the paraspinal muscles on one side, and the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall on the other. It spans the length of the back, extending between the neck superiorly and the sacrum inferiorly. It entails the fasciae and aponeuroses of the latissimus dorsi muscle, serratus posterior inferior muscle, abdominal internal oblique muscle, and transverse abdominal muscle.

The iliolumbar ligament is a strong ligament which attaches medially to the transverse process of the 5th lumbar vertebra, and laterally to back of the inner lip of the iliac crest.

In anatomy, the transverse ligament of the atlas is a broad, tough ligament which arches across the ring of the atlas posterior to the dens to keep the dens in contact with the atlas. It forms the transverse component of the cruciform ligament of atlas.

The tectorial membrane of atlanto-axial joint is a tough membrane/broad, strong band representing the superior-ward prolongation of the posterior longitudinal ligament.
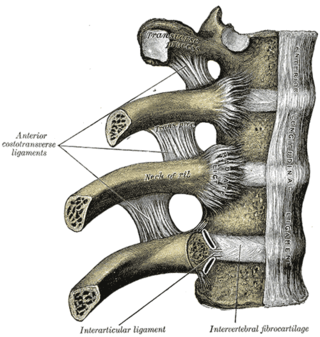
The radiate ligament of head of rib is a ligament of the costovertebral joint that typically connects the anterior edge of the head of each rib, and the side of the bodies of two adjacent vertebrae and their intervertebral discs. The ligament is formed as a thickening of the anterior portion of the joint capsule of the costovertebral joint, and thus reinforces it anteriorly.
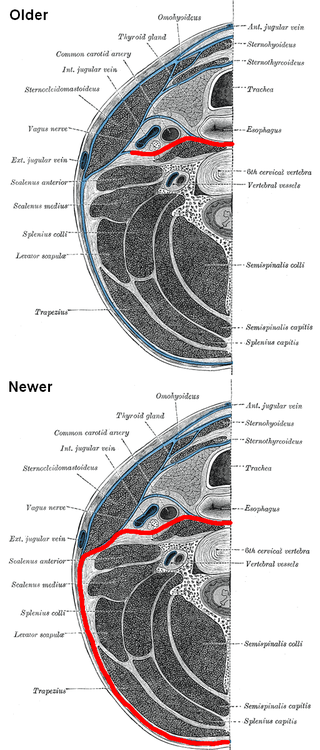
The prevertebral fascia is the layer of deep cervical fascia that surrounds the vertebral column. It is the deepest layer of deep cervical fascia.
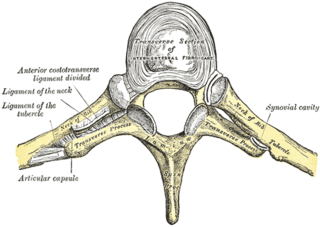
The costotransverse joint is the joint formed between the facet of the tubercle of the rib and the adjacent transverse process of a thoracic vertebra. The costotransverse joint is a plane type of synovial joint which, under physiological conditions, allows only gliding movement.
The lateral costotransverse ligament is a short, thick, though ligament of the costotransverse joint which strengthens the joint posteriorly. It connects the tubercle of a rib, and the transverse process of the corresponding vertebra.
A costotransverse ligament is ligament of the costotransverse joint which attaches at the neck of a rib, and at the transverse process of its corresponding vertebra. It extends posteriorly from the rib to the vertebra.
The lumbar fascia is the lumbar portion of the thoracolumbar fascia. It consists of three fascial layers - posterior, middle, and anterior - that enclose two muscular compartments. The anterior and middle layers occur only in the lumbar region, whereas the posterior layer extends superiorly to the inferior part of the neck, and the inferiorly to the dorsal surface of the sacrum. The quadratus lumborum is contained in the anterior muscular compartment, and the erector spinae in the posterior compartment. Psoas major lies anterior to the anterior layer. Various superficial muscles of the posterior thorax and abdomen arise from the posterior layer - namely the latissimus dorsi, and serratus posterior inferior.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The pelvis is the lower part of an anatomical trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.

Each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species.
References
- 1 2 3 Moore, Keith L.; Dalley, Arthur F.; Agur, Anne M. R. (2018). Clinically Oriented Anatomy (8th ed.). Wolters Kluwer. p. 298. ISBN 978-1-4963-4721-3.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 581. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - 1 2 3 Ibrahim AF, Darwish HH, The costotransverse ligaments in human: a detailed anatomical study, Clin Anat. 2005 Jul;18(5):340-5