Related Research Articles
The Toledo War (1835–1836), also known as the Michigan–Ohio War or Ohio–Michigan War, was a boundary dispute between the U.S. state of Ohio and the adjoining territory of Michigan over what is now known as the Toledo Strip. Control of the mouth of the Maumee River and the inland shipping opportunities it represented, and the good farmland to the west were seen by both parties as valuable economic assets.

The Province of Upper Canada was a part of British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the Province of Quebec since 1763. Upper Canada included all of modern-day Southern Ontario and all those areas of Northern Ontario in the Pays d'en Haut which had formed part of New France, essentially the watersheds of the Ottawa River or Lakes Huron and Superior, excluding any lands within the watershed of Hudson Bay. The "upper" prefix in the name reflects its geographic position along the Great Lakes, mostly above the headwaters of the Saint Lawrence River, contrasted with Lower Canada to the northeast.

British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, Virginia, and more substantially with the founding of the Thirteen Colonies along the Atlantic coast of North America.
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolution. Established in 1787 by the Congress of the Confederation through the Northwest Ordinance, it was the nation's first post-colonial organized incorporated territory.

The Public Land Survey System (PLSS) is the surveying method developed and used in the United States to plat, or divide, real property for sale and settling. Also known as the Rectangular Survey System, it was created by the Land Ordinance of 1785 to survey land ceded to the United States by the Treaty of Paris in 1783, following the end of the American Revolution. Beginning with the Seven Ranges in present-day Ohio, the PLSS has been used as the primary survey method in the United States. Following the passage of the Northwest Ordinance in 1787, the Surveyor General of the Northwest Territory platted lands in the Northwest Territory. The Surveyor General was later merged with the United States General Land Office, which later became a part of the U.S. Bureau of Land Management (BLM). Today, the BLM controls the survey, sale, and settling of lands acquired by the United States.
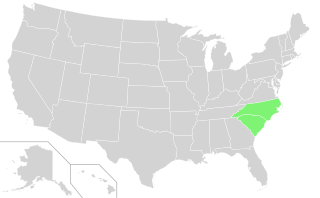
The Carolinas, also known simply as Carolina, are the U.S. states of North Carolina and South Carolina considered collectively. They are bordered by Virginia to the north, Tennessee to the west, and Georgia to the southwest. The Atlantic Ocean is to the east.

The Land Ordinance of 1785 was adopted by the United States Congress of the Confederation on May 20, 1785. It set up a standardized system whereby settlers could purchase title to farmland in the undeveloped west. Congress at the time did not have the power to raise revenue by direct taxation, so land sales provided an important revenue stream. The Ordinance set up a survey system that eventually covered over three-quarters of the area of the continental United States.

The Province of North Carolina, originally known as Albemarle Province, was a proprietary colony and later royal colony of Great Britain that existed in North America from 1712 to 1776.(p. 80) It was one of the five Southern colonies and one of the thirteen American colonies. The monarch of Great Britain was represented by the Governor of North Carolina, until the colonies declared independence on July 4, 1776.
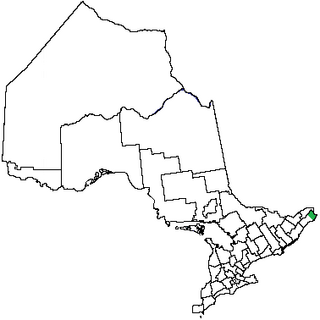
Glengarry County, an area covering 288,688 acres (1,168 km2), is a county in the province of Ontario, Canada. It is still inhabited by the descendants of 18th and early 19th-century Scottish Highland pioneer settlers from Lochaber, was historically a Gàidhealtachd community, and Canadian Gaelic language revival efforts are currently taking place there. Glengarry County consists of the townships of North Glengarry and South Glengarry. It borders the Saint Lawrence River to the south, the county of Stormont and City of Cornwall to the west, the province of Quebec to the east, and the United Counties of Prescott-Russell to the north.

The Algonquians are one of the most populous and widespread North American indigenous North American groups, consisting of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages. They historically were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and in the interior regions along Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes.
A capital district, capital region, or capital territory is normally a specially designated administrative division where a country's seat of government is located. As such, in a federal model of government, no state or territory has any political or economic advantage relative to the others because of the national capital lying within its borders. A capital territory can be a specific form of federal district.
Thomas Hutchins was an American military engineer, cartographer, geographer and surveyor. In 1781, Hutchins was named Geographer of the United States. He is the only person to hold that post.

British America, known as English America before 1707, comprised the colonial territories of the Kingdom of England (and Kingdom of Scotland) of the overseas English Empire, and the successor British Empire, in the Americas from the founding of Jamestown in the new Virginia colony in 1607 to 1783. These colonies were formally known as British America and the British West Indies immediately prior to thirteen of the colonies rebelling in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) and forming the newly-independent United States of America.
A quadripoint is a point on Earth where four distinct political territories meet. The territories can be of different types, such as national and provincial. In North America, several such places are commonly known as Four Corners. Several examples exist throughout the world that use other names.

The history of post-confederation Canada began on July 1, 1867, when the British North American colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia were united to form a single Dominion within the British Empire. Upon Confederation, the United Province of Canada was immediately split into the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The colonies of Prince Edward Island and British Columbia joined shortly after, and Canada acquired the vast expanse of the continent controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company, which was eventually divided into new territories and provinces. Canada evolved into a fully sovereign state by 1982.
A province is an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman provincia, which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term province has since been adopted by many countries. In some countries with no actual provinces, "the provinces" is a metaphorical term meaning "outside the capital city".

The Royal Colonial Boundary of 1665 marked the border between the Colony of Virginia and the Province of Carolina from the Atlantic Ocean westward across North America. The line follows the parallel 36°30′ north latitude that later became a boundary for several U.S. states as far west as the Oklahoma Panhandle, and also came to be associated with the Missouri Compromise of 1820.
Tuckasegee, named after the historic Cherokee town of that name located near here, is an unincorporated community in Jackson County, North Carolina, United States. It followed the earlier Cherokee town as developing on the upper Tuckaseegee River, at the confluence of its East and West forks.

The North Carolina–Tennessee–Virginia Corners is a tripoint at which North Carolina, Tennessee and Virginia meet. The landmark is located in the Iron Mountains, and is roughly 16 miles (26 km) north of Snake Mountain, and 8 miles (13 km) southwest of Mount Rogers.
References
- ↑ DeLancey, Edward Floyd (1886). Origin and History of Manors in the Province of New York and in the County of Westchester. p. 153. Retrieved 29 October 2019.