The Maisonneuve fracture is a spiral fracture of the proximal third of the fibula associated with a tear of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis and the interosseous membrane. There is an associated fracture of the medial malleolus or rupture of the deep deltoid ligament of the ankle. This type of injury can be difficult to detect.

Hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the hip joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant, that is, a hip prosthesis. Hip replacement surgery can be performed as a total replacement or a hemi (half) replacement. Such joint replacement orthopaedic surgery is generally conducted to relieve arthritis pain or in some hip fractures. A total hip replacement consists of replacing both the acetabulum and the femoral head while hemiarthroplasty generally only replaces the femoral head. Hip replacement is currently one of the most common orthopaedic operations, though patient satisfaction short- and long-term varies widely. Approximately 58% of total hip replacements are estimated to last 25 years. The average cost of a total hip replacement in 2012 was $40,364 in the United States, and about $7,700 to $12,000 in most European countries.

Hyaline cartilage is the glass-like (hyaline) but translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is pearl-grey in color, with a firm consistency and has a considerable amount of collagen. It contains no nerves or blood vessels, and its structure is relatively simple.
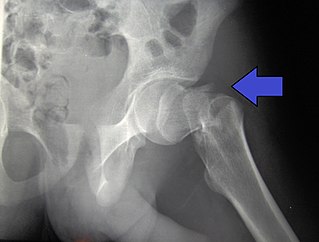
A hip fracture is a break that occurs in the upper part of the femur. Symptoms may include pain around the hip, particularly with movement, and shortening of the leg. Usually the person cannot walk.
The drawer test is used in the initial clinical assessment of suspected rupture of the cruciate ligaments in the knee. The patient should be supine with the hips flexed to 45 degrees, the knees flexed to 90 degrees and the feet flat on table. The examiner positions himself by sitting on the examination table in front of the involved knee and grasping the tibia just below the joint line of the knee. The thumbs are placed along the joint line on either side of the patellar tendon. The tibia is then drawn forward anteriorly. An increased amount of anterior tibial translation compared with the opposite limb or lack of a firm end-point may indicate either a sprain of the anteromedial bundle or complete tear of the ACL. If the tibia pulls forward or backward more than normal, the test is considered positive. Excessive displacement of the tibia anteriorly suggests that the anterior cruciate ligament is injured, whereas excessive posterior displacement of the tibia may indicate injury of the posterior cruciate ligament.

A Lisfranc injury, also known as Lisfranc fracture, is an injury of the foot in which one or more of the metatarsal bones are displaced from the tarsus.

The ulnar canal or ulnar tunnel (also known as Guyon's canal or tunnel) is a semi-rigid longitudinal canal in the wrist that allows passage of the ulnar artery and ulnar nerve into the hand. The roof of the canal is made up of the superficial palmar carpal ligament, while the deeper flexor retinaculum and hypothenar muscles comprise the floor. The space is medially bounded by the pisiform and pisohamate ligament more proximally, and laterally bounded by the hook of the hamate more distally. It is approximately 4 cm long, beginning proximally at the transverse carpal ligament and ending at the aponeurotic arch of the hypothenar muscles.

An accessory navicular bone is an accessory bone of the foot that occasionally develops abnormally in front of the ankle towards the inside of the foot. This bone may be present in approximately 2-21% of the general population and is usually asymptomatic. When it is symptomatic, surgery may be necessary.

A Salter–Harris fracture is a fracture that involves the epiphyseal plate or growth plate of a bone, specifically the zone of provisional calcification. It is thus a form of child bone fracture. It is a common injury found in children, occurring in 15% of childhood long bone fractures. This type of fracture and its classification system is named for Robert B. Salter and William H. Harris who created and published this classification system in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery in 1963.
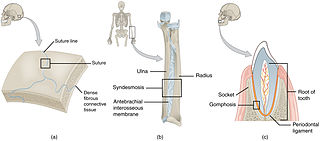
In anatomy, fibrous joints are joints connected by fibrous tissue, consisting mainly of collagen. These are fixed joints where bones are united by a layer of white fibrous tissue of varying thickness. In the skull the joints between the bones are called sutures. Such immovable joints are also referred to as synarthroses.

A Barton's fracture is an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dislocation of the radiocarpal joint.
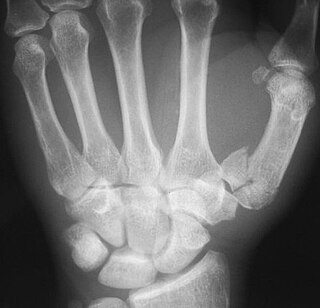
The Rolando fracture is a comminuted intra-articular fracture through the base of the first metacarpal bone. It was first described in 1910 by Silvio Rolando. This is a fracture consisting of 3 distinct fragments; it is typically T- or Y-shaped.
A high ankle sprain, also known as a syndesmotic ankle sprain (SAS), is a sprain of the syndesmotic ligaments that connect the tibia and fibula in the lower leg, thereby creating a mortise and tenon joint for the ankle. High ankle sprains are described as high because they are located above the ankle. They comprise approximately 15% of all ankle sprains. Unlike the common lateral ankle sprains, when ligaments around the ankle are injured through an inward twisting, high ankle sprains are caused when the lower leg and foot externally rotates.
Epiphysiodesis is a pediatric orthopedic surgery procedure that aims at altering or stopping the bone growth naturally occurring through the growth plate also known as the physeal plate. There two types of epiphysiodesis: temporary hemiepiphysiodesis and permanent epiphysiodesis. Temporary hemiepiphysiodesis is also known as guided growth surgery or growth modulation surgery. Temporary hemiepiphysiodesis is reversible i.e. the metal implants used to achieve epiphysiodesis can be removed after the desired correction is achieved and the growth plate can thus resume its normal growth and function. In contrast, permanent epiphysiodesis is irreversible and the growth plate function cannot be restored after surgery. Both temporary hemiepiphysiodesis and permanent epiphysiodesis are used to treat a diverse array of pediatric orthopedic disorders but the exact indications for each procedure are different.
Pigeon toe, also known as in-toeing, is a condition which causes the toes to point inward when walking. It is most common in infants and children under two years of age and, when not the result of simple muscle weakness, normally arises from underlying conditions, such as a twisted shin bone or an excessive anteversion resulting in the twisting of the thigh bone when the front part of a person's foot is turned in.
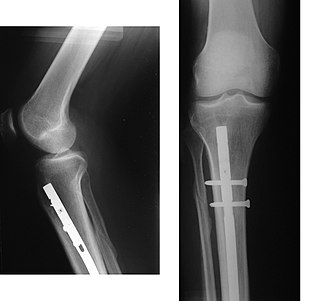
An intramedullary rod, also known as an intramedullary nail or inter-locking nail or Küntscher nail, is a metal rod forced into the medullary cavity of a bone. IM nails have long been used to treat fractures of long bones of the body. Gerhard Küntscher is credited with the first use of this device in 1939, during World War II, for soldiers with fractures of the femur. Prior to that, treatment of such fractures was limited to traction or plaster, both of which required long periods of inactivity. IM nails resulted in earlier return to activity for the soldiers, sometimes even within a span of a few weeks, since they share the load with the bone, rather than entirely supporting the bone.

Fibular hemimelia or longitudinal fibular deficiency is "the congenital absence of the fibula and it is the most common congenital absence of long bone of the extremities." It is the shortening of the fibula at birth, or the complete lack thereof. Fibula Hemimelia is a catastrophic deformity of the leg which often causes severe knee instability due to the absence of multiple ligaments including the ACL and lack of functionality in any remaining ligaments. Severe forms of Fibula Hemimelia in a patient can result in a non functional locked and malformed ankle which is significantly smaller as well as missing toes. This condition also results in a warped leg which lacks circulation and has nerve damage. In many cases of the deformity almost all types of tissue within the patients leg are deformed and seriously affected. It can lead to serious and debilitating problems and has a significant impact on a patients quality of life. In humans, the disorder can be noted by ultrasound in utero to prepare for amputation after birth or complex bone lengthening surgery. The amputation usually takes place at six months with removal of portions of the legs to prepare them for prosthetic use. The other treatments which include repeated corrective osteotomies and leg-lengthening surgery are costly and associated with residual deformity. It is noted however that these treatments have very little effect on the multitude of problems such as severe knee instability that fibula hemimelia causes. Fibula Hemimelia is a degenerative and lifelong condition which can result in a leg which is unable to bear any weight and can rapidly worsen without any acute injuries.

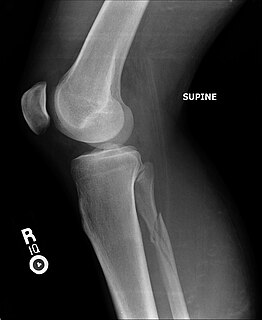
A tibial plateau fracture is a break of the upper part of the tibia (shinbone) that involves the knee joint. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and a decreased ability to move the knee. People are generally unable to walk. Complication may include injury to the artery or nerve, arthritis, and compartment syndrome.
Limb-sparing techniques, also known as limb-saving or limb-salvage techniques, are performed in order to give patients an alternative to amputation. There are many different types of limb-sparing techniques, including arthrodesis, arthroplasty, alloprosthetic composite, endoprosthetic reconstruction, prosthetic implants, and rotationplasty.

Freiberg disease, also known as a Freiberg infraction, is a form of avascular necrosis in the metatarsal bone of the foot. It generally develops in the second metatarsal, but can occur in any metatarsal. Physical stress causes multiple tiny fractures where the middle of the metatarsal meets the growth plate. These fractures impair blood flow to the end of the metatarsal resulting in the death of bone cells (osteonecrosis). It is an uncommon condition, occurring most often in young women, athletes, and those with abnormally long metatarsals. Approximately 80% of those diagnosed are women.
















