
QuickTime is an extensible multimedia framework developed by Apple Inc., capable of handling various formats of digital video, picture, sound, panoramic images, and interactivity. First made in 1991, the latest Mac version, QuickTime X, is available for Mac OS X Snow Leopard up to macOS Mojave. Apple ceased support for the Windows version of QuickTime in 2016, and ceased support for QuickTime 7 on macOS in 2018.

macOS Server, formerly Mac OS X Server and OS X Server, is a series of Unix-like server operating systems developed by Apple Inc., based on macOS and later add-on software packages for the latter. macOS Server adds server functionality and system administration tools to macOS and provides tools to manage both macOS-based computers and iOS-based devices.

iPhoto was a digital photograph manipulation software application developed by Apple Inc. It was included with every Macintosh personal computer from 2002 to 2015, when it was replaced with Apple's Photos application. Originally sold as part of the iLife suite of digital media management applications, iPhoto was able to import, organize, edit, print and share digital photos.
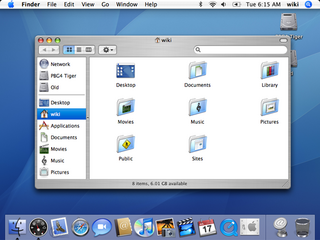
Mac OS X Tiger is the fifth major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Mac computers. Tiger was released to the public on April 29, 2005 for US$129.95 as the successor to Mac OS X 10.3 Panther. Some of the new features included a fast searching system called Spotlight, a new version of the Safari web browser, Dashboard, a new 'Unified' theme, and improved support for 64-bit addressing on Power Mac G5s. Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger offered a number of features, such as fast file searching and improved graphics processing, that Microsoft had spent several years struggling to add to Windows with acceptable performance.

Disk Utility is a system utility for performing disk and disk volume-related tasks on the macOS operating system by Apple Inc.

Keychain is the password management system in macOS, developed by Apple. It was introduced with Mac OS 8.6, and has been included in all subsequent versions of the operating system, now known as macOS. A Keychain can contain various types of data: passwords, private keys, certificates, and secure notes.
NetBoot was a technology from Apple which enabled Macs with capable firmware to boot from a network, rather than a local hard disk or optical disc drive. NetBoot is a derived work from the Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP), and is similar in concept to the Preboot Execution Environment. The technology was announced as a part of the original version of Mac OS X Server at Macworld Expo on 5 January 1999. NetBoot has continued to be a core systems management technology for Apple, and has been adapted to support modern Mac Intel machines. NetBoot, USB, and FireWire are some of the external volume options for operating system re-install. NetBoot is not supported on newer Macs with T2 security chip or Apple silicon.

Directory Utility is a utility included with the macOS operating system to configure connections to directory services.
The Apple Developer Tools are a suite of software tools from Apple to aid in making software dynamic titles for the macOS and iOS platforms. The developer tools were formerly included on macOS install media, but are now exclusively distributed over the Internet. As of macOS 10.12, Xcode is available as a free download from the Mac App Store.
This page is a comparison of notable remote desktop software available for various platforms.
RAID Admin is a Mac OS X Server only application by Apple Computer for administering and controlling RAIDs, usually Xserve RAIDs. Part of the server tools install, it is only installed on the server itself.

OS X Lion, also known as Mac OS X Lion, is the eighth major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers.

AppleDisk Image is a disk image format commonly used by the macOS operating system. When opened, an Apple Disk Image is mounted as a volume within the Macintosh Finder.

Gatekeeper is a security feature of the macOS operating system by Apple. It enforces code signing and verifies downloaded applications before allowing them to run, thereby reducing the likelihood of inadvertently executing malware. Gatekeeper builds upon File Quarantine, which was introduced in Mac OS X Leopard and expanded in Mac OS X Snow Leopard. The feature originated in version 10.7.3 of Mac OS X Lion as the command-line utility spctl. A graphical user interface was originally added in OS X Mountain Lion (10.8) but was backported to Lion with the 10.7.5 update.
The following outline of Apple Inc. is a topical guide to the consumer electronics, software, retail stores, corporate acquisitions, timeline, and personnel under the purview of the American multinational corporation Apple Inc. The company's best-known hardware products are the Macintosh, the iPod, the iPhone, and the iPad. Its best-known software includes the macOS and iOS operating systems, and the iTunes media browser. As of March 2014, Apple has 425 retail stores in 16 countries, and an online store.

macOS Sierra is the thirteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. The name "macOS" stems from the intention to uniform the operating system's name with that of iOS, watchOS and tvOS. Sierra is named after the Sierra Nevada mountain range in California and Nevada. Its major new features concern Continuity, iCloud, and windowing, as well as support for Apple Pay and Siri.
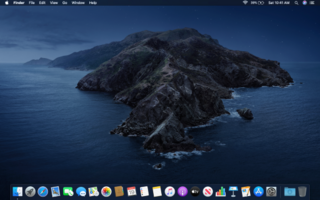
macOS Catalina is the sixteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop operating system for Macintosh computers. It is the successor to macOS Mojave and was announced at WWDC 2019 on June 3, 2019 and released to the public on October 7, 2019. Catalina is the first version of macOS to support only 64-bit applications and the first to include Activation Lock. It is also the last version of macOS to have the version number prefix of 10. Its successor, Big Sur, is version 11. macOS Big Sur, released on November 12, 2020, succeeded macOS Catalina.











