
The compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format that was co-developed by Philips and Sony to store and play digital audio recordings. It uses the Compact Disc Digital Audio format which typically provides 74 minutes of audio on a disc. In later years, the compact disc was adapted for non-audio computer data storage purposes as CD-ROM and its derivatives. First released in Japan in October 1982, the CD was the second optical disc technology to be invented, after the much larger LaserDisc (LD). By 2007, 200 billion CDs had been sold worldwide.

An optical disc is a flat, usually disc-shaped object that stores information in the form of physical variations on its surface that can be read with the aid of a beam of light. Optical discs can be reflective, where the light source and detector are on the same side of the disc, or transmissive, where light shines through the disc to be detected on the other side.

Windows Media Player, is the first media player and media library application that Microsoft developed to play audio and video on personal computers. It has been a component of the Microsoft Windows operating system, including Windows 9x, Windows NT, Pocket PC, and Windows Mobile. Microsoft also released editions of Windows Media Player for classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, and Solaris, but has since discontinued them.
Shovelware is a term for individual video games or software bundles known more for the quantity of what is included than for the quality or usefulness.

Super Audio CD (SACD) is an optical disc format for audio storage introduced in 1999. It was developed jointly by Sony and Philips Electronics and intended to be the successor to the compact disc (CD) format.

Knoppix, stylized KNOPPIX, is an operating system based on Debian designed to be run directly from a CD / DVD or a USB flash drive. It was first released in 2000 by German Linux consultant Klaus Knopper, and was one of the first popular live distributions. Knoppix is loaded from the removable medium and decompressed into a RAM drive. The decompression is transparent and on-the-fly.

Pioneer Corporation, commonly referred to as Pioneer, is a Japanese multinational corporation based in Tokyo, that specializes in digital entertainment products. The company was founded by Nozomu Matsumoto on January 1, 1938 in Tokyo as a radio and speaker repair shop. Its current president is Shiro Yahara.
SafeDisc is a copy protection program for Microsoft Windows applications and games distributed on optical disc. Created by Macrovision Corporation, it was aimed to hinder unauthorized disc duplication. The program was first introduced in 1998 and was discontinued on March 31, 2009.

LightScribe is an optical disc recording technology that was created by the Hewlett-Packard Company. It uses specially coated recordable CD and DVD media to produce laser-etched labels with text or graphics, as opposed to stick-on labels and printable discs. Although HP is no longer developing the technology, it is still maintained and supported by a number of independent enthusiasts.

Sonic Solutions was an American computer software company headquartered in Novato, California. In addition to having a number of offices in the U.S., the company also maintained offices in Europe and Asia. It was acquired by Rovi Corporation in 2010.

Labelflash is a technology which allows users to burn custom designs or images onto proprietary DVD media first announced in October 2005 as a collaboration between Yamaha and Fujifilm. While Yamaha developed the optical drives, Fujifilm manufactured the proprietary Labelflash optical discs. NEC manufactured the first Labelflash compatible drive, the ND4551, which was released in December 2005.
Amiga software is computer software engineered to run on the Amiga personal computer. Amiga software covers many applications, including productivity, digital art, games, commercial, freeware and hobbyist products. The market was active in the late 1980s and early 1990s but then dwindled. Most Amiga products were originally created directly for the Amiga computer, and were not ported from other platforms.

DiscT@2 is a method of writing text and graphics to the data side of a CD-R or DVD disc first introduced by Yamaha in 2002. While often compared with the later LabelFlash and LightScribe technologies, which also offered users consumer-grade computerized disc labeling, DiscT@2 is different in that it required no proprietary media and wrote the graphics to the data side of the disc.

A ROM cartridge, usually referred to in context simply as a cartridge, cart, or card, is a replaceable part designed to be connected to a consumer electronics device such as a home computer, video game console or, to a lesser extent, electronic musical instruments.
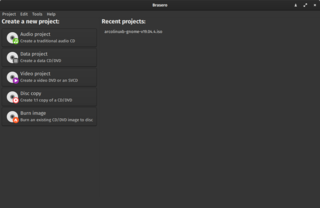
Brasero is a free and open-source disc-burning program for Unix-like operating systems, it serves as a graphical front-end to cdrtools, cdrskin, growisofs, and (optionally) libburn. Licensed under the terms of the GNU General Public License.

Toshiba Samsung Storage Technology Corporation is an international joint venture company of Toshiba (Japan) and Samsung Electronics. Toshiba used to own 51% of its stock, while Samsung used to own the remaining 49%. The company specialized in optical disc drive manufacturing. The company was established in 2004.

A CD-ROM is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains data computers can read—but not write or erase—CD-ROMs. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold both computer data and audio with the latter capable of being played on a CD player, while data is only usable on a computer.

MicrosoftEncarta is a discontinued digital multimedia encyclopedia published by Microsoft from 1993 to 2009. Originally sold on CD-ROM or DVD, it was also available online via annual subscription, although later articles could also be viewed for free online with advertisements. By 2008, the complete English version, Encarta Premium, consisted of more than 62,000 articles, numerous photos and illustrations, music clips, videos, interactive content, timelines, maps, atlases and homework tools.

Nero Burning ROM, commonly called Nero, is an optical disc authoring program from Nero AG. The software is part of the Nero Multimedia Suite but is also available as a stand-alone product. It is used for burning and copying optical media such as CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray disks. The program also supports the label printing technologies LightScribe and LabelFlash, and can be used to convert audio files into other audio formats.

The Apple QuickTake is one of the first consumer digital camera lines. It was launched in 1994 by Apple Computer and was marketed for three years before being discontinued in 1997. Three models of the product were built including the 100 and 150, both built by Chinon; and the 200, built by Fujifilm. The QuickTake cameras had a resolution of 640 x 480 pixels maximum.















